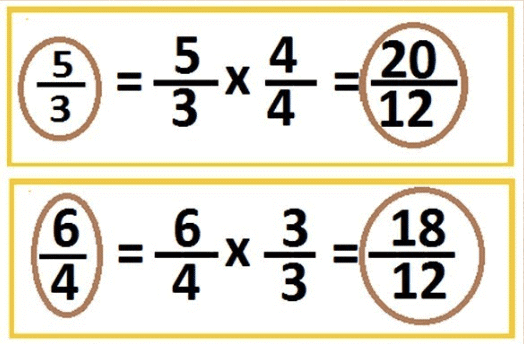Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Mathematics (Maths) Class 6 > NCERT Summary: Fractions
Fractions Summary Class 6 Maths Chapter 7
Fractions
- Fraction is a number representing part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects.

Fractions on the number line
- In order to show 1/3 on a number line. We divide the length between 0 and 1 into 3 equal parts and show one part as 1/3.

Proper Fractions
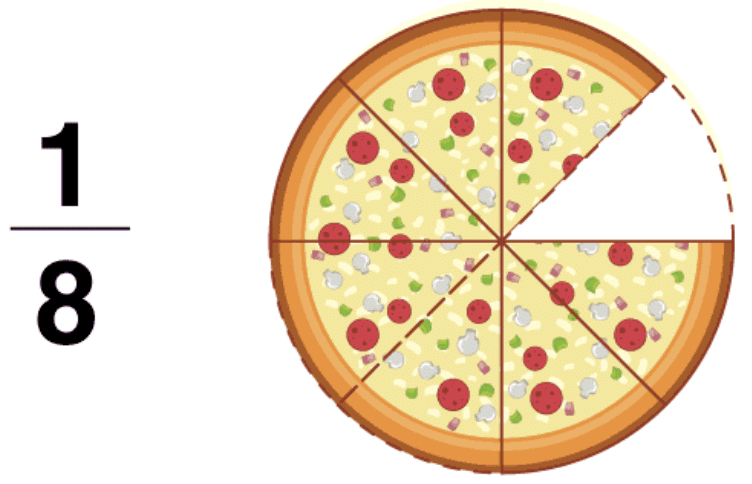
- A proper fraction is a number representing part of a whole.
- In a proper fraction the denominator shows the number of parts into which the whole is divided and the numerator shows the number of parts which have been considered. Therefore, in a proper fraction the numerator is always less than the denominator.

Improper Fractions
- The fractions where the numerator is bigger than the denominator are called improper fractions.

Mixed Fractions
- A mixed fraction has a combination of a whole and a part.

- We can express an improper fraction as a mixed fraction by dividing the numerator by denominator to obtain the quotient and the remainder. Then the mixed fraction will be written as Quotient × Remainder/Divisor.

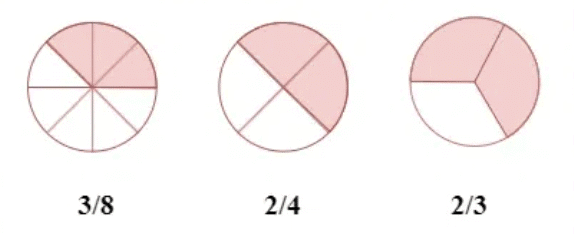
Equivalent Fractions
- Two or more fractions representing the same part of a whole.
- To find an equivalent fraction of a given fraction, you may multiply both the numerator and the denominator of the given fraction by the same number. For example, Equivalent fractions of 1/3 are 2/6, 3/9.
- To find an equivalent fraction, we may divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same number. For example, Equivalent fraction of 12/15 is 4/5.
 Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent Fractions
Question for NCERT Summary: FractionsTry yourself: What is a proper fraction?View Solution
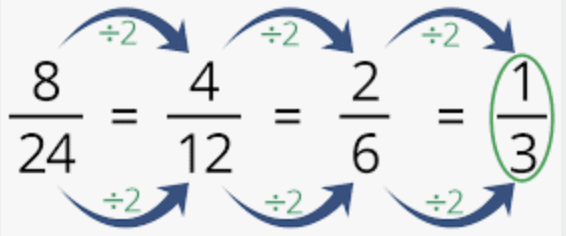
Simplest Form of a Fraction
- A fraction is said to be in the simplest (or lowest) form if its numerator and denominator have no common factor except 1.
- The shortest way to find the equivalent fraction in the simplest form is to find the HCF of the numerator and denominator, and then divide both of them by the HCF.

Like Fractions
- Fractions with same denominator is called Like Fractions.
- Comparing Like Fractions: Between two like fractions with the same denominator, the fraction with the bigger numerator is greater. For example, 2/5 < 3/5 < 4/5.
- Addition and Subtraction of Like Fractions: You can do these operations just by adding or subtracting the numerators.

Unlike Fractions
- Fractions with different denominator is called Unlike Fractions.
- Addition and Subtraction of Unlike Fractions: You can do these operations by converting them into like fractions and adding or subtracting the numerators.

Comparing Unlike Fractions: There are two ways with same numerator and different numerator.
- Unlike Fractions with the same numerator: If the numerator is the same in two fractions, the fraction with the smaller denominator is greater of the two. For example, 2/3 < 2/5.
- Unlike Fractions with the different numerator: We can compare them by converting into like fractions. Or we can cross multiply and check.
For example, Compare 4/5 and 5/6
4 × 6 /5 × 6 = 24/30 and 5× 5 /6 × 5 = 25/30 = 24/30 < 25/30.
Convert Like Fractions into Unlike Fractions
- First find the LCM (lowest common multiple) of the denominators of the given fractions.
- Then convert each fraction to its equivalent fraction with denominator equal to the LCM obtained in previous step.

The document Fractions Summary Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 is a part of the Class 6 Course Mathematics (Maths) Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
92 videos|348 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Fractions Summary Class 6 Maths Chapter 7
| 1. What is a fraction and how is it represented? |  |
Ans.A fraction is a way to represent a part of a whole. It is written with two numbers separated by a slash, such as 1/2, where the number above the slash (numerator) indicates how many parts we have, and the number below the slash (denominator) indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into.
| 2. What are the different types of fractions? |  |
Ans.The different types of fractions include proper fractions (where the numerator is less than the denominator, e.g., 3/4), improper fractions (where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator, e.g., 5/3), and mixed numbers (which combine a whole number and a proper fraction, e.g., 1 1/2).
| 3. How do you add and subtract fractions? |  |
Ans.To add or subtract fractions, they must have a common denominator. If they do not, you need to find the least common denominator (LCD), convert the fractions, and then add or subtract the numerators. For example, to add 1/4 and 1/2, convert 1/2 to 2/4, then add 1/4 + 2/4 = 3/4.
| 4. What is the process for multiplying fractions? |  |
Ans.To multiply fractions, you simply multiply the numerators together and the denominators together. For example, to multiply 2/3 by 3/4, multiply 2 × 3 to get 6 and 3 × 4 to get 12, resulting in the product 6/12, which can be simplified to 1/2.
| 5. How do you divide fractions? |  |
Ans.To divide fractions, you multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. For example, to divide 2/3 by 1/4, you multiply 2/3 by 4/1, resulting in (2 × 4)/(3 × 1) = 8/3.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches