Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Reproduction in Animals
Reproduction in Animals Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 6
Asexual reproduction
- The type of reproduction which involves only a single parent and new individuals are formed without the fusion of gametes is known as asexual reproduction.
- Three common methods of asexual reproduction are:
Budding
- It involves the formation of new individuals from the bulging of the parent body.
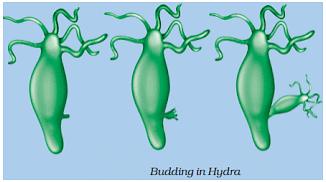
- This phenomenon is very common in plants, fungi and animals such as Hydra and yeast.
Fission
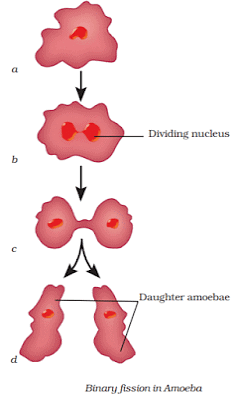
- Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction that occurs in Amoeba.
- It is a type of asexual reproduction in which a single cell divides into two halves.
Cloning

- Cloning is the process used to create an exact copy of a cell, tissue or organism.
- Dolly, a sheep was the first mammal to be cloned. It was cloned by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues in 1996.
Oviparous animals
- The animals that lay eggs are called oviparous animals.

- Examples include all kinds of birds, lizards, snakes, and frogs.
Viviparous animals
- The animals that give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals.
- The examples include cows, dogs, and humans.
Metamorphosis
- The biological process of transformation of larva into an adult is known as metamorphosis.
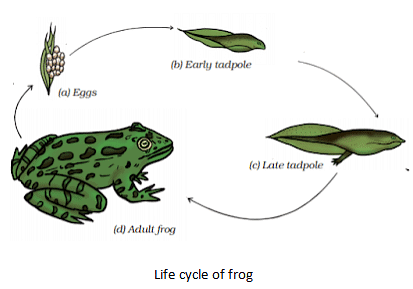
- The life cycle of frog consists of the following stages:
Egg → Tadpole (larva) → Adult - Hormones controlling metamorphosis in frogs
- Thyroxin (produced by the thyroid gland) initiates the process of a tadpole’s metamorphosis into an adult frog.
- In the absence of thyroxin, the tadpole does not transform into an adult and remains in the tadpole stage.
Life cycle of silkworm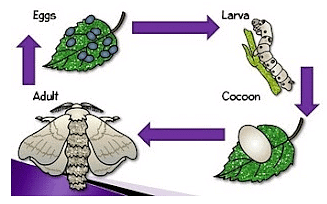
- Silkworm grows on mulberry trees and feeds on its leaves.
- During a stage in its life cycle, silkworm spins a cocoon around itself.
- Silk is obtained from this cocoon.
Hormone responsible for metamorphosis in insects
- In insects, metamorphosis is controlled by the insect hormones. Some of the insect hormones are:
(i) Prothoracicotropic Hormone (PTTH)
(ii) Ecdysone
(iii) Juvenile Hormone (JH)
Sexual Reproduction
Male Reproductive System- It consists of testis, sperm duct and penis.
- Testes are involved in the production of male gametes called sperms.
- Millions of sperms are produced by the testes.
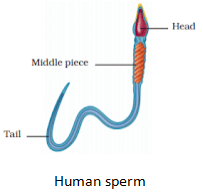
- Each sperm consists of three parts: Head, middle piece and tail.
Female reproductive system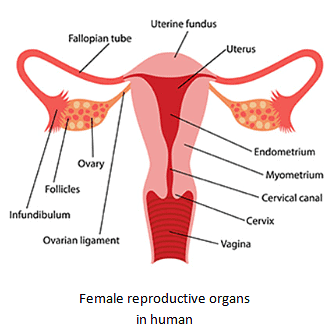
- It consists of ovaries, oviduct and uterus.
- Ovaries produce ova or eggs.
- A single matured egg is released from ovary into oviduct every month.
- Baby develops in the uterus.
- Egg is also single celled like sperm.
Fertilization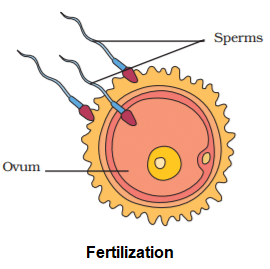
- The process of fusion of male and female gametes (egg and sperm) to form zygote is known as fertilization.
- It is of two types:
(i) Internal fertilization
(ii) External fertilization
Internal fertilization
- In this, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place inside the female's body.
- It occurs in cows, dogs and humans.
External fertilization
- In this, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place outside the female's body in a surrounding medium, generally water.
- It occurs in frogs, fishes, starfish, etc.
Test tube baby
- A baby conceived by fertilization that occurs outside the mother’s body is called test tube baby.
- Development of the embryo
- The zygote repeatedly divides to form a ball of cells.
- The ball of cells then starts differentiating into tissues and organs. At this stage, it is called embryo.
- Embryo gets attached to the wall of the uterus and develops various body parts such as hands and legs.
- Foetus is a stage of embryo that shows main recognizable feature of mature organism.
- Foetus develops for nine months inside the mother’s womb and is finally delivered.
Fertilization in Humans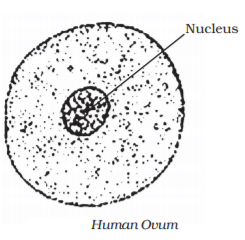
- Fusion of the nucleus of the sperm with the ovum to form a zygote. It occurs in the fallopian tube of females.
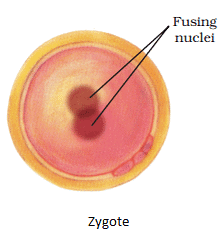
- Zygote divides to form an embryo.
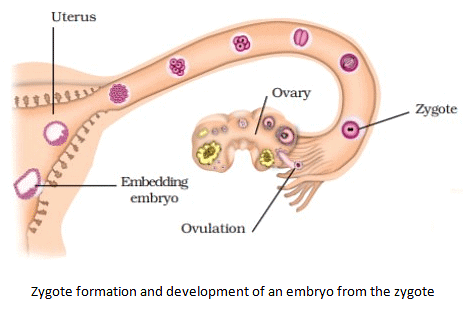
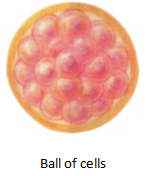
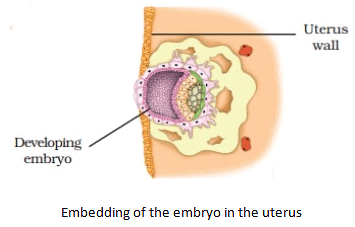
- Embryo is implanted in the uterus.
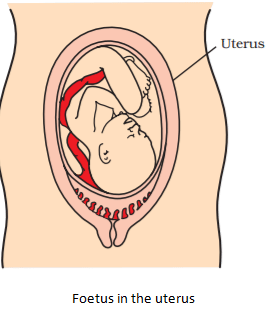
- Foetus develops inside the mother’s body for nine months (gestation period).
The document Reproduction in Animals Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 6 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
90 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Reproduction in Animals Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 6
| 1. What is asexual reproduction and how does it differ from sexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction where a single organism can produce offspring without the involvement of gametes (sperm and egg). The offspring are genetically identical to the parent. In contrast, sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in offspring that have genetic variations from both parents.
| 2. What are oviparous animals and can you give some examples? |  |
Ans. Oviparous animals are those that lay eggs, with the development of the embryo occurring outside the mother's body. Examples of oviparous animals include birds, reptiles, amphibians, and most fish. These animals often provide some form of parental care for their eggs until they hatch.
| 3. Can you explain the life cycle of a silkworm? |  |
Ans. The life cycle of a silkworm consists of four stages: egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (cocoon), and adult moth. The female moth lays eggs, which hatch into larvae. The larvae feed on mulberry leaves and grow, eventually spinning a cocoon around themselves to become pupae. After a few weeks, the adult moth emerges from the cocoon, ready to reproduce.
| 4. What are the main parts of the male reproductive system? |  |
Ans. The male reproductive system primarily consists of the testes, which produce sperm and hormones, the epididymis where sperm mature, the vas deferens which transports sperm, and accessory glands such as the seminal vesicles and prostate gland that contribute to semen formation. Finally, the penis serves as the organ for delivering sperm during reproduction.
| 5. How does fertilization occur in animals? |  |
Ans. Fertilization in animals occurs when a sperm cell successfully merges with an egg cell to form a zygote. This process can happen internally, inside the female’s body, or externally, in the environment, depending on the species. After fertilization, the zygote begins to divide and develop into an embryo.
Related Searches

















