SSC CHSL Exam > SSC CHSL Notes > Current Affairs & General Knowledge > National Income and the Income Tax Structure
National Income and the Income Tax Structure | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - SSC CHSL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Relating To The Domestic Product |

|
| Relating to the National Product |

|
| Indian Tax Structure |

|
| Structure Of Taxes |

|
Relating To The Domestic Product
- Gross Domestic Product at Market price = Market value of final output of goods and services produced within the country’s domestic economy in a period of one year.
- Net Domestic Product at Market Price = GDP – Depreciation
- Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost = NDP (MP) – Indirect Taxes + Subsidies
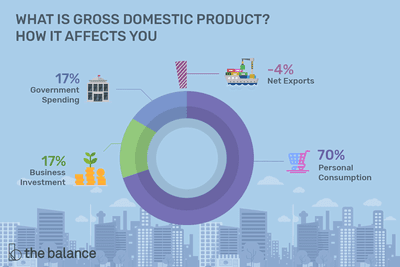 Gross Domestic Product
Gross Domestic Product
Relating to the National Product
- Gross National Product at Market Price = GDP (MP) + Net Factor Income from Abroad
- Net National Product at Market Price =GNP (MP) – Depreciation
- Net National Product at Factor Cost
Or
National Income = National product (MP) – Indirect Taxes + Subsidies
- Per Capita Product/Income = National Income/Population
OR
= Net National Product at Factor Cost/Population.
Note
The Ist estimate of National Income was prepared by Dadabhai Naoroji for the year 1867-68.
- The Ist scientific estimate was made by Prof. V. K. R. V. Rao for the year 1931-32.
- After independence, recognizing the importance of estimate of national income and its various components, the Government of India appointed the National Income Committee in 1949, with C. P. Mahalanobic as the Chairman.
- Following the report of this committee, the task of national income was entrusted to the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO).
Indian Tax Structure
Distribution
- Some taxes are levied, collected and retained by the Centre. These include Customs duty, corporation tax, taxes on capital (other than agricultural land) etc.
- Some taxes are levied and collected by the Centre but shared with the States. These include taxes on income other than agricultural income and union excise duties on goods included in Union List, excepting medicinal and toilet preparations.
- Some taxes are levied and collected by the Centre but the proceeds are to be distributed among States. These include succession and estate duties in respect of property other than agricultural Land, terminal tax on goods and passengers, tax on railway fares and freights, taxes on transaction in stick exchanges and future markets and taxes on sale or purchase of newspapers and ads.
- Some taxes are levied by the Centre but collected and appropriated by the States. These include stamp duties other than included in Union List and excise duties on medicinal and toilet preparations.
- Taxes belonging to State exclusively are land revenue, stamp duty, etc.
Structure Of Taxes
Direct Taxes
- Include taxes on income and property, the important ones being personal income tax, corporate tax, estate duty and wealth tax.
- Income tax is progressive in India, i.e., the rate of tax is not uniform but rises progressively with the rice in money income.
- During the last two decades, there has been a continuous reduction in the tax rate because high rates of income tax had merely encouraged tax evasion and growth in black money.
Indirect Taxes
- Include Sales Tax, Excise Duties, Customs Duties, etc.
- The Government of India earns maximum from Union Excise Duty.
The document National Income and the Income Tax Structure | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - SSC CHSL is a part of the SSC CHSL Course Current Affairs & General Knowledge.
All you need of SSC CHSL at this link: SSC CHSL
|
128 videos|293 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on National Income and the Income Tax Structure - Current Affairs & General Knowledge - SSC CHSL
| 1. What is the Indian tax structure? |  |
Ans. The Indian tax structure refers to the system of tax laws and regulations in India. It includes various types of taxes such as income tax, goods and services tax (GST), corporate tax, customs duty, and excise duty.
| 2. How does the income tax structure in India work? |  |
Ans. The income tax structure in India is progressive, which means that the tax rate increases as the income level increases. It is divided into different slabs or brackets, with each slab having a different tax rate. Individuals are required to pay taxes based on their income falling within these slabs.
| 3. What is the relationship between national income and the income tax structure? |  |
Ans. The income tax structure is designed to collect taxes from individuals and businesses based on their income. The national income, on the other hand, is the total income earned by all individuals and businesses in a country. The income tax structure is directly linked to the national income as it helps in generating revenue for the government.
| 4. What are the different types of taxes included in the national tax structure? |  |
Ans. The national tax structure in India includes various types of taxes such as income tax, corporate tax, goods and services tax (GST), customs duty, excise duty, and other indirect taxes. These taxes are levied on different aspects of the economy, including individuals, businesses, and goods and services.
| 5. How does the Indian tax structure impact the domestic product? |  |
Ans. The Indian tax structure can have an impact on the domestic product through its effect on the overall economy. Taxes levied on businesses can affect their profitability and investment decisions, which in turn can impact the production and growth of the domestic product. Additionally, taxes on individuals can influence their disposable income, consumption patterns, and savings, all of which can have a direct or indirect effect on the domestic product.
|
128 videos|293 docs|30 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for SSC CHSL exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















