Living Things Class 5 Notes Science
Introduction
- Have you ever noticed the buzzing bees, colourful butterflies, and tall trees around you?
- All these amazing things are called living things!
- In this chapter, we will find out what makes something alive.
- We’ll learn about the special features of living things, like how they breathe, grow, and interact with their surroundings.
- We’ll also look at non-living things and see how they are different from living things.
- Let’s go on this fun journey to discover the wonders of life around us!

- All creatures that breathe, eat, develop, move, reproduce, and have senses are called living things.
- Non-living things are not capable of eating, growing, breathing, moving, or reproducing. They lack all senses.
- All living things, like trees, have life, even if we can’t always see it. Unlike people, trees don’t move or react when we talk to or touch them. If we tap or hit a tree, it won’t respond, but it still shows it’s alive in its own special way.
 Tree: Living or Non-Living?
Tree: Living or Non-Living? - Just because some things don't show clear signs of life doesn't mean they aren't alive. Sometimes, life exists in ways that are hard to see or understand.
- Let's explore the important differences between living and non-living things and discover the unique traits that help us identify what is alive. Let’s dive in and learn how to spot the hidden signs of life around us!
What are Living Things?
- Living things are beings that are alive and are built from tiny structures called cells. They grow and can move.
- They go through processes like metabolism, which involves building and breaking down substances.
- Metabolism is the process by which your body turns the food you eat into energy to help you grow, move, and stay healthy.
- Living things can make new life through reproduction and have a specific lifespan, meaning they don't live forever.
- Reproduction is the process by which living things make more of their own kind, like how plants grow new seeds or animals have babies.
- To stay alive, living things use a process called Cellular Respiration to get energy. They eat to get energy from food and get rid of waste from their bodies.
- Through cellular respiration, cells take in oxygen and break down food to release energy that the body can use.
- The life cycle of living beings can be summed up as birth, growth, reproduction, and eventually, death.
- Examples of living things include animals, birds, insects, and humans.
Characteristics of Living Things
The following are the essential characteristics of living things:

1. Locomotory Motion
- Locomotory motion is the movement of an animal or person from one place to another, like walking, running, swimming, or flying.
- Animals have special body parts called locomotory organs that help them move.
- For example, earthworms move through the soil using their muscles.
- Plants also move, but in a different way—they grow towards sunlight to help them make food through photosynthesis.
2. Respiration
- Living things breathe through a process called respiration.
- This chemical reaction happens inside their cells as they take in oxygen and helps release energy from food.
- During respiration, gases are transported, and the food we eat is broken down to produce energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
3. Sensitivity
- Living things can sense changes around them.
- They respond to touch and other stimuli in their environment, allowing them to react and adapt.
4. Growth
- Living things grow and develop through different stages of life.
- This process involves maturing from one form to another over time.
5. Reproduction
- One key feature of living things is their ability to reproduce.
- They can create offspring of their own kind, passing on genetic information from parents to their young.
6. Nutrition
- Living things need food to survive.
- They take in food, which is broken down and digested to provide energy and nutrients.
- Some living organisms, like plants, are autotrophic, meaning they can make their own food using sunlight.
7. Excretion
- After digestion, living things get rid of waste through a process called excretion.
- This is essential for maintaining health and balance within their bodies.
What are Non-Living Things?
- Non-living things are not alive, i.e., they do not possess life.
- They do not have cells and do not grow or show locomotion/movement.
- They do not undergo metabolism with anabolic and catabolic reactions.
- They do not reproduce.
- Non-living things do not have a life span.
- They do not respire, nor do they require food for energy and hence do not excrete.
- They do not fall into any cycle of birth, growth or death.
- They are created and destroyed by external forces.
- Examples of non-living things include stones, pens, books, cycles, bottles, etc.
Characteristics of Non-Living Things
The important characteristics of non-living things are mentioned below:

Lifeless
Non-living things do not have life. They lack cells and protoplasm, which are essential for life to exist.No Metabolic Activities
Since they do not have protoplasm, non-living things do not undergo any metabolic processes, such as growth or energy production.No Fixed Size
Non-living things do not have a definite size. They take the shape of the container they are in; for example, a liquid will adapt to fit the shape of its container. Stones, rocks, and boulders can change shape due to environmental factors.Growth by Accretion
Non-living things can "grow" through a process called accretion, which means they increase in size by adding external materials. For instance, a snowball gets larger as it gathers more snow on its surface.Immortality
Non-living things do not die because they lack cells and do not have a lifespan. They can exist indefinitely unless altered or destroyed by external forces.Absence of Life Processes
Non-living things do not perform any fundamental life processes, such as reproduction, digestion, or excretion. They do not have the capabilities that living beings possess.
Difference Between Living and Non-Living Things
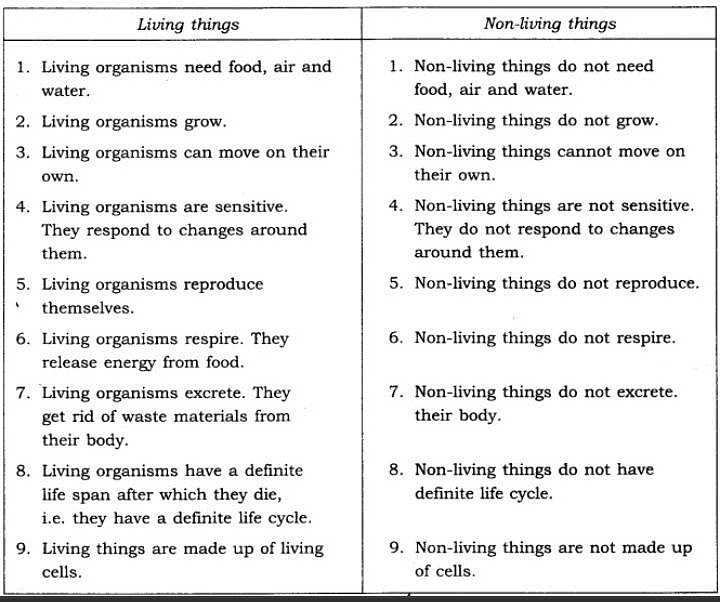
Criteria for Differentiating Living Things from Non-Living Things
To easily tell apart living and non-living things, scientists have identified specific traits for each category. This classification helps prevent confusion and ensures accurate understanding.
The criteria to identify living things include the following:
 Criteria to identify living things
Criteria to identify living things
If something does not meet all these criteria, it cannot be classified as a living thing. For example, an icicle may grow in size, but it is considered non-living because it cannot reproduce or respond to stimuli.
Non-living things do not have any life processes. They do not grow, reproduce, or respond to their environment. Examples include stones, mountains, and watches. These objects do not possess the qualities that define living beings.
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Living Things Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What are the main characteristics of living things? |  |
| 2. How do we define non-living things? |  |
| 3. What are the key differences between living and non-living things? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of living and non-living things? |  |
| 5. What criteria can be used to differentiate living things from non-living things? |  |





















