Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Newton's Second Law
Newton's Second Law | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Newton's Second Law
- Newton's second law of motion states:
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and inversely proportional to the object's mass - This law elucidates the following principles:
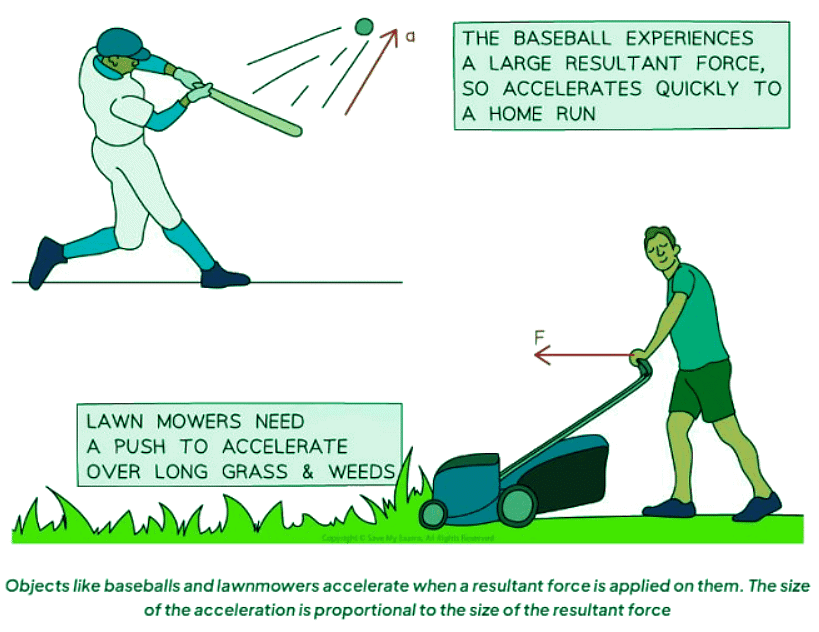
- Objects will accelerate, altering their velocity, due to a resultant force.
- Acceleration increases with larger resultant forces.
- With a constant force, acceleration decreases as the object's mass increases.
- Examples depicted in the image below illustrate Newton's second law in practical scenarios:

Calculations Using Newton's Second Law
- Newton's second law can be expressed as an equation: F = ma
- Where:
- F = resultant force on the object in Newtons (N)
- m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
- a = acceleration of the object in meters per second squared (m/s2)
- The force and the acceleration act in the same direction
- This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle:

The document Newton's Second Law | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Newton's Second Law - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How can Newton's Second Law of Motion be applied in real-life situations? |  |
Ans. Newton's Second Law of Motion can be applied in real-life situations by calculating the force required for an object to accelerate or decelerate. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
| 2. What is the formula for calculating force using Newton's Second Law? |  |
Ans. The formula for calculating force using Newton's Second Law is F = ma, where F is the force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration. This formula helps in determining the force needed to accelerate an object of a certain mass.
| 3. How is acceleration related to force according to Newton's Second Law? |  |
Ans. According to Newton's Second Law, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it. This means that the greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration will be, and vice versa.
| 4. Can Newton's Second Law be used to calculate the force required to stop a moving object? |  |
Ans. Yes, Newton's Second Law can be used to calculate the force required to stop a moving object. By considering the acceleration as negative (deceleration), the formula F = ma can be used to determine the force needed to bring the object to a stop.
| 5. How does Newton's Second Law help in understanding the motion of objects like shopping trolleys? |  |
Ans. Newton's Second Law helps in understanding the motion of objects like shopping trolleys by explaining how the force applied to them affects their acceleration. By calculating the force required for acceleration or deceleration, one can better understand how external forces influence the motion of objects in real-life scenarios.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches