Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) Overview
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 that engages in financial activities such as loans and advances, acquiring shares, stocks, bonds, and other marketable securities, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance, and chit fund activities. However, it does not include institutions primarily involved in agriculture, industrial activities, buying or selling goods (excluding securities), or real estate. Additionally, an NBFC that accepts deposits under any scheme or arrangement, whether in lump sums or installments, is known as a Residuary Non-Banking Company.
Differences Between Banks and NBFCs
- Demand Deposits: NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits.
- Payment Systems: NBFCs are not part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheques.
- Deposit Insurance: Depositors in NBFCs do not have deposit insurance provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation, unlike those in banks.
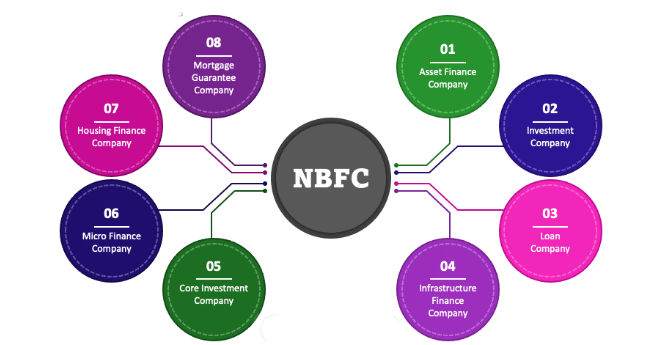
Types of NBFCs Registered with RBI
- Asset Finance Company (AFC): Primarily finances physical assets like vehicles and industrial machines.
- Investment Company (IC): Focuses on acquiring securities.
- Loan Company (LC): Provides loans or advances for activities other than its own.
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): Invests at least 75% of its assets in infrastructure loans, has a minimum net owned fund of ₹300 crore, a credit rating of ‘A’ or equivalent, and a Capital to Risk-weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) of 15%.
- Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC-ND-SI): Engages in acquiring shares and securities.
- Infrastructure Debt Fund-NBFC (IDF-NBFC): Raises long-term debt for infrastructure projects through bonds.
- Non-Banking Financial Company - Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI): Provides microfinance with specific asset and income criteria for borrowers.
- Non-Banking Financial Company - Factors (NBFC-Factors): Specializes in factoring services, with a significant portion of its assets and income coming from factoring.
- Mortgage Guarantee Companies (MGC): Engages in mortgage guarantee business with specific financial thresholds.
- NBFC - Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC): Holds a new bank and other financial services companies regulated by the RBI.
Actions Against Misleading Claims
Making false claims of being regulated by the Reserve Bank to mislead the public is illegal. Such entities are liable for penal action under the Indian Penal Code. Reports can be made to the nearest RBI office or the police.
Finding Registered NBFCs
The list of registered NBFCs and instructions issued to them can be found on the Reserve Bank of India's website at www.rbi.org.in.
Precautions for Depositors
- Ensure the NBFC is registered with the RBI and authorized to accept deposits. Check the RBI’s list of authorized NBFCs.
- Verify that the NBFC displays its Certificate of Registration (CoR) prominently, which should confirm its deposit-taking authority.
- Confirm that the NBFC’s interest rate on deposits does not exceed 12.5%, as regulated by the RBI.
- Obtain a proper receipt for the deposit, signed by an authorized officer, detailing all relevant information.
- Verify the legitimacy of brokers or agents collecting deposits on behalf of the NBFC.
- Remember that NBFC deposits are unsecured, and deposit insurance is not available.
- The RBI does not guarantee the financial soundness of the company or the repayment of deposits.
Chit Fund Business
Chit funds are regulated under the Chit Funds Act, 1982, administered by state governments. Only registered chit funds can legally conduct business.
Money Circulation/Ponzi/Multi-Level Marketing Schemes
These schemes promise easy money through membership recruitment rather than genuine asset creation or product sales. Ponzi schemes involve collecting money on promises of high returns without any real investment, leading to inevitable collapse. Multi-level marketing and chain marketing schemes require continuous recruitment of new members to sustain the returns for those at the top, causing losses for those lower in the chain.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are the key functions of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)? |  |
| 2. How are Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) regulated in India? |  |
| 3. What distinguishes Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) from traditional banks? |  |
| 4. How do Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) contribute to the Indian economy? |  |
| 5. What are the risks associated with investing in Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)? |  |





















