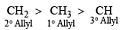Non-Metal Based Reagents | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Non-Metal Based Reagents |

|
| SeO2 [Selenium Dioxide] |

|
| DCC |

|
| Dichloro Dicyano Quinone [DDQ] |

|
| Peroxy Acid [RCO3H] |

|
| Ozone [O3] |

|
| HIO4 [periodic acid] |

|
| N-Bromo Succinimide [NBS] |

|
Non-Metal Based Reagents
Some Non- Metal Based Reagents are:
- SeO2
- DCC
- DDQ
- Peroxyacid
- Ozone
- Periodic Acid
- NBS
SeO2 [Selenium Dioxide]
It is a very important oxidizing reagent which is used for the oxidation of allyl or allylic hydrogen into alcohol.

There are some important points that must be followed during the oxidation process be SeO2.
- Rule 1: Oxidation always occurs at the more substituted site of double bond.
- Rule 2: If there is the possibility of two different types of allylic position out of which one present in the ring & other present outside the ring then SeO2 performs oxidation at the allylic position present in the ring.
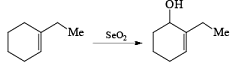
- Rule 3: Oxidation does not occur at bridgehead position.
- Rule 4: Order of reactivity of allyl and allylic carbon:

- Examples of formation of 1,2 dicarbonyl compounds:
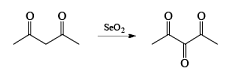
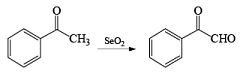
Mechanism & Examples of Oxidation by SeO2
Allylic Oxidation Mechanism
During the process of oxidation with SeO2 first of all ene reaction will occur which will followed by [2, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement and after the hydrolysis process, allylic alcohol is formed.
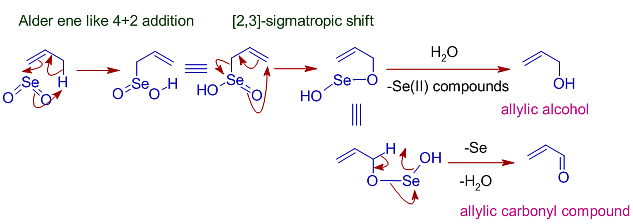 Allylic Oxidation Mechanism
Allylic Oxidation Mechanism
Examples:

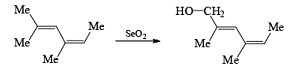
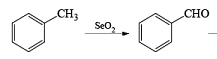

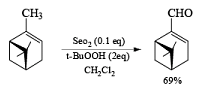
- If the alkene possesses a methyl substituent, oxidative cleavage of C (elimination of a selenium atom and water) furnishes the corresponding, β-unsaturated aldehyde. Lower yields of products were obtained when using stoichiometric amounts of SeO2. t-Butyl hydroperoxide is used to reoxidize selenium.
- Besides giving the desired carbonyl compounds, the reaction may also produce allylic alcohols as side products.
- In some cases, SeO2 can also behave as a dehydrogenating reagent.
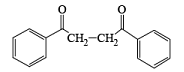
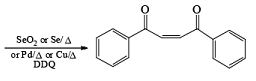
- In the case of alkynes & alkenes, it can also give hydroxylation & the mechanism of hydroxylation is anti-hydroxylation or trans-hydroxylation.
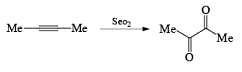
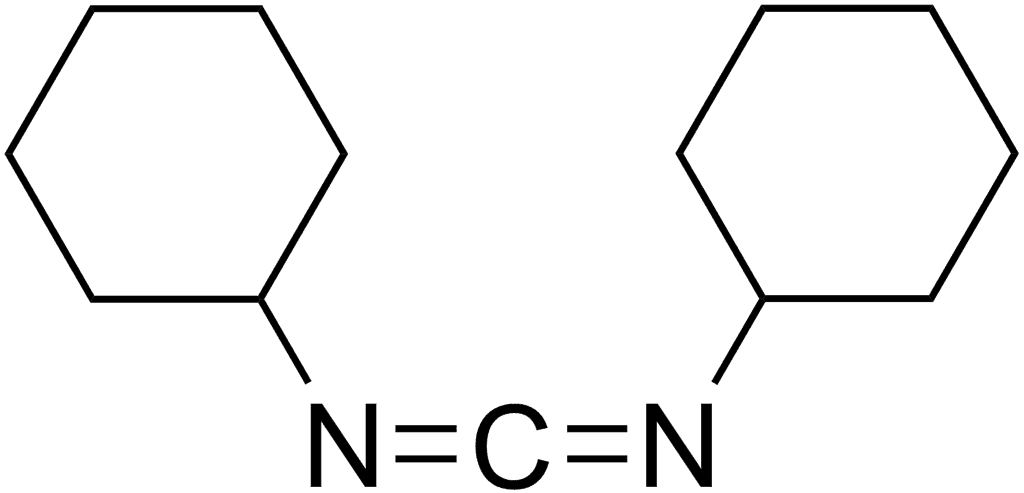
DCC
DCC (acronym for N,N'- dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) was one of the first carbodiimides developed as a reagent. It is widely used for amide and ester formation.
- It will behave as a coupling reagent by condensation.
- It acts as a dehydrating reagent; hence it is stored under an anhydrous condition.
 DCC
DCC
Application of DCC in Organic Chemistry
(i) Esterification or lactonization
(ii) Amide formation of Lactan formation peptide synthesis
(iii) Anhydride formation
(iv) Peroxide formation
Synthesis of DCC
- Preparation from Urea
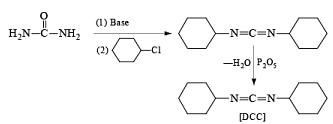
- Esterification or lactonization: Fisher Esterification
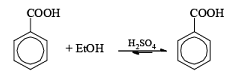
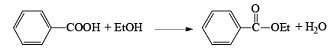
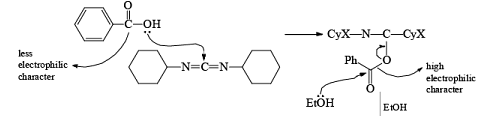
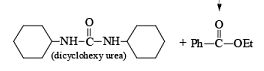
After the reaction, DCC is converted into cyclohexyl urea DCU.
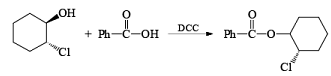
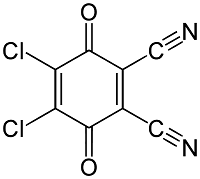
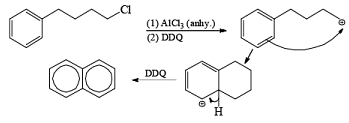
Dichloro Dicyano Quinone [DDQ]
It is the special reagent which helps in the removal of hydrogen from the substrate means it will behave as dehydrogenating agent.
- In many cases, if the cyclic ring is present then it will aromatize that ring and gain aromaticity.
 DDQ
DDQ
Mechanism of DDQ
In the mechanism of DDQ, first of all, it will abstract the hydride from the substrate and form the cation and then followed by the removal of proton produce the double bond.
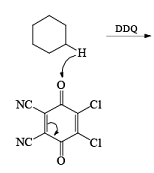
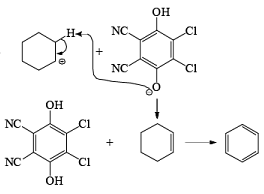
Problem:
Peroxy Acid [RCO3H]
The reaction of alkenes with peroxy acids provides for convenient and selective oxidation of double bonds.
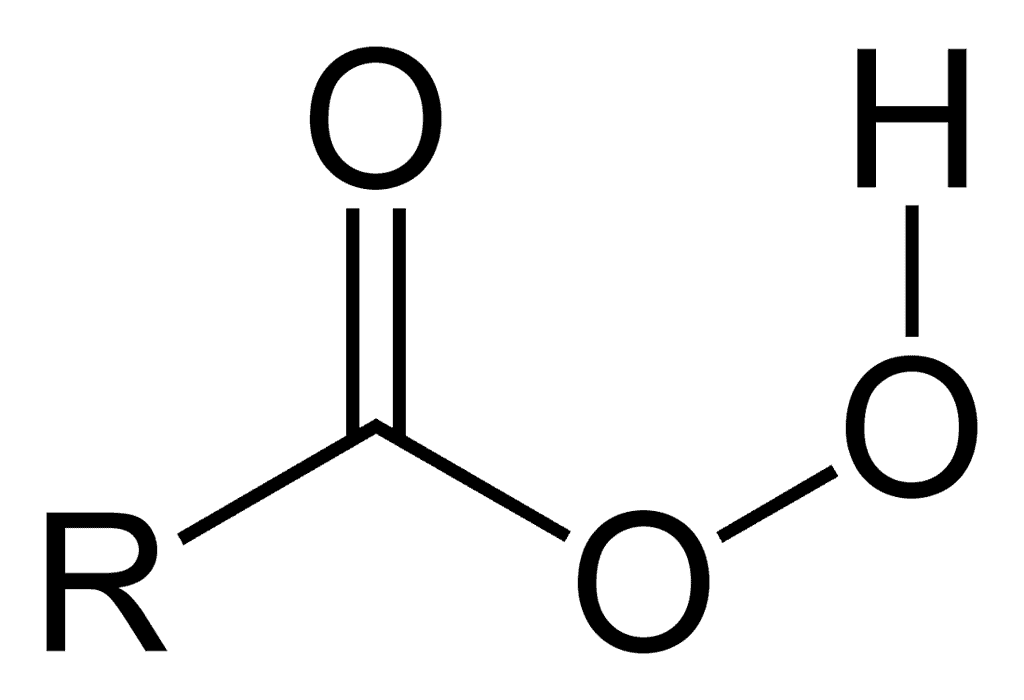 General Formula: Peroxy Acid
General Formula: Peroxy Acid
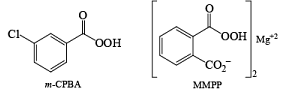
- The peroxy acids most commonly used in the laboratory are m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (mCPBA), monoperoxyphthalic acid magnesium salt (MMPP), peroxybenzoic acid, peroxyformic acid, peroxyacetic acid, trifluoroperoxyacetic acid, and t-butyl hydroperoxide [(CH3)3COOH].
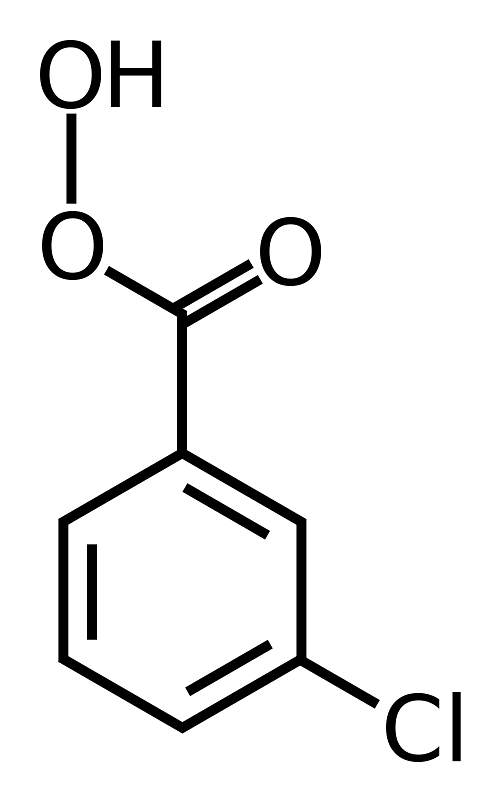 mCPBA
mCPBA
- The order of reactivity for epoxidation of alkenes follows the trend CF3CO3H > mCPBA ~ HCO3H > CH3CO3H >> H2O2 >
[Intext Question]
Stereoselectivity
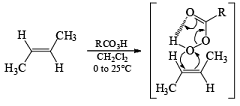
Epoxidation involves an electrophilic syn-addition of the oxygen moiety of the peroxy acid to the double bond. The concerted formation of two new C—O bonds ensures that the reaction is stereospecific: cis alkenes furnish the corresponding cis-epoxides and trans-alkenes the corresponding trans-isomers (racemic).

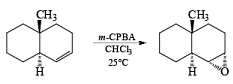
With conformationally rigid cyclic alkenes, the reagent preferentially approaches the double bond from the less hindered side.
Chemoselectivity
The rate of epoxidation increases with the number of electron-donating substituents on the double bond. The order of alkene reactivity with peroxy acids is as follows

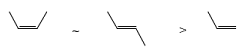
Hence, the more nucleophilic (more substituted) double bonds of the diene and triene depicted below undergo preferential epoxidation when treated with an equimolar amount of the peroxy acid.

Conjugation of the alkene double bond with an electron-withdrawing group reduces the rate of epoxidation. Thus, α, β-unsaturated carboxylic acids, and esters require a stronger oxidant, such as trifluoroperoxyacetic acid, for oxidation.
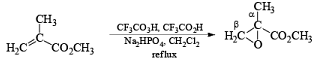
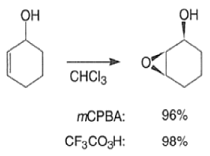
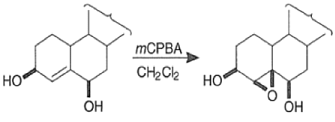
Hydroxyl-Directed Epoxidation with Peroxy Acids
Although epoxidation of cyclic alkenes occurs preferentially from the less hindered side, the presence of a polar substituent near the double bond may reverse the facial direction of attack by the peroxide.
- For example, the introduction of an allylic OH group onto the substrate provides a means for interaction with the peroxy acid by hydrogen bonding and thereby promotes stereoselective epoxidation.
- Cycloalkenes with an OH group at the allylic position are attacked by peroxy acids syn to the double bond to give the corresponding cis-epoxy alcohol diastereomers, even if that face is sterically more hindered.
- It is assumed that the directive effect of the hydroxyl group is due to hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl group and the peroxy acid, stabilizing the transition state for epoxidation.
- If the OH group is replaced by an acetate group, a nearly equimolar mixture of diastereomeric epoxides is observed.
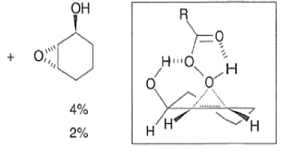
- The hydroxyl-directed epoxidation of alkenes using peroxy acids is sensitive to the nature of the solvent.
- In the example below, alkene epoxidation occurs on the more accessible a-face when Et2O is used as a solvent, whereas the use of CH2C12 promotes hydroxyl-directed epoxidation on the b-face of the alkene.
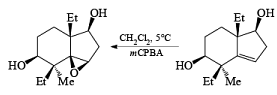
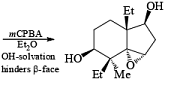
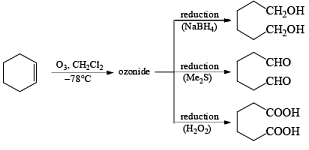
Ozone [O3]
Ozonolysis is widely used both in degradation work to locate the position of double bonds and in the preparation of aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
[Question: 991405]
Chemoselective Cleavage
The electrophilic ozone preferentially attacks a more nucleophilic double bond it is possible to achieve chemoselective cleavage in compounds containing two or more double bonds by limiting the amount of ozone. The relative reactivity of double bonds toward ozone decreases in the following order:
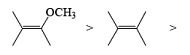
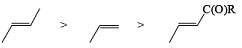
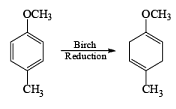
The example depicted below indicates preferential cleavage of the electron-rich enol ether double bond over the trisubstituted one by the electrophilic ozone. Thus, Birch reduction of methoxy-substituted benzenes followed by ozonolysis of the resultant enol ethers provides a powerful route to functionally substituted (Z) alkenes.
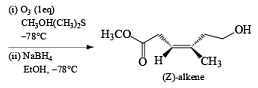
In the competition with a more nucleophilic trisubstituted double bond with a terminal disubstituted one, ozone exhibits a high preference for the former.
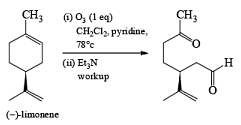
Ozone is a l,3-dipolar species and undergoes 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions with alkenes.
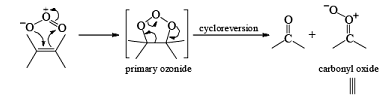
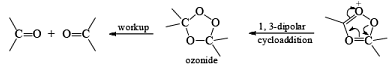
There are two modes used to decompose ozonides:
1. Reductive: Me2S, Zn—AcOH, H2/Pd, KI-CH3OH, metal hydrides
2. Oxidative: H2O2
HIO4 [periodic acid]
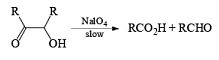
Cleavage of glycols derived from OsO4 or KMnO4 oxidation of alkenes by periodates or by periodic acid (HIO4·2H2O) results in two carbonyl fragments whose structures depend on the degree of substitution of the double bond.
Mechanism
The mechanism for periodate cleavage of glycols involves a cyclic periodate ester, which undergoes decomposition into two carbonyl fragments. Both cis- and trans- l,2-dihydroxycyclo-hexanes are cleaved but the trans-isomer at slower rate.
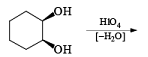
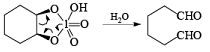
Below are summarized some cleavage possibilities of 1,2-diols, an a-hydroxy ketone, and a 1,2-ketone with sodium periodate in EtOH—H2O.
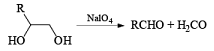
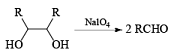
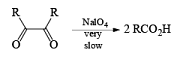
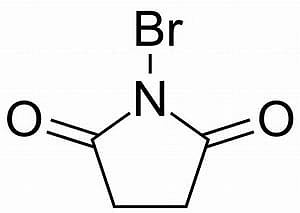
N-Bromo Succinimide [NBS]
Most important use of N-bromo succinimide is bromination at allylic, benzylic or propargylic position bromination.
The mechanism of this bromination is free radical substitution there are two ways for this free radical substitution.
(1) NBS + hv or NBS/CCl4/Δ 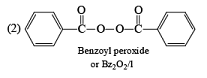
The rate of bromination at propargylic position is more than that of allylic position.
The free radical substitution at bridgehead position can possible with NBS. The free radical substitution at chiral carbon proceeds with retention in configuration.
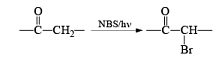
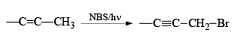


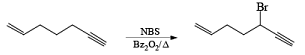
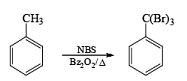
If NBS is used in the presence of any nucleophilic source or any nucleophile then it will give the electrophilic addition reaction across the double bond through ionic mechanism via formation of Brominium ion.
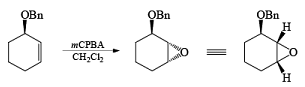
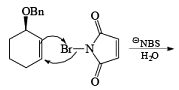
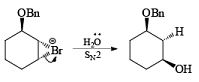
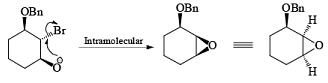
The addition of NBS with a double bond is according to the Markovnikov rule.
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Non-Metal Based Reagents - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What are some examples of non-metal based reagents commonly used in chemistry? |  |
| 2. How do non-metal based reagents like SeO2 and DDQ play a role in various chemical reactions? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of using peroxy acid as a non-metal based reagent in organic synthesis? |  |
| 4. Why is ozone considered a versatile non-metal based reagent in organic chemistry? |  |
| 5. How does N-Bromo Succinimide (NBS) function as a non-metal based reagent in organic reactions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|