Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Non-Renewble Fossil Fuels
Non-Renewble Fossil Fuels | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
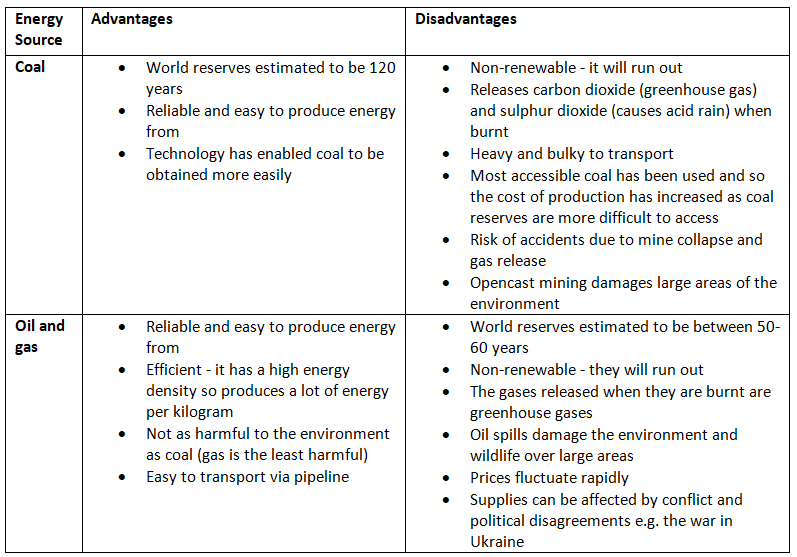
Importance of Non-Renewable Fossil Fuels
- The global demand for energy is on the rise.
- Population growth and development are the primary factors contributing to this increased energy demand. For instance:
- The growing need for food leads to more intensive farming practices, necessitating additional energy for machinery, lighting, and heating.
- Industries require energy for various operations like heating, lighting, and running machinery.
- Increased transportation activities demand energy in the form of petrol, diesel, or electricity.
- Urbanization, a result of development, leads to higher usage of domestic appliances, lighting, and heating.
- Rising wealth levels prompt people to purchase more appliances and technology that rely on energy consumption.

Question for Non-Renewble Fossil FuelsTry yourself: What are some factors contributing to the global demand for energy?View Solution
Impact of Fossil Fuels on Global Energy Supply
- More than 80% of the world's energy is currently sourced from fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and gas.
- Oil constitutes 33% of the global energy supply.
- Coal accounts for 27% of the global energy supply.
- Gas contributes 24% to the global energy supply.
- Fossil fuels originate from the remnants of living organisms like plants and animals.
- These resources are finite and non-renewable as their rate of consumption surpasses their replacement speed.
- Based on present consumption rates and availability, it is projected that gas and oil reserves may be depleted by 2080.

World Energy Mix
- The utilization of nuclear and renewable energy sources is on the rise, although non-renewable fossil fuels still predominantly drive energy production.
- Predictions indicate that the usage of gas and oil will persist in its growth over the next three decades, with fossil fuels projected to account for over 75% of global energy by 2040.
Energy use
- More economically developed countries (MEDCs) generally consume more energy compared to less economically developed countries (LEDCs).
- MEDCs with the highest energy consumption per capita include nations like Canada, Norway, and Saudi Arabia.
- LEDCs, primarily located in Africa such as Niger, Chad, and Tanzania, exhibit the lowest energy consumption per person.
- Significant energy consumption growth is observed in LEDCs and emerging economies like China and India due to developmental activities in industries, households, and transportation sectors.
Energy Use per Person in kwh

Energy Security
- An energy gap arises when a nation cannot fulfill its energy needs using internal resources.
- In such cases, countries resort to importing energy to bridge the shortfall.
- Energy insecurity ensues when a country faces an energy gap.
- Energy security necessitates:
- Consistent energy supply.
- Affordable energy.
- Accessible energy.
- The UK grapples with a widening energy gap, compromising its energy security because:
- Renewable energy lacks the efficiency to fully replace fossil fuels.
- Importing fossil fuels proves cheaper than exploiting domestic resources.
- Global efforts to combat climate change and reduce fossil fuel usage exacerbate energy insecurity.
- Factors affecting energy security include:
- Depletion of energy sources.
- Conflict or war.
- Natural disasters.
- Political disputes.
Energy Mix
- The composition of energy sources in countries varies depending on their level of development.
- The most economically advanced nations demonstrate a broader reliance on renewable energy and nuclear power.

- Newly emerging economies rely more heavily on fossil fuels.

- The least economically developed countries primarily rely on biofuels, predominantly fuel wood, for heating and cooking, especially in rural regions.

Question for Non-Renewble Fossil FuelsTry yourself: What percentage of the global energy supply is currently sourced from fossil fuels?View Solution
The document Non-Renewble Fossil Fuels | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Non-Renewble Fossil Fuels - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are non-renewable fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. Non-renewable fossil fuels are natural resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas that were formed millions of years ago from the remains of plants and animals. Once these resources are used up, they cannot be replenished within a human timescale.
| 2. Why are non-renewable fossil fuels important? |  |
Ans. Non-renewable fossil fuels are important because they provide a significant portion of the world's energy needs. They are used for electricity generation, transportation, heating, and manufacturing, making them essential for modern society's functioning.
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of using non-renewable fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. The burning of non-renewable fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to climate change and global warming. Additionally, the extraction and processing of these fuels can cause habitat destruction, water pollution, and air pollution.
| 4. How long are non-renewable fossil fuels expected to last? |  |
Ans. The availability of non-renewable fossil fuels varies depending on the type and rate of consumption. While some estimates suggest that we have several decades' worth of oil and gas left, coal reserves are more abundant. However, continued reliance on these resources raises concerns about future energy security.
| 5. What are some alternatives to non-renewable fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power offer sustainable alternatives to non-renewable fossil fuels. Investing in energy efficiency measures and transitioning to electric vehicles can also help reduce our dependence on finite resources.
Related Searches



















