Note: Fractions & Decimals | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
What is a Fraction?
A fraction is a part of a whole. If a whole is divided into equal parts, each part is called a fraction. It is made up of two parts.
Fractions can be used to
- name a part of a single thing.
 Here, 1 part out of 4 equal parts is red, we write it as 1 / 4.
Here, 1 part out of 4 equal parts is red, we write it as 1 / 4. 1 / 4 of the cake has been taken by Neha.
1 / 4 of the cake has been taken by Neha. - name a part of a group of things.
 In this aquarium, you have 7 fish, out of which 2 are starfish. So, we write 2 / 7 are starfish.
In this aquarium, you have 7 fish, out of which 2 are starfish. So, we write 2 / 7 are starfish.
Representation of a Fraction on a Number Line
The fraction 3 / 8 is shown on the number line as: 3 / 8 < 1, so we draw the number line from 0 to 1 and divide it into 8 equal parts. (∵ denominator = 8). The arrow shows the fraction 3 / 8.
3 / 8 < 1, so we draw the number line from 0 to 1 and divide it into 8 equal parts. (∵ denominator = 8). The arrow shows the fraction 3 / 8.
Types of Fractions
- Proper Fractions
The fractions in which the numerator is less than the denominator are called proper fractions.
For example, 0 / 2, 1 / 4, 2 / 5, 3 / 7, 81 / 100, etc., are all proper fractions. All proper fractions are less than 1. - Improper Fractions
The fractions in which the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator are called improper fractions.
For example, 6 / 6, 7 / 4, 21 / 20, 121 / 100, etc., are all improper fractions.
All improper fractions are greater than or equal to 1. (i) Mixed Numbers
(i) Mixed Numbers
A mixed number has two parts, a whole number part (except 0) and a part with a fraction.
For example, are all mixed numbers.
are all mixed numbers.
- Unit Fractions
A fraction whose numerator is 1 and the denominator is greater than 1 is called a unit fraction,
For example, 1 / 8, 1 / 3, 1 / 5, etc. - Like Fractions
Fractions that have the same denominator are called like fractions.
For example, 8 / 12, 7 / 12, 17 / 12, 23 / 12 are all like fractions. - Unlike Fractions
Fractions whose denominators are different are called unlike fractions.
For example, 4 / 6, 3 / 8, 12 / 15, 23 / 35 are all unlike fractions.
Edurev Tips: We can write a mixed number as an improper fraction and an improper fraction as a mixed number.
Example 1: Write 7 / 5 as a mixed number.
Method 1: Pictorially, it can be shown as:
It can also be represented on the number line as:
Jump five-fifths to land on 1. Jump 2 more fifths to land on 7 / 5.This is same as jumping to 1 and then to another 2 / 5.∴ 7 / 5 as a mixed number is
Method 2: By Division Method,
Edurev Tips:
Example 2: Write  as an improper fraction.
as an improper fraction.
Pictorially, it can be shown as:
Multiply the whole number part by the denominator and add numerator to the product.Alternatively,
Equivalent Fractions
Consider the following fraction bars.
Fractions that name the same part of the whole are called equivalent fractions. Therefore, 1 / 4, 2 / 8 and 3 / 12 are equivalent fractions and we write 1 / 4 = 2 / 8 = 3 / 12.
Therefore, 1 / 4, 2 / 8 and 3 / 12 are equivalent fractions and we write 1 / 4 = 2 / 8 = 3 / 12.
Edurev Tips:
Thus, to find equivalent fractions, we either multiply or divide the numerator and denominator by the same number.
Example 3: Fill in the missing numbers.



Writing a Fraction in its Simplest Form
A fraction is in its simplest form when its numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1.
Fractions such as 1 / 2, 3 / 5, 5 / 8 are all fractions in their simplest form. In 1 / 2, there is no common factor of 1 and 2 except 1. Likewise, the only common factor of 3 and 5 in 3 / 5 is 1 and of 5 and 8 in 5 / 8 is 1.
The fraction 10 / 15 is not in its simplest form because 5 is a common factor of 10 and 15.
Similarly, 3 / 21 is not in its simplest form because 3 is a common factor of both 3 and 21.
Example 4: Express the following fractions in their simplest form.
(a) 6 / 8
(b) 15 / 30
(c) 210 / 330
(a) Divide both numerator and denominator by a common factor.
Dividing 6 and 8 by 2, we have,
(b)
Hence, 15 / 30 in its simplest form = 1 / 2, because 1 and 2 have no common factor except 1.Alternative Method:
Method: To reduce a fraction to its simplest form, keep dividing by common factors until the only common factor is 1.
(c)
Comparing Fractions
1. Comparing Fractions with Like Denominators
Example 5: For a singing competition, 6 / 15 of the children are girls and 9 / 15 are boys. Whose number is greater in the competition, of boys or of girls?
To answer this question we have to compare 6 / 15 and 9 / 15. We can use two ways for comparing them and then state a general rule.
Method 1: Comparing PictoriallyOn comparing the shaded parts, you can see that 9 / 15 > 6 / 15.
∴ The number of boys is more.
Method 2: Comparing on Number Line9 / 15 is to the right of 6 / 15, therefore, 9 / 15 > 6 / 15.
Rule: If two or more fractions have the same denominator, the fraction with the greater numerator is the greater number, e.g., 6 / 7 > 5 / 7 or 5 / 7 < 6 / 7.
2. Comparing Fractions with Unlike Denominators
Example 6: Which is greater: 1 / 3 or 2 / 5?
Pictorially, 1 / 3 and 2 / 5 can be compared as:
Method 1On comparing the shaded parts, you can see that 2 / 5 > 1 / 3.Method 2
Comparing fractions on number line, you can see that 2 / 5 is on the right of 1 / 3.
3. By Finding Equivalent Fractions Using LCM
To compare 1 / 3 and 2 / 5, we convert them into equivalent fractions both having the same denominator.
The common denominator in this case will be taken as the LCM of 3 and 5.
LCM of 3 and 5 = 3 × 5 = 15.

Edurev Tips: This is the most commonly used method for comparing and ordering unlike fractions.
Ordering Fractions
Now that you know how to compare fractions, you can order them in any order— increasing or decreasing.
Example 7: Arrange the fractions 7 / 8, 5 / 12, 15 / 16 in increasing order.
Step 1: Find the LCM of the denominators 8, 12 and 16.
LCM of 8, 12 and 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 2 = 48Step 2: Find the equivalent fractions with denominator 48.
Step 3: Compare the equivalent fractions:
Arranging the fractions in increasing order,
You can write the same fractions in decreasing order as
Ordering Unit Fractions
A unit fraction has 1 as its numerator, but the denominator can vary.
For example, 1 / 2, 1 / 3, 1 / 4, 1 / 5 are unit fractions. What conclusion do you draw from the following diagrams? It can be clearly seen that
It can be clearly seen that Thus, if the numerator is the same, the fraction with the least denominator is the greatest.
Thus, if the numerator is the same, the fraction with the least denominator is the greatest.
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
1. To Add or Subtract Like Fractions (Fractions with the Same Denominator)
When we add or subtract fractions with the same denominator, we just add or subtract the numerators and keep the denominator same.

2. To Add or Subtract Unlike Fractions
Example 8: Ravi and Nisha are painting a wall. Ravi painted 1 / 2 of the wall and Nisha painted 1 / 4 of the wall. What part of the wall did they paint altogether?
Wall painted by Ravi = 1 / 2
Wall painted by Nisha = 1 / 4
Total part of the wall painted = 1 / 4 + 1 / 2
To be able to add these, first change one or both of the fractions to fractions having common denominator. Therefore, 3 / 4 part of the wall was painted by Ravi and Nisha.
Therefore, 3 / 4 part of the wall was painted by Ravi and Nisha.
Rule: When we add fractions with different denominators, we change the fractions to fractions having the same denominator. This common denominator is the least common denominator of the given fractions.
What is meant by least common denominator?
Study the two rows of fractions given below: The numbers 12, 24 and 36 are some of the common denominators of 1 6 and 34. Of these, 12 is the least common denominator. Also, we can see that 12 is the LCM of 6 and 4. Thus, the least common denominator of two fractions is the same as the least common multiple of their denominators.
The numbers 12, 24 and 36 are some of the common denominators of 1 6 and 34. Of these, 12 is the least common denominator. Also, we can see that 12 is the LCM of 6 and 4. Thus, the least common denominator of two fractions is the same as the least common multiple of their denominators.
To add or subtract unlike fractions, write the given fractions as equivalent fractions with the least common denominator (LCM of the denominators) and then add or subtract like fractions.
Example 9: Add:

Method 1: LCM of 4 and 5 = 4 × 5 = 20
Method 2: You may also set your work as under:
Step 1: LCM of 4 and 5 = 20
Step 2: Divide 20 by the denominator of the first fraction. 20 ÷ 4 = 5
Multiply quotient 5 by numerator 3 and write 3 × 5.
Divide 20 by the denominator of the second fraction. 20 ÷ 5 = 4
Multiply quotient 4 by numerator 2 and write 2 × 4.
Now, complete as shown.LCM of 6 and 10 = 30.Changing 5 / 6 and 1 / 10 to equivalent fractions having the same denominator 30.
Example 10: Subtract:

Method 1
LCM of 8 and 4 = 8.Method 2
LCM of 7 and 11 is 7 × 11 = 77.
Addition of Mixed Fractions
Type I: With Same Denominators
Example 11: When released, a gas balloon first rose by  and then again by
and then again by
 What is the total height to which the gas balloon rose?
What is the total height to which the gas balloon rose?
Pictorially, the problem can be represented as:
Thus, we can add mixed numbers by first adding whole numbers and then proper fractions. Therefore, the above work can be set as:
Example 12: A cow gave  litres of milk in the morning and
litres of milk in the morning and  litres in the evening. Find the total quantity of the milk given by the cow.
litres in the evening. Find the total quantity of the milk given by the cow.
Method 1
Method 2
Total quantity of milk given by the cowConvert each mixed number to improper fraction.
∴ So, the cow gave
litres of milk in all.
Type II: With Different Denominators
Example 13: Add:
Method 1
LCM of 2 and 4 = 4.
Method 2
By changing into improper fractions
Example 14: Add:
Method 1
LCM of 4, 6, 12 = 2 × 2 × 3 = 12.Method 2
Edurev Tips: Method 1 is particularly useful when the whole number parts of given fraction are large numbers such as in
Subtraction of Mixed Fractions
Example 15: Subtract:
Example 16: Subtract
Method 1
Step 1: Subtract the whole numbers.
Step 2: Change fractions to equivalent fractions, 1 / 4 = 3 / 12.
Step 3: Subtract the fractions.
Method 2
Convert mixed fractions into improper fractions.
Subtracting from Whole Numbers
Subtracting from 1
Example 17: Mira is preparing a sweet dish. She used 5 / 8 litre of milk from a jug containing 1 litre milk. How much milk is left in the jug?
Quantity of milk remaining in jug
Or
Mira still has 3 / 8 litre of milk left in the jug.
Example 18: David lives 3 kilometres away from a town. Paul lives 56 of a kilometre away from the town. How much closer does Paul live to the town than David?
Method 1
Paul livesThus, Paul lives
km closer to the town as compared to David.Method 2
Paul liveskm closer.
Thus, Paul lives
km closer to the town as compared to David.
Edurev Tips: In subtraction sums like
where whole number parts are large numbers, it may be easier and more convenient to apply method 1.Thus,
Example 19: Subtract:
Method 1
Method 2
Method 2 is generally preferred.
Properties of Addition of Fractions
- Changing the order of two addends does not change the sum.
 Pictorially, it can be shown as:
Pictorially, it can be shown as:
 Similarly, by actual addition, you can verify that;
Similarly, by actual addition, you can verify that;

- Changing the way in which we group the addends does not change the sum.


 Thus,
Thus, Or
Or

 This is called the grouping property of addition of fractions.
This is called the grouping property of addition of fractions. - Additive property of 0.
 Thus, the sum of a fraction and 0 is the fraction itself.
Thus, the sum of a fraction and 0 is the fraction itself.
Decimals
A decimal is another way of expressing a fraction.
1. Tenths The fraction 1 / 10, as a decimal, is written as 0.1 and read as zero point one. The following shaded parts can be read as:
The fraction 1 / 10, as a decimal, is written as 0.1 and read as zero point one. The following shaded parts can be read as:


The dot or the point between the two digits is called the decimal point.
Whole numbers and decimal numbers can also be combined as shown below: The picture given alongside shows, on a ruler, a length of 1 cm + 7 parts out of 1 cm. Since each cm is further divided into 10 equal parts (as can be seen), the above given number can be written as 1.7. 1.7 is also a decimal number and is read as one point seven.
1.7 is also a decimal number and is read as one point seven. 2. Hundredths
2. Hundredths
Let us now divide a whole into 100 equal parts.


We read
- 0.01 as zero point zero one,
- 0.08 as zero point zero eight,
- 0.75 as zero point seven five.
0.41 is 41 hundredths or 4 tenths 1 hundredth.
 Similarly,
Similarly,
 So, a decimal number has two parts—the whole number part and the decimal part separated by a decimal point. Number of digits after the decimal point is called the number of decimal places.
So, a decimal number has two parts—the whole number part and the decimal part separated by a decimal point. Number of digits after the decimal point is called the number of decimal places. In the above number, there are 2 decimal places after the whole number part.
In the above number, there are 2 decimal places after the whole number part.
Edurev Tips: Whenever there is no whole number part, do not forget to write 0 before the decimal point, e.g., .65 is always written as 0.65.
3. Thousandths
If we divide one whole into thousand equal parts, then each part of the whole represents one-thousandth.
Thus, 1 / 1000 = 0.001 or one-thousandth read as zero point zero zero one.
The decimal 0.716 = 716 / 1000 (716 thousandths) represents 716 parts out of 1000 parts.
Sumit and Ritu are both reading the number 0.716 in different ways. Tick  the correct one?
the correct one? In expanded form, we write 0.716 as:
In expanded form, we write 0.716 as: Similarly, 49.107 is forty-nine and one hundred seven thousandths and is read as forty-nine point one zero seven.
Similarly, 49.107 is forty-nine and one hundred seven thousandths and is read as forty-nine point one zero seven.
In expanded form, Notice the following pattern.
Notice the following pattern.
The number of digits after the decimal point in the decimal numeral is equal to the number of zeros after 1 in the denominator of the corresponding common fraction.
Place Value and Decimals
The place value chart shown below can also be used to understand decimals. The place value of each digit in the number 2222.222 is shown below. The first place to the right of the decimal point is the tenths place, the second place to the right is the hundredths place and so on. The last place after the decimal point tells us how to name the decimal part.
The first place to the right of the decimal point is the tenths place, the second place to the right is the hundredths place and so on. The last place after the decimal point tells us how to name the decimal part.
Edurev Tips: Digit at each place has a place value one-tenth (1 / 10) that of the place to its left.
Here it is 222 thousandths.
Using the place value chart, we can write the expanded form of any decimal number. Take the number 1279.364. 1279.364 = 1 thousand + 2 hundreds + 7 tens + 9 ones + 3 tenths + 6 hundredths + 4 thousandths= 1 × 1000 + 2 × 100 + 7 × 10 + 9 × 1 + 3 × 1 / 10 + 6 × 1 / 100 + 4 × 10 / 100Or
1279.364 = 1 thousand + 2 hundreds + 7 tens + 9 ones + 3 tenths + 6 hundredths + 4 thousandths= 1 × 1000 + 2 × 100 + 7 × 10 + 9 × 1 + 3 × 1 / 10 + 6 × 1 / 100 + 4 × 10 / 100Or = 1000 + 200 + 70 + 9 + 3 / 10 + 6 / 100 + 4 / 1000 (Fractional form)
= 1000 + 200 + 70 + 9 + 3 / 10 + 6 / 100 + 4 / 1000 (Fractional form)
= 1000 + 200 + 70 + 9 + 0.3 + 0.06 + 0.004 (Decimal form)
Converting Fractions to Decimals and Vice versa
- Converting Fractions to Decimals
Fractions whose denominators are 10, 100 or 1000 can be easily converted to decimals by putting the decimal point in the numerator accordingly.
Examples:




 For fractions which can be converted to equivalent fractions having denominators 10 or multiples of 10, we apply the same method as above.
For fractions which can be converted to equivalent fractions having denominators 10 or multiples of 10, we apply the same method as above. Similarly,
Similarly,

- Converting Decimals to Fractions
Decimals can also be converted to fractions as under: Pictorial representation of how to convert a decimal to a fraction
Pictorial representation of how to convert a decimal to a fraction Fractions in simplest form
Fractions in simplest form
Equivalent Decimals
Decimals that name the same amount are called equivalent decimals.
Observe the following. As can be seen, these two pictures name the same amount, so 0.8 = 0.80.8 tenths = 80 hundredths8 / 10 = 80 / 100
As can be seen, these two pictures name the same amount, so 0.8 = 0.80.8 tenths = 80 hundredths8 / 10 = 80 / 100
Thus, 0.8 = 0.80 = 0.800 = 0.8000 = ______
Similarly, 1.8 = 1.80 = 1.800 ; 37.41 = 37.410 = 37.4100, etc.
From the above it is clear that writing zeros at the right hand end of a decimal number does not change its value.
1. Like Decimals and Unlike Decimals
Decimals having the same number of decimal places are called like decimals. Decimals having different number of decimal places are called unlike decimals.Thus, 1.2, 4.03, 0.895 are all unlike decimals.2. Converting Unlike Decimals to Like Decimals
Decimals having different number of decimal places are called unlike decimals.Thus, 1.2, 4.03, 0.895 are all unlike decimals.2. Converting Unlike Decimals to Like Decimals
Unlike decimals can be converted to like decimals by finding their equivalent decimals.
Example 1: Convert 6.8, 7.83 and 12.040 to like decimals.
The greatest number of decimal places is 3, so we convert all of them to equivalent decimals with 3 decimal places.
6.8 → 6.800, 7.83 → 7.830, 12.040
Hence, 6.8, 7.83 and 12.040 when converted to like decimals becomes 6.800, 7.830, 12.040.
Comparing and Ordering Decimals
1. Comparing Decimals
To compare decimal numbers, we follow the following steps.
Step 1: Convert the decimals into like decimals.
Step 2: First, compare the whole number parts. The number with the greater whole number part is greater.
Step 3: If the whole number parts are the same, compare the tenths digits. The decimal number having greater tenths digit names a greater number.
Step 4: If the tenths digits are the same, compare the hundredths digits and so on.
Example 2: Which number is bigger: 3.612 or 3.621?
The numbers are
On comparing the digits from the left, you find that the hundredths digits differ. Since 2 hundredths > 1 hundredths, therefore, 3.621 > 3.612.
2. Ordering Decimals
Example 3: Arrange 21.012, 21.002, 24.102 in increasing order.
On comparing the whole number parts, you find that 24.102 is the greatest. Now, compare 210.12 and 21.002.
The whole number parts being the same, we start comparing from the tenths digit.The digits at the hundredths differ. Since 1 hundredths > 0 hundredth, so 21.012 > 21.002.Thus, the given numbers in increasing order are: 21.002, 21.012, 24.102.
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
1. Addition
To add two or more decimals, we follow these steps.
Step 1: Convert the decimal to like decimals.
Step 2: Line up the decimal points, i.e., the addends are placed one below the other such that the tens digit is below tens, ones is below ones, decimal points below the decimal point, tenths below the tenths and so on.
Step 3: Add, as in case of whole numbers. Carry wherever necessary.
Step 4: Place the decimal point in the sum directly below the decimal point in the addends.
Example 4: Add: 4.83, 312.9 and 23.031.
First, we convert the numbers to be added to like decimals.
We have: 4.83 → 4.830, 312.9 → 312.900, 23.031.
Now, line up the decimals and add.
Example 5: Add: 6.9, 3.405 and 9.46.
First, we convert the numbers to be added to like decimals.
Converting into like decimals 6.9 → 6.900, 3.405, 9.46 → 9.460.
Now, line up the decimals and add.
Edurev Tips: A whole number can be expressed in the decimal form as: 12 = 12.0 or 12.00 or 12.000 and so on.
2. Subtraction
To subtract one decimal number from the other, we follow the steps given below.
Step 1: Convert the decimal to like decimals.
Step 2: Line up the decimal points.
Step 3: Subtract in each place value.
Step 4: Regroup, wherever necessary.
Example 6: Subtract 6.253 from 16.67.
- Convert into like decimals as 16.67 → 16.670, 6.253 and line up the decimal points.
- Subtract the thousandths.
You cannot subtract 3 thousandths from 0 thousandths, so borrow 1 hundredths from 7 hundredths leaving behind 6 hundredths.
1 hundredths = 10 thousandths
0 thousandths → 10 thousandths
Now, subtract thousandths, 10 – 3 = 7 thousandths.- Subtract the hundredths.
6 – 5 = 1 hundredth- Subtract the tenths.
6 – 2 = 4 tenths- Subtract the ones.
6 – 6 = 0 ones- Subtract the tens.
1 – 0 = 1 tenSo, 16.67 – 6.253 = 10.417.
Example 7: Find 312.8 – 59.98.
Multiplication of Decimals
1. Multiplication by 10, 100, 1000
Observe the following examples.
(i)
 5 tenths × 10 = 5 ones0.5 × 10 = 5
5 tenths × 10 = 5 ones0.5 × 10 = 5
(ii) 
 2 ones 7 tenths × 10 = 2 tens 7 ones2.7 × 10 = 27
2 ones 7 tenths × 10 = 2 tens 7 ones2.7 × 10 = 27
We observe that:
Multiplying a decimal by 10 moves the decimal point 1 place to the right.
(iii) 
 1 ones 7 tenths 8 hundredths × 100= 1 hundreds 7 tens 8 ones
1 ones 7 tenths 8 hundredths × 100= 1 hundreds 7 tens 8 ones
(iv) 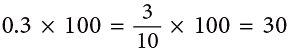
 3 tenths × 100 = 3 tens
3 tenths × 100 = 3 tens
We observe that:
Multiplying a decimal by 100 moves the decimal point 2 places to the right.
(v) 
 2 thousandths × 1000 = 2 ones
2 thousandths × 1000 = 2 ones
Edurev Tips: A number without a decimal point is considered to have the decimal point to the extreme right. 317 means 317.0
(vi) 
 1 one 8 tenths = 1 thousand 8 hundreds(vii)
1 one 8 tenths = 1 thousand 8 hundreds(vii) 

We observe that:
Multiplying a decimal by 1000 moves the decimal point 3 places to the right.
2. Multiplication by a Counting Number
Example 8: If one litre of petrol costs ₹ 74.03, what will be the cost of 12 litres of petrol?
Cost of 12 L petrol = ₹ 74.03 × 12
Step 1: Multiply, as you would multiply counting numbers.
Step 2: Place the decimal point in the product at a place so that the number of decimal places in the product is equal to the total number of decimal places of the factors.
Example 9: Multiply 6.095 by 45.
3. Multiplication of a Decimal Number by a Decimal Number
Lets us find the product of 12.7 and 0.4. The above work can also be set as:
The above work can also be set as:
Working Multiply, as you would multiply the counting numbers.
Multiply, as you would multiply the counting numbers. The total number of decimal places in the product is equal to the sum of the decimal places of the factors.
The total number of decimal places in the product is equal to the sum of the decimal places of the factors.
Example 10: Multiply:
(a) 0.8 × 0.3
(b) 0.007 × 0.03
(c) 0.009 × 1.2
(a)
(b)
(c)
Example 11: Multiply 23.02 by 0.12.
Example 12: Multiply 1.035 by 2.95.
Example 13: Multiply:
(a) 2.6 by 30
(b) 13.46 by 600
(a) 2.6 × 30 = 2.6 × 3 × 10 = 7.8 × 10 = 78.
(b) 13.46 × 600 = 13.46 × 6 × 100 = 80.76 × 100 = 8076.
Division of Decimals
1. Division by 10, 100, 1000
Observe the following examples.
(i) 
 2 ones ÷ 10 = 2 tenths = 0.2
2 ones ÷ 10 = 2 tenths = 0.2
(ii) 
 6 tenths ÷ 10 = 6 hundredths = 0.06
6 tenths ÷ 10 = 6 hundredths = 0.06
We observe that:
Dividing a decimal by 10 moves the decimal point one place to the left.
(iii) 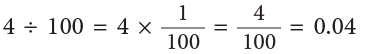

4 ones ÷ 100 = 4 hundredths = 0.04
(iv) 
 2 ones 7 tenths ÷ 100 = 2 hundredths 7 thousandths = 0.027
2 ones 7 tenths ÷ 100 = 2 hundredths 7 thousandths = 0.027
Dividing a decimal by 100 moves the decimal point 2 places to the left.
(v) 
 7 ones ÷ 1000 = 7 thousandths = 0.007
7 ones ÷ 1000 = 7 thousandths = 0.007
(vi) 
(vii) 
Dividing a decimal by 1000 moves the decimal point 3 places to the left.
2. Division by a Counting Number
Example 14: Find: 20.22 ÷ 6.
Compare the two workings shown below.
Step 1:1. 20.22 / 6
Step 2:2.
Step 3:
3. 2022 / 6 = 337
Step 4:4. 337 ÷ 100 = 3.37
Actual Working
Method:
1. Divide, as you would divide counting numbers.
2. Place the decimal point in the quotient directly above the decimal point in the dividend.
Short formSo, 20.22 ÷ 6 = 3.37
Example 15: Divide: 2.67 by 3.
3 > 2, so we put a zero in the quotient.Check
3 × 0.89 = 2.67
∴ 2.67 ÷ 3 = 0.89.
Example 16: Solve: 1414.332 ÷ 17.
∴ 1414.332 ÷ 17 = 83.196.
Example 17: Divide the following.
(a) 14.448 ÷ 14
(b) 262.85 ÷ 35
(a)
∴ 14.448 ÷ 14 = 1.032.
(b)∴ 262.85 ÷ 35 = 7.51.
Check
35 × 7.51 = 262.85
If the last remainder is not zero, write as many zeros on the right of the dividend as are necessary to make the last remainder zero.
Example 18: Find: 9.2 ÷ 16.
∴ 9.2 ÷ 16 = 0.575.
When the divisor is a multiple of 10 or 100 or 1000, etc., then the process of division can be shortened, as shown below.
Example 19: Find: 94.24 ÷ 80.
∴ 94.24 ÷ 80 = 1.178
Short form:
Edurev Tips: 94.24 ÷ 10 = 9.424
3. Division of a Decimal Number by a Decimal Number
You have learnt how to divide a decimal number by a whole number. To divide a decimal number by a decimal number, we make the divisor a whole number.
Look at the following example.
(i) Multiply the divisor by a multiple of 10 to make it a whole number.
Thus, 0.7 × 10 = 7.
(ii) Multiply the dividend by the same multiple of 10.
Thus, 4.41 × 10 = 44.1.
Now, divide as usual:
44.1 ÷ 7 = 44.1 / 7 = 6.3 The work can be set as:
The work can be set as:
Example 20: Divide : (a) 6.265 ÷ 0.07 (b) 1.8 ÷ 0.003
(a)
(b)
Example 21: Divide: 4.20 by 1.05.
4.20 ÷ 1.05 = 4.20 / 1.05
2 decimal places in divisor, s o shif t de cima l p oint 2 places to the right both in divisor and dividend.
∴ 4.20 ÷ 1.05 = 4.
Example 22: Find 20.169 ÷ 0.83.
Shift decimal point 2 places to the right.
∴ 20.169 ÷ 0.83 = 24.3.
Example 23: Divide 66.468 by 76.4.
∴ 66.468 ÷ 76.4 = 0.87.
Example 24: Divide:
(a) 90 ÷ 0.60
(b) 36 ÷ 0.06
(a)
(b)
Changing Common Fractions to Decimal Fractions
Example 25: Change 4 / 5 to a decimal fraction.
To convert 4 / 5 to a decimal, we divide the numerator 4 by the denominator 5, as follows.
Put decimal point after the whole number and add 1 zero to ensure complete division.∴ 4 / 5 = 0.8.
Example 26: Express 85 / 16 as a decimal.
To convert 85 / 16 to a decimal, divide the numerator 85 by the denominator 16.
Put decimal point after the whole number and add 4 zeros to ensure complete division.∴ 85 / 16 = 5.3125.
|
41 videos|151 docs|72 tests
|
FAQs on Note: Fractions & Decimals - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What is a fraction? |  |
| 2. How do you find equivalent fractions? |  |
| 3. How do you write a fraction in its simplest form? |  |
| 4. How do you compare fractions? |  |
| 5. How do you add and subtract fractions? |  |
|
41 videos|151 docs|72 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CTET & State TET exam
|

|
 Here, 1 part out of 4 equal parts is red, we write it as 1 / 4.
Here, 1 part out of 4 equal parts is red, we write it as 1 / 4. 1 / 4 of the cake has been taken by Neha.
1 / 4 of the cake has been taken by Neha. In this aquarium, you have 7 fish, out of which 2 are starfish. So, we write 2 / 7 are starfish.
In this aquarium, you have 7 fish, out of which 2 are starfish. So, we write 2 / 7 are starfish. (i) Mixed Numbers
(i) Mixed Numbers are all mixed numbers.
are all mixed numbers.

 It can also be represented on the number line as:
It can also be represented on the number line as: Jump five-fifths to land on 1. Jump 2 more fifths to land on 7 / 5.This is same as jumping to 1 and then to another 2 / 5.∴ 7 / 5 as a mixed number is
Jump five-fifths to land on 1. Jump 2 more fifths to land on 7 / 5.This is same as jumping to 1 and then to another 2 / 5.∴ 7 / 5 as a mixed number is  Method 2: By Division Method,
Method 2: By Division Method,



 Multiply the whole number part by the denominator and add numerator to the product.Alternatively,
Multiply the whole number part by the denominator and add numerator to the product.Alternatively,





 Dividing 6 and 8 by 2, we have,
Dividing 6 and 8 by 2, we have, (b)
(b) 
 Hence, 15 / 30 in its simplest form = 1 / 2, because 1 and 2 have no common factor except 1.Alternative Method:
Hence, 15 / 30 in its simplest form = 1 / 2, because 1 and 2 have no common factor except 1.Alternative Method:


 On comparing the shaded parts, you can see that 9 / 15 > 6 / 15.
On comparing the shaded parts, you can see that 9 / 15 > 6 / 15. 9 / 15 is to the right of 6 / 15, therefore, 9 / 15 > 6 / 15.
9 / 15 is to the right of 6 / 15, therefore, 9 / 15 > 6 / 15. On comparing the shaded parts, you can see that 2 / 5 > 1 / 3.Method 2
On comparing the shaded parts, you can see that 2 / 5 > 1 / 3.Method 2 Comparing fractions on number line, you can see that 2 / 5 is on the right of 1 / 3.
Comparing fractions on number line, you can see that 2 / 5 is on the right of 1 / 3.
 Step 2: Find the equivalent fractions with denominator 48.
Step 2: Find the equivalent fractions with denominator 48. Step 3: Compare the equivalent fractions:
Step 3: Compare the equivalent fractions: Arranging the fractions in increasing order,
Arranging the fractions in increasing order, You can write the same fractions in decreasing order as
You can write the same fractions in decreasing order as
 Method 1: LCM of 4 and 5 = 4 × 5 = 20
Method 1: LCM of 4 and 5 = 4 × 5 = 20 Method 2: You may also set your work as under:
Method 2: You may also set your work as under:


 Step 1: LCM of 4 and 5 = 20
Step 1: LCM of 4 and 5 = 20 LCM of 6 and 10 = 30.Changing 5 / 6 and 1 / 10 to equivalent fractions having the same denominator 30.
LCM of 6 and 10 = 30.Changing 5 / 6 and 1 / 10 to equivalent fractions having the same denominator 30.

 Method 1
Method 1 Method 2
Method 2
 LCM of 7 and 11 is 7 × 11 = 77.
LCM of 7 and 11 is 7 × 11 = 77.
 Thus, we can add mixed numbers by first adding whole numbers and then proper fractions. Therefore, the above work can be set as:
Thus, we can add mixed numbers by first adding whole numbers and then proper fractions. Therefore, the above work can be set as:
 Method 2
Method 2 Convert each mixed number to improper fraction.
Convert each mixed number to improper fraction. ∴ So, the cow gave
∴ So, the cow gave litres of milk in all.
litres of milk in all. LCM of 2 and 4 = 4.
LCM of 2 and 4 = 4. Method 2
Method 2 By changing into improper fractions
By changing into improper fractions




 Method 2
Method 2





 Step 1: Subtract the whole numbers.
Step 1: Subtract the whole numbers.




 Thus, Paul lives
Thus, Paul lives km closer to the town as compared to David.Method 2
km closer to the town as compared to David.Method 2 km closer.
km closer. Thus, Paul lives
Thus, Paul lives km closer to the town as compared to David.
km closer to the town as compared to David. where whole number parts are large numbers, it may be easier and more convenient to apply method 1.Thus,
where whole number parts are large numbers, it may be easier and more convenient to apply method 1.Thus,

 Method 2
Method 2
 Method 2 is generally preferred.
Method 2 is generally preferred. Pictorially, it can be shown as:
Pictorially, it can be shown as:
 Similarly, by actual addition, you can verify that;
Similarly, by actual addition, you can verify that;



 Thus,
Thus, Or
Or

 This is called the grouping property of addition of fractions.
This is called the grouping property of addition of fractions. Thus, the sum of a fraction and 0 is the fraction itself.
Thus, the sum of a fraction and 0 is the fraction itself.




 For fractions which can be converted to equivalent fractions having denominators 10 or multiples of 10, we apply the same method as above.
For fractions which can be converted to equivalent fractions having denominators 10 or multiples of 10, we apply the same method as above. Similarly,
Similarly,

 Pictorial representation of how to convert a decimal to a fraction
Pictorial representation of how to convert a decimal to a fraction Fractions in simplest form
Fractions in simplest form On comparing the digits from the left, you find that the hundredths digits differ. Since 2 hundredths > 1 hundredths, therefore, 3.621 > 3.612.
On comparing the digits from the left, you find that the hundredths digits differ. Since 2 hundredths > 1 hundredths, therefore, 3.621 > 3.612. The digits at the hundredths differ. Since 1 hundredths > 0 hundredth, so 21.012 > 21.002.Thus, the given numbers in increasing order are: 21.002, 21.012, 24.102.
The digits at the hundredths differ. Since 1 hundredths > 0 hundredth, so 21.012 > 21.002.Thus, the given numbers in increasing order are: 21.002, 21.012, 24.102.

 So, 16.67 – 6.253 = 10.417.
So, 16.67 – 6.253 = 10.417.

 Step 1: Multiply, as you would multiply counting numbers.
Step 1: Multiply, as you would multiply counting numbers. Step 2: Place the decimal point in the product at a place so that the number of decimal places in the product is equal to the total number of decimal places of the factors.
Step 2: Place the decimal point in the product at a place so that the number of decimal places in the product is equal to the total number of decimal places of the factors.


 (b)
(b)
 (c)
(c)



 1. 20.22 / 6
1. 20.22 / 6 2.
2.  Step 3:
Step 3: 3. 2022 / 6 = 337
3. 2022 / 6 = 337 4. 337 ÷ 100 = 3.37
4. 337 ÷ 100 = 3.37

 3 > 2, so we put a zero in the quotient.Check
3 > 2, so we put a zero in the quotient.Check ∴ 1414.332 ÷ 17 = 83.196.
∴ 1414.332 ÷ 17 = 83.196. ∴ 14.448 ÷ 14 = 1.032.
∴ 14.448 ÷ 14 = 1.032. ∴ 262.85 ÷ 35 = 7.51.
∴ 262.85 ÷ 35 = 7.51. ∴ 9.2 ÷ 16 = 0.575.
∴ 9.2 ÷ 16 = 0.575. ∴ 94.24 ÷ 80 = 1.178
∴ 94.24 ÷ 80 = 1.178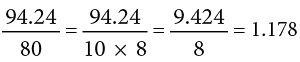


 2 decimal places in divisor, s o shif t de cima l p oint 2 places to the right both in divisor and dividend.
2 decimal places in divisor, s o shif t de cima l p oint 2 places to the right both in divisor and dividend. ∴ 4.20 ÷ 1.05 = 4.
∴ 4.20 ÷ 1.05 = 4. Shift decimal point 2 places to the right.
Shift decimal point 2 places to the right. ∴ 20.169 ÷ 0.83 = 24.3.
∴ 20.169 ÷ 0.83 = 24.3. ∴ 66.468 ÷ 76.4 = 0.87.
∴ 66.468 ÷ 76.4 = 0.87. (b)
(b)
 Put decimal point after the whole number and add 1 zero to ensure complete division.∴ 4 / 5 = 0.8.
Put decimal point after the whole number and add 1 zero to ensure complete division.∴ 4 / 5 = 0.8. Put decimal point after the whole number and add 4 zeros to ensure complete division.∴ 85 / 16 = 5.3125.
Put decimal point after the whole number and add 4 zeros to ensure complete division.∴ 85 / 16 = 5.3125.
















