Notes: Disaster Management | People, Development and Environment for UGC NET PDF Download
Disaster Management
Disaster management involves a series of complex processes aimed at mitigating the impact of disasters.
 It is a challenging task encompassing three key stages:
It is a challenging task encompassing three key stages:
Before a Disaster
- Objective: Reduce potential human, material, and environmental losses caused by hazards.
- Actions: Implement preventive measures to minimize the impact of disasters when they strike.
During a Disaster
- Objective: Ensure the needs and provisions of victims are met to alleviate suffering.
- Actions: Provide emergency response services and immediate relief to those affected by the disaster.
After a Disaster
- Objective: Achieve rapid and durable recovery, returning to normal life.
- Actions: Involve debris cleanup, financial assistance, rebuilding infrastructure, and providing essential services. This stage also includes sustained care for displaced human and animal populations.
Disaster Management Act, 2005
The Disaster Management Act, 2005 is a central legislation enacted to manage disasters effectively in India. It established a three-tier structure for disaster management at the national, state, and district levels. 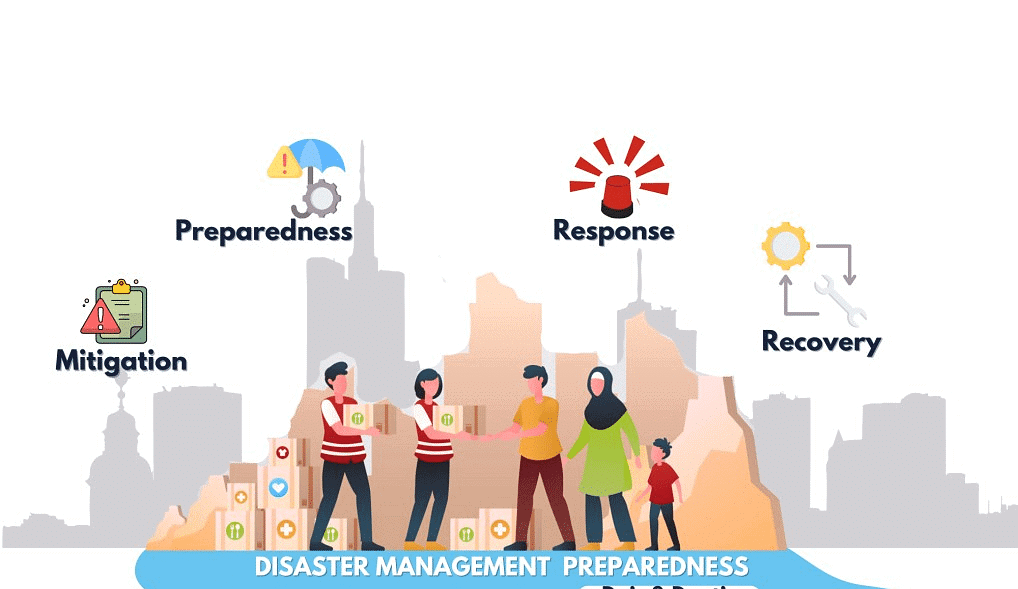 The Act ensures that various government departments make provisions for funds and activities as part of their disaster management plans.
The Act ensures that various government departments make provisions for funds and activities as part of their disaster management plans.
National Disaster Management Policy, 2009
The National Disaster Management Policy, 2009 was approved by the Government of India in November 2009. It lays down the policy framework for disaster management in the country with the following main objectives:
- Promoting Prevention, Preparedness, and Resilience: Foster a culture of disaster prevention and preparedness at all levels through knowledge, innovation, and education.
- Encouraging Mitigation Measures: Implement measures based on technology, traditional wisdom, and environmental sustainability.
- Efficient Risk Assessment and Monitoring: Develop mechanisms for the identification, assessment, and monitoring of disaster risks.
- Contemporary Forecasting and Early Warning Systems: Enhance systems for timely forecasting and early warnings.
- Efficient Response and Early Relief Measures: Ensure effective and timely response and relief efforts.
- Reconstruction Efforts: Undertake reconstruction activities to restore normalcy.
National Disaster Management Plan, 2016
The National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP) 2016 is the first-ever national plan prepared for disaster management in India. It aligns with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030, to which India is a signatory. The salient features of the NDMP are:
- Objective: Make India disaster-resilient and significantly reduce the loss of lives and assets.
- Framework: Based on the four priority themes of the Sendai Framework: understanding disaster risk, improving disaster risk governance, investing in disaster risk reduction, and enhancing disaster preparedness.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers all phases of disaster management - prevention, mitigation, response, and recovery.
- Major Activities: Identifies key activities such as early warning, information dissemination, medical care, fuel supply, transportation, search and rescue, evacuation, etc., serving as a checklist for responding agencies.
Environment-Related Important International Agreements/Conferences
- UN Conference on the Human Environment: Stockholm (1972)
- Convention on Migratory Species: Bonn (1979)
- Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer: Vienna (1985)
- Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer: Montreal (1987)
- Convention on the Transboundary Movement of Hazardous Wastes: Basel (1989)
- Earth Summit (UN Conference on Environment and Development): Rio de Janeiro (1992)
- Convention on Prior Informed Consent: Rotterdam (1998)
- UN Conference on Sustainable Development: Rio de Janeiro (2012)
- Nagoya Protocol on Genetic Resources: Nagoya (2010)
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD-CoP-11): Hyderabad (2012)
- UN Climate Change Conference (CoP-20): Lima (2014)
- Paris Climate Conference (CoP-21): Paris (2015)
- Bonn Climate Conference (CoP-23): Bonn (2017)
- Katowice Climate Conference (CoP-24): Poland (2018)
These agreements and conferences highlight global efforts to address environmental challenges, promote sustainable development, and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
|
26 videos|23 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Disaster Management - People, Development and Environment for UGC NET
| 1. What is the significance of the Disaster Management Act, 2005 in India? |  |
| 2. How does the National Disaster Management Policy, 2009 contribute to disaster management in India? |  |
| 3. What are the key components of the National Disaster Management Plan, 2016? |  |
| 4. How do international agreements and conferences contribute to environment-related disaster management efforts? |  |
| 5. How does disaster management play a crucial role in reducing the vulnerability of communities to disasters? |  |
|
26 videos|23 docs|8 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|

















