Notes: Evaluation and Assessment in Mathematics | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
This chapter is crucial for CTET and state TETs exams as it focuses on evaluation processes and their types. It emphasizes the importance of formative and summative evaluations at the school level. Analysis of previous year CTET and state TETs exams reveals that typically 2 to 3 questions are asked from this chapter annually.
Evaluation is a process of assessing how much knowledge a student has acquired and to what extent the objectives of teaching have been achieved. It is the means through which the educational achievements of both teachers and students are measured.
Relationship Between Objectives and Learning Experiences
The relationship among educational objectives, learning experiences, and evaluation techniques can be diagrammatically represented as follows:
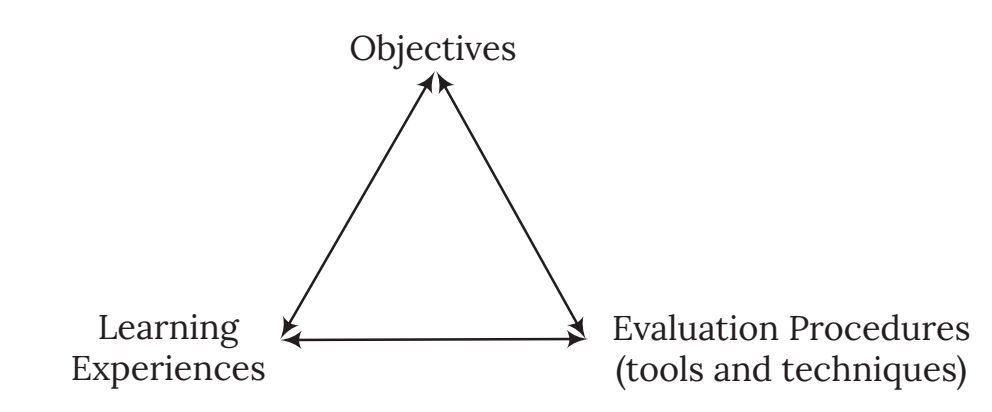
- All three steps (objectives, learning experiences, and evaluation) are inter-related.
- The objectives of teaching are central, upon which both learning experiences and evaluation techniques are based.
- Evaluation is a natural step within the teaching-learning process.
- Evaluation, based on teaching objectives and learning experiences, assesses the extent to which the objectives have been realized.
Therefore, in the classroom, teachers organize suitable teaching-learning activities to promote desired changes in behavior. The learning experiences provided are directly linked to predetermined educational objectives.
Teaching-learning activities are objective-based rather than being solely content or textbook-based. The extent to which these activities lead to experiences that achieve specific objectives is determined through evaluation. Evaluation can be classified as follows:
- Evaluation is both a quantitative and qualitative process, whereas measurement is only quantitative or numerical.
- Evaluation is a continuous process and an integral part of the teaching-learning process.
- Teaching is a conscious and planned activity where educational objectives are set. Based on these objectives, learning experiences are provided, and evaluation determines whether these objectives have been achieved.
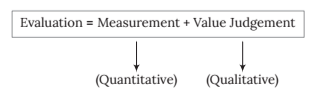
Definitions of Evaluation
The most comprehensive definition of evaluation according to NCERT is Evaluation is any systematic and continuous process of determining-
- The extent to which specified educational objectives, previously identified and defined, are attained.
- The effectiveness of the learning experiences provided in the classroom.
- How well the goals of education have been accomplished.
From the above definitions, the following points are evident:
- Evaluation is a wider concept than testing, measurement, and examination.
- The teaching-learning process becomes dynamic and self-developing through evaluation.
- It is a continuous as well as a comprehensive process.
- Evaluation is directly related to the objectives of education.
- It helps in determining the interests and potential of children.
- Day-to-day records make it easy to know the present status of children.
- Evaluation improves the attitudes, habits, appreciations, interests, manipulative skills, and understanding of children, and helps teachers diagnose children’s difficulties.
- It involves self-appraisal by children and their successes and failures.
Purposes and Functions of Evaluation
Based on the concept and definitions of evaluation, the following are the purposes and functions:
- Assessing Current Status: Evaluation helps determine the current status of children in the teaching-learning process.
- Motivating Better Learning: It serves to motivate children for improved learning outcomes.
- Providing Guidance and Counseling: Evaluation offers guidance and counseling to support children's educational journeys.
- Measuring Progress: It helps measure the rate of progress of children and collect evidence for curriculum improvement.
- Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses: Evaluation identifies children’s strengths and weaknesses to tailor instruction accordingly.
- Assessing Examination System: It measures the effectiveness of the examination system.
- Improving Teacher Efficiency: Evaluation aims to improve the efficiency and success of teachers.
- Measuring Behavioral Changes: It measures the behavioral changes of children.
- Discovering Innovative Teaching Methods: Evaluation helps discover innovative and effective teaching methods.
- Classifying Children: It aids in classifying children into different categories.
- Enhancing Teaching Techniques: Evaluation contributes to improving teaching techniques and strategies.
- Basis for Remedial Teaching: It provides a basis for remedial teaching based on the strengths and weaknesses of children.
- Encouraging Action Research: Evaluation encourages teachers to engage in action research.
- Providing Reinforcement and Feedback: It offers reinforcement and feedback to both teachers and pupils.
Characteristics of a Good Evaluation Programme
- It measures the direction and extent of behavioral changes.
- Evaluation is a quantitative and qualitative estimation of specific changes in children’s behavior.
- Evaluation is diagnostic so that it may provide a basis for remedial teaching.
- Evaluation is a continuous and comprehensive process, offering feedback to the entire educational system.
- Evaluation is pupil-oriented.
- Evaluation is activity-based.
- Evaluation may be used to improve instructions, curriculum, methods, and examinations, etc.
Process of Evaluation
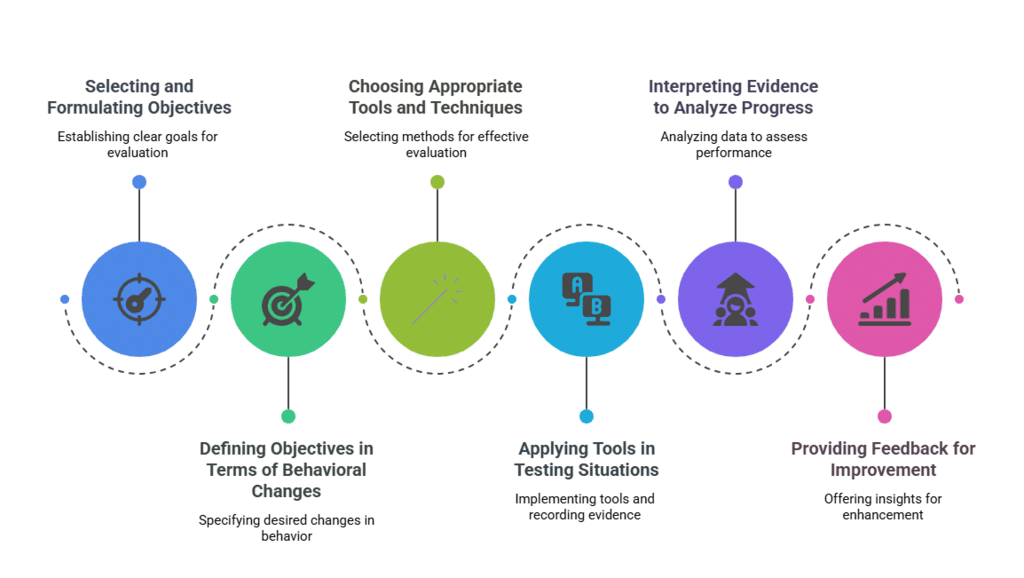
The evaluation process involves several critical steps:
- Selection and Formulation of Objectives: Objectives to be tested are chosen and clearly defined before evaluation. A Mathematics teacher must establish clear instructional objectives which serve as the basis for constructing test items.
- Defining Objectives in Terms of Behavioral Changes: After formulating objectives, they must be defined in terms of the expected changes in a pupil's behavior.
- Selection of Tools and Techniques of Evaluation: The choice of appropriate tools and techniques depends on the type of evidence required to assess teaching objectives effectively.
- Use of Tools and Techniques and Making Results: Tools are applied in testing situations, and evidence regarding behavioral changes is recorded. Conclusions are drawn based on this evidence.
- Interpretation and Generalization of Results: Evidence from various evaluation tools is interpreted to analyze progress and compare individual performance within the class, providing valuable data on achievement levels.
- Feedback of Results for Improvement in Teaching-Learning Process: Analysis of test results provides feedback to students, parents, and teachers. This feedback is essential for diagnosing strengths and weaknesses, allowing for appropriate remedial teaching.
Formative Evaluation
Formative evaluation is the process of monitoring the instructional process to ensure that learning is occurring. It is not intended to make final judgments but to enhance the teaching-learning process through continuous evaluation:
- Enhancing Teaching-Learning Process: Formative evaluation is focused on continuous feedback to both teachers and students, helping to identify learning difficulties and adjust instructional methods.
- Continuous Feedback: Through unit tests, class tests, and assignments, formative evaluation provides ongoing feedback to improve learning outcomes.
- Diagnosing Learning Difficulties: It diagnoses weaknesses in student learning through classroom teaching, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments.
- Improving Learning: Formative evaluation supports improvement in the learning process by identifying and rectifying drawbacks in the current teaching methods.
According to Tanner (1972), "Formative evaluation refers to the use of tests and other evaluative procedures while the course and instructional programme is in progress." Groxlund (1976) pointed out that formative evaluation aims to plan corrective actions to overcome learning difficulties, motivate learning, and enhance retention and transfer of learning.
Need and Importance of Formative Evaluation
The process of formative evaluation is highly necessary for the following reasons:
- Modifying Instruction: Provides information to teachers for modifying instruction and teaching methods.
- Individual Remedial Programs: Helps in prescribing group and individual remedial programs.
- Monitoring Learning Progress: Useful in monitoring pupils' learning progress.
- Feedback to Teachers and Pupils: Provides feedback to both teachers and pupils, facilitating retention and transfer of learning.
- Adjusting Instruction: Enables teachers to adjust their instruction according to the needs of students.
- Correcting Learning Deficiencies: Helps teachers in correcting learning deficiencies.
- Reinforcing Learning: Reinforces learning for high achievers, stimulating better performance.
- Self-Evaluation Device: Formative tests can be used as a self-evaluation device by students.
- Immediate Feedback: Provides immediate feedback to students.
- Diagnosing Strengths and Weaknesses: Helpful in diagnosing a child's strengths and weaknesses.
Summative Evaluation
Summative evaluation is the later process that occurs at the end of the session, aiming to obtain overall results of the teaching-learning process:
- Evaluation Components: Includes class tests, unit tests, quizzes, and term tests, annual tests, and external examinations.
- Purpose: The purpose of summative evaluation is classification and promotion of students.
- Focus: Focuses on measurement of pupils' achievement and certification.
- End of Course Activity: Treated as an end-of-course activity.
- Feedback: Does not provide feedback to students or teachers.
- Timing: Done at the end of the academic session/year.
- Results Usage: Results are used for classification, placement, and predicting future success.
Difference between Formative and Summative Evaluation:
| Formative Evaluation | Summative Evaluation |
|---|---|
| The purpose is to diagnose strengths and weaknesses of pupils. | The purpose is classification and promotion of students. |
| Provides continuous feedback to both pupil and teacher. | Does not provide feedback. |
| Integral part of teaching-learning process. | Treated as an end-of-course activity. |
| Provides relevant information to improve classroom instructions. | Provides the overall results of the teaching-learning process. |
| Results are used for providing remedial measures and enrichment programs. | Results are used for classification, placement, and predicting future success. |
Both types of evaluations are crucial for ensuring all-round development in children and should be implemented considering all necessary aspects.
Techniques of Evaluation
Evaluation is an integral part of teaching and learning. There are several techniques of evaluation, and it's important for the evaluator to select the most appropriate technique to suit the purpose.
The decision to select an appropriate evaluation technique or combination of techniques depends on various factors:
- Contents or Learning Experiences: The evaluation technique should align with the content or learning experiences provided to the learner.
- Behavioral Region: Whether the evaluation focuses on cognitive, conative, or affective domains where behavior changes are measured or assessed.
- Emphasis on Mastery Learning: Techniques should support the mastery of learning objectives.
- Acquisition of Required Performance Level: Evaluating the attainment of required performance levels.
- Reliable Comparability and Grading: Ensuring techniques provide reliable comparisons and grading.
- Nature of Evaluation Techniques: Using techniques suitable for serving particular or required purposes.
The diagram below illustrates various types of evaluation techniques:
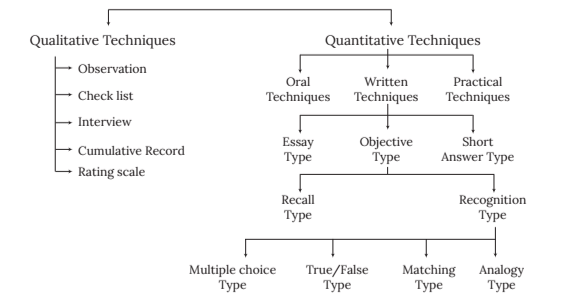
Choosing the correct evaluation technique is crucial for effective assessment and improvement of the teaching-learning process.
|
82 videos|273 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Evaluation and Assessment in Mathematics - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What is the relationship between objectives and learning experiences in mathematics evaluation and assessment? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of a good evaluation program in mathematics assessment? |  |
| 3. Why is formative evaluation important in mathematics assessment? |  |
| 4. What are some techniques of evaluation commonly used in mathematics assessment? |  |
| 5. What are the purposes and functions of evaluation in mathematics assessment according to CTET & State TET guidelines? |  |
















