Notes: Gerunds | Basic Grammar for IELTS PDF Download
Gerunds are an important grammar form to understand and to be able to use effectively in the IELTS test and in your English more generally.
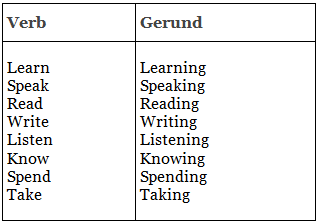
They are nouns and they are formed by adding -ing onto a verb. Take a look at this paragraph - the gerunds are bold.
Learning vocabulary is very important for the IELTS test. Though it is important not to neglect the other skills of speaking, reading, writing and listening, knowing a broad range of words will help you with all the other parts of the test. Unfortunately, many students dislike spending the time that is needed to fully understand each word, but not taking vocabulary seriously could be a big mistake.
Here are examples of the words before and after they are changed:
How are they used?
1. As a subject
- Walking 'is' a good form of exercise
Notice that a gerund takes a singular verb ('is' in this case). You must use the singular verb, even if there are multiple objects:
- Eating bananas, apples and oranges everyday 'is' good for you.
However, if there is more than one, then the plural verb is used:
- Walking and swimming 'are' both good forms of exercise.
To make the sentence negative, 'not' is placed before the gerund.
- Not exercising regularly is dangerous for your health.
2. As a direct object
- Some people like swimming to keep fit.
3. As subject complements after the verb "to be"
- A good way to improve your English is watching American TV series.
This sentence is also commonly written this way:
- Watching American TV series is a good way to improve your English.
4. Objects of prepositions
In this usage, it is after the preposition:
- Another method of learning English is to read lots of fiction books.
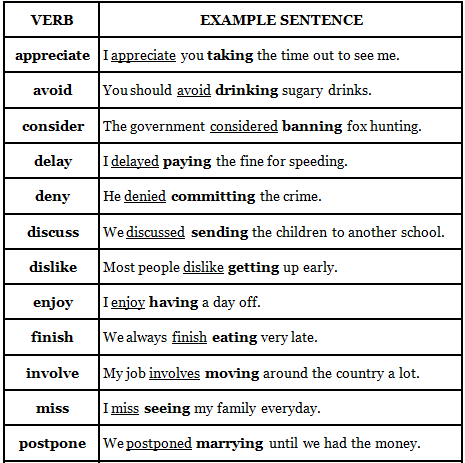
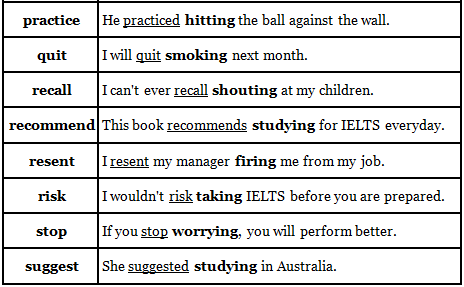
Common verbs before gerunds
If you wish to put two verbs together, then the second verb will need to be a gerund and / or infinitive.
For example, you can't say this:
- We always finish eat very late.
- We always finish to eat very late.
If "finish" is followed by another verb, it needs to be a gerund.
- We always finish eating very late.
There is no grammatical reason for this as such, so you just need to learn the verbs and practice writing some sentences with those verbs.
Remember, certain verbs should be followed by an infinitive, not a gerund, and some verbs can be followed by either. For example:
- I like to swim (verb + infinitive)
Or - I like swimming (verb + gerund)
Here is a list of verbs that are very commonly followed by a gerund (not an infinitive):
Verbs Commonly Followed By A Gerund
A Verb After a Preposition
If you place a verb after a preposition, the gerund form is used.
Here are some examples:
- I am interested in learning a new language.
- There are many advantages of taking a sabbatical from work.
- I passed my exams without trying too hard.
- I'm worried about sitting for the IELTS test.
- I got a band 7 by studying very hard.
- I was shocked upon hearing the news.
- I'm sorry for talking so loud.
The best way to learn these is to understand collocations - words that commonly go together.
For example, we always talk about being "interested in" something, or the "advantages of" something.
Talking about an activity
We also use them to talk about an activity with the word 'go'.
For example:
- I wanted to go jogging but my friend said he'd prefer to go swimming instead.
With reduced adverb clauses
They are also used to make reduced adverbial clauses. Below are some examples.
However, there are various rules for reducing adverbial clauses so you should make sure you understand these rules before attempting them.
While I study, I listen to music.
- Reduced: While studying, I listen to music
Before I went out, I turned the lights off.
- Reduced: Before going out, I turned the lights off
I locked the doors after I got home.
- Reduced: I locked the doors after getting home.
Because I was tired, I could not study any longer.
- Reduced: Being tired, I could not study any longer.
As mentioned above, you should avoid using them until you have studied and practiced them, otherwise you may make mistakes.
|
18 videos|54 docs
|
FAQs on Notes: Gerunds - Basic Grammar for IELTS
| 1. What is a gerund? |  |
| 2. How are gerunds used in sentences? |  |
| 3. Can you give examples of gerunds used in different contexts? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific rules for using gerunds? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my understanding and usage of gerunds? |  |





















