Interactive Model - Communication Notes
Introduction
The Interactional Model of Communication depicts communication as a dynamic process where individuals interchangeably assume roles as senders and receivers.
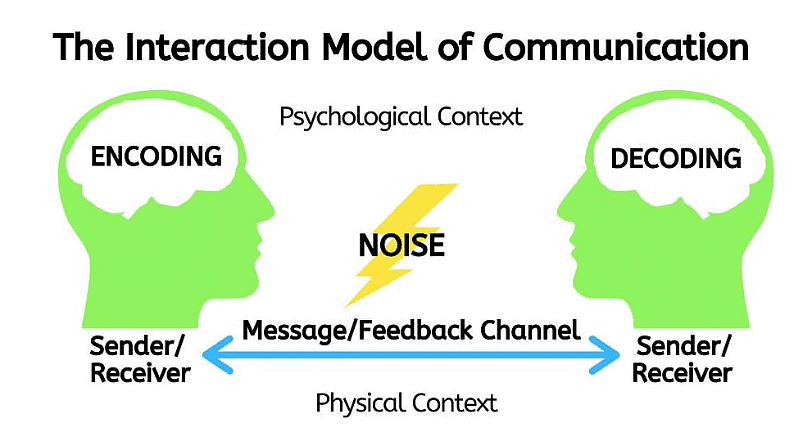
- The Interaction Model of Communication differs from the traditional linear model by integrating feedback, transforming communication into a dynamic, interactive exchange.
- For instance, in a classroom discussion, a teacher might respond to student questions or comments, enhancing understanding through dialogue. Similarly, in daily interactions, like searching for a remote control, individuals respond directly to inquiries, demonstrating the reciprocal nature of communication.
How did Interactive model evolve?
- The main flaw in the linear model is that it depicts communication as a one-way process where speakers only speak and never listen. It also implies that listeners listen and never speak or send messages. Schramm came out with a more interactive model that saw the receiver or listener providing feedback to the sender or speaker. The speaker or sender of the message also listens to the feedback given by the receiver or listener.
 Interactive Model
Interactive Model
- Both the speaker and the listener take turns to speak and listen to each other. Feedback is given either verbally or non-verbally, or in both ways. This model also indicates that the speaker and listener communicate better if they have common fields of experience, or fields which overlap.
This model is described in Schramm’s book “The Process and Effects of Communication”.

Concepts of Schramm’s Communication Model
Schramm’s model of communication includes the source which is also known as the encoder, the message or the signal, and the destination which is also recognized as the decoder. The model addresses the sociological aspects involved in communication. Communication or commonness can take place if the fields of the source and destination overlap as shown in the figure below as the field of experience.
It is a Circular Model, so that communication is something circular in nature
- Encoder – Who does encoding or Sends the message (message originates)
- Decoder – Who receives the message
- Interpreter – Person trying to understand (analyses, perceive) or interpret
[Question: 0]
Advantages
- Circular communication gives opportunity to both parties to give their opinion.
- As it is dynamic and ever changing model, it is helpful in general practice.
- Sender and receiver interchanges and both are equally active.
- Semantic noise included as a concept helps in understanding problems that can occur during interpretation of message.
- Feedback makes it easier to know if the message is interpreted by the receiver as intended or not.
- Concept of interpretation makes the communication effective.
- Field of experience (psychological effect) helps to understand the communication process in many other ways than the traditional ones..
- Concept of context makes the environmental factor be included in interpretation of message and brings change in the message value.
Disadvantages
- This model can not deal with multiple levels of communication and complex communication processes.
- There can only be two sources communicating, many sources complicates the process and the model can not be implemented.
- Message sent and received might be interpreted differently than intended.
|
5 videos|18 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Interactive Model - Communication Notes
| 1. How did the Interactive model of communication evolve? |  |
| 2. What are the key concepts of Schramm's Communication Model? |  |
| 3. Why is feedback important in the Interactive model of communication? |  |
| 4. How does the Interactive model differ from other communication models? |  |
| 5. How can the Interactive model be applied in everyday communication? |  |


















