Notes: Learning & Acquisition | English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Types of Learning |

|
| Factors Affecting Learning |

|
| Right to Education (RTE) Act |

|
| Concept of Acquisition |

|
| Language Development in Children |

|
| Development of Vocabulary |

|
Learning is the process of acquiring new skills or knowledge and enhancing existing abilities. Through learning, individuals experience changes in their knowledge and behavior. The rate at which people acquire skills varies, meaning everyone learns at different speeds. Several factors influence a person's learning experience, including the environment, the learner's ability and motivation, and the teacher's effectiveness and methods of imparting knowledge.

Here are some definitions of learning from various educationists:
Richard E. Mayer: “Learning is the relatively permanent change in a person’s knowledge or behavior due to experience.”
According to this definition, we focus on three key aspects:
- The duration of the change is long-term rather than short-term.
- The change pertains to the content and structure of knowledge in memory or the learner's behavior.
- The cause of the change is the learner's experience in the environment, rather than factors like fatigue, motivation, or physical condition.
Susan Ambrose: “Learning is a process that leads to change, which occurs as a result of experience and increases the potential for improved performance and future learning.”
From this, we can conclude that learning is a process of gaining knowledge and expertise.
Types of Learning
There are three types of learning:
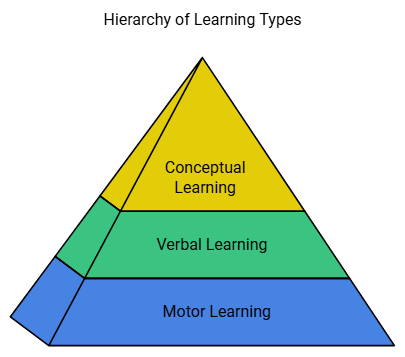
1. Motor Learning
This type of learning involves motor activities that we perform in daily life, such as walking, running, driving, and climbing. These activities require muscular coordination.
2. Verbal Learning
Verbal learning involves the use of language and communication methods such as signs, pictures, symbols, words, and sounds. These tools facilitate various verbal activities.
3. Conceptual Learning
Conceptual learning requires higher-order mental processes like thinking, reasoning, and intelligence. Through these processes, a child learns different concepts.
Factors Affecting Learning
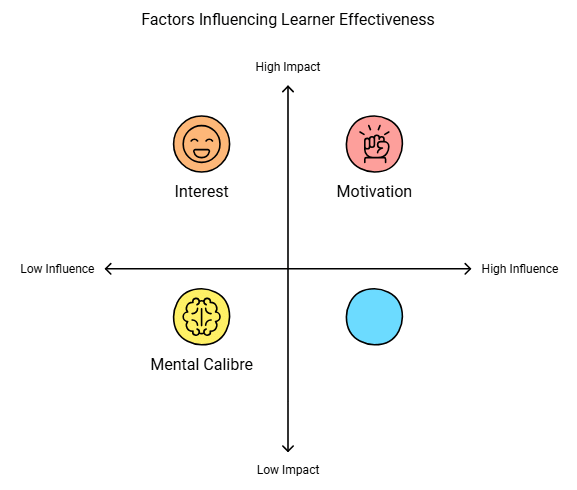
Certain factors affect the learning of individuals. These factors can be categorized as follows:
Factors Related to Learner
- Motivation: The learner's motivation determines the speed and intensity of learning. A motivated learner learns more effectively and permanently.
- Mental Calibre: An intelligent learner tends to learn more effectively.
- Interest: A learner's interest in a particular subject makes them more inclined towards learning it.
Factors Related to Teacher
- Competence: A competent teacher can motivate learners, making their role crucial.
- Communication: Effective communication and good pronunciation by the teacher make learning more lasting and effective.
- Infrastructure: The size and structure of the classroom affect learning. Crowded or poorly structured classrooms can disturb learners.
- Availability of Materials: The non-availability of textbooks or resource books can impair the learning process.
Factors Related to the Environment
- Conducive Environment: A suitable environment is essential for effective learning.
- Natural Surroundings: Climatic and atmospheric conditions, such as high temperature and humidity, can decrease mental efficiency.
Right to Education (RTE) Act
The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act) was enacted by the Parliament of India on 4th August 2009. It describes the importance of free and compulsory education for children between 6 and 14 years in India. The RTE Act is the first legislation in the world that places the responsibility of ensuring enrolment, attendance, and completion of elementary education on the government.
The RTE Act stipulates that no child admitted to a school shall be held back in any class or expelled until the completion of elementary education. It also prohibits physical punishment or mental harassment of children, advocating for a child-friendly learning environment.
Concept of Acquisition
When language is learnt naturally without systematic practice, it is called acquisition. The terms 'learning' and 'acquisition' are complementary. Learners acquire a language when it is used in their natural environment.
Language Acquisition
- Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the ability to perceive, produce, and use words to communicate.
- This process involves acquiring syntax, phonetics, and an extensive vocabulary. It can be vocal (speech) or manual (sign language).
- Language acquisition typically refers to first language acquisition in infants, while second language acquisition deals with learning additional languages.
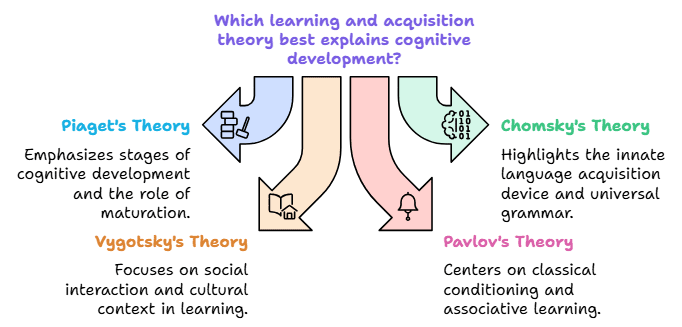
Concepts Associated with Acquisition and Learning
Piaget’s Concept
- Piaget's cognitive theory states that learning starts with adaptation, achieved through assimilation and accommodation.
- Assimilation involves taking in information and making sense of it, sometimes changing the information to fit existing knowledge.
- Accommodation involves changing thought patterns based on new information.
- Classification of words and sounds is important for language learning.
- Criticism: Lev Vygotsky argued that Piaget's theory overlooked cultural differences and the need for assistance in certain learning tasks.
Chomsky’s Concept
- Noam Chomsky believes that children are born with an innate ability to learn any human language, with certain linguistic structures pre-imprinted on their minds.
- Chomsky introduced the concept of the Language Acquisition Device (LAD), a hypothetical tool in the brain that helps children learn syntax and vocabulary.
- Critics argue that language learning might be due to general learning abilities and social interactions rather than an innate LAD.
Vygotsky’s Concept of Learning and Acquisition
- Vygotsky's theory is based on constructivist learning, where knowledge is acquired through social experiences.
- Social and language interactions with more experienced community members are crucial for learning.
- Community plays a central role in making meaning and developing culturally organized psychological functions.
- Language learning involves guided discovery, where parents and teachers help children internalize language skills.
- Vygotsky's theory opposes Piaget's, emphasizing the social origins of higher mental processes.
Pavlov’s Concept of Learning
- Ivan Pavlov proposed the theory of Classical Conditioning, where a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response originally evoked by another stimulus.
- Pavlov's experiments with dogs showed that they could be conditioned to salivate at the sound of a bell, demonstrating automatic learning.
- Pavlov suggested that humans also learn through stimuli, and this concept can be applied to teaching students.
BF Skinner's Concept of Learning
BF Skinner proposed the theory of learning known as operant conditioning, which is based on habit formation. According to Skinner, humans and other creatures respond due to reinforcement. He believed that classical conditioning was too simplistic to explain complex human behavior fully.
Skinner emphasized understanding behavior by examining the causes of actions and their consequences. Operant conditioning focuses on intentional actions (operants) that affect the environment. Skinner aimed to identify processes that made certain operant behaviors more or less likely to occur.
Language Development in Children
Effective communication between people who know and respect each other is crucial for a child's language development. Language allows children to understand their surroundings, express feelings, and communicate with others. When children can express new ideas and complex matters, their self-esteem is boosted. Difficulty in verbalizing feelings can lead to frustration and reduced self-esteem.
Encouraging Language Development in Children
- Talking with babies helps them learn the sounds of a language. Babies may respond by babbling.
- Responding to babies' attempts to communicate fosters language development.
- Daily conversations and using diverse vocabulary enhance a child's language skills. Parents should talk to toddlers about their activities.
- Encouraging children to tell stories and discuss past and future events supports language growth.
- Reading with children and sharing books significantly aid in language development.
Initial Stage of Language Development
The desire to communicate begins at birth. Babies quickly learn to get their needs met through crying, cooing, and making eye contact with their immediate family. A child's overall development and mental health are greatly influenced by their ability to communicate in various ways.
- Words are essential for connecting a child to their family and the wider world.
- Through words, children store information and share their feelings and experiences.
- By age three, children possess a remarkable knowledge of language structure and syntax, challenging existing learning theories to explain their acquisition.
Actual Stage of Language Development
The early years of childhood are preparation time for language learning. Language development starts with oral expressions as children learn to use words, sentences, and then complex structures.
- When children start school, they develop reading and writing skills.
- Gradually, children become proficient in listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
- Proficiency in language helps children use it as a tool for expression, acquire knowledge, and develop into well-rounded individuals.
Development of Vocabulary
As children grow, their vocabulary expands significantly. Typically, children understand or recognize more words than they can speak, especially in the early years.
Vocabulary Growth in Early Childhood
- At around 1 to 1.5 years old, children understand more words than they can speak.
Children's Vocabulary at Different Ages
| Age | Vocabulary |
|---|---|
| Birth to 8 months | 0 words |
| 9 months to 1.5 years | 3 to 12 words |
| Up to 2 years | 272 words |
| Up to 2.5 years | 450 words |
| Up to 3 years | 1000 words |
| Up to 3.5 years | 1250 words |
| Up to 4 years | 1600 words |
| Up to 5 years | 2100 words |
| Up to 11 years | 50,000 words |
| Up to 14 years | 80,000 words |
| 16 years and beyond | More than 100,000 words |
Vocabulary Learning
As children reach school age and enter kindergarten, they typically have a vocabulary of around 2000 words. Talking and reading are excellent sources for vocabulary development. Here are some strategies to encourage vocabulary growth:
- Parents and family members should engage children in conversations about their day at school, their teachers, books they checked out from the library, and any funny events that occurred.
- Encouraging vocabulary development is crucial for children to develop the language and literacy skills needed for school success.
Strategies to Increase Vocabulary
- Follow the child's interests: Talking about topics that interest the child helps them pay attention and learn new words.
- Avoid overwhelming the child: Introduce new words gradually, allowing time for the child to respond and use their vocabulary to express feelings.
- Repetition: Children need to hear a word multiple times to remember it.
- Explain new words: Help children understand the meaning of new words.
- Use actions or gestures: Accompany new words with actions or gestures to help children acquire them more easily.
|
47 videos|208 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Learning & Acquisition - English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the main types of learning that can affect language acquisition? |  |
| 2. How do factors related to the learner influence language acquisition? |  |
| 3. What role does the teacher play in the language acquisition process? |  |
| 4. How does the environment impact language learning? |  |
| 5. What are the initial and actual stages of language development? |  |
















