Notes: Teaching Aptitude | Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Objectives of Teaching |

|
| Bloom's Taxonomy |

|
| Gagne and Briggs Model |

|
| Nature and Characteristics of Teaching |

|
| Different Levels of Teaching |

|
Introduction
Teaching Aptitude tests help determine if a person has the skills and abilities needed to be a good teacher. These tests predict how well someone might perform as a teacher in the future by focusing on specific skills important for teaching.
Teaching aptitude includes the basic qualities required to become a successful teacher. This involves having the right knowledge, good communication skills, a positive attitude, intelligence, and other important traits that make an effective teacher.

Concept of Teaching
- Teaching is a methodology involving various activities. It originates from "to teach," signifying instruction.
- It denotes a process where an individual acquires knowledge from a more knowledgeable person.
- Teaching is the skillful application of knowledge, experience, and scientific principles to create a conducive learning environment.
- Teaching aptitude involves shaping students' behaviour in alignment with societal needs, cultures, and ideologies.
- Comprising "Teaching" and "Aptitude," teaching aptitude embodies a teacher's quality in imparting knowledge.
- Teaching aptitude encompasses teaching aids, methodologies, and activities essential for effective teaching.
- It focuses on the teacher-student relationship within a conducive and controlled educational setting.
Definitions of Teaching
- HC Morrison: Teaching is described as an intimate interaction between a more mature individual and a less mature one, with the purpose of advancing the latter's education.
- NL Gage: Teaching is portrayed as a form of interpersonal influence directed towards altering the behavioural potential of another person.
- Albert Einstein: Teaching is defined as a supreme art that aims to inspire joy in creative expression and knowledge.
- Clerk Teaching: Refers to activities intended to elicit specific behaviours in students.
- APJ Abdul Kalam: Views teaching as a noble profession that molds an individual's character, abilities, and future. He aspires to be remembered as a good teacher.
- Edmund Amidon: Describes teaching as an interactive process primarily involving classroom discussions between teacher and student during specific activities.
Objectives of Teaching
Teaching is an interactive process between students and teaching sources. It is essential for the guidance, progress, and development of students. The objective of teaching and learning should be integrated at the end of instruction. A good objective should be outcome-based and measurable.
The objectives of teaching are:
- to bring desired changes in students' attitude.
- to shape the behaviour and conduct of students.
- to develop children into a social and efficient member of society.
- to develop conceptual, intellectual, and subject-specific skills.
- to develop understanding.
- to improve the learning skills of students including methodological critical thinking, creative writing, etc.
An instructional objective should be specific, outcome-based, and measurable in nature. It describes an intended result of instruction rather than the process of instruction.
There are two ways of classifying instructional objectives: one given by Bloom and another by Gagne and Briggs.
Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy, developed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives by level of complexity and specificity. The three lists cover learning objectives in the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains.
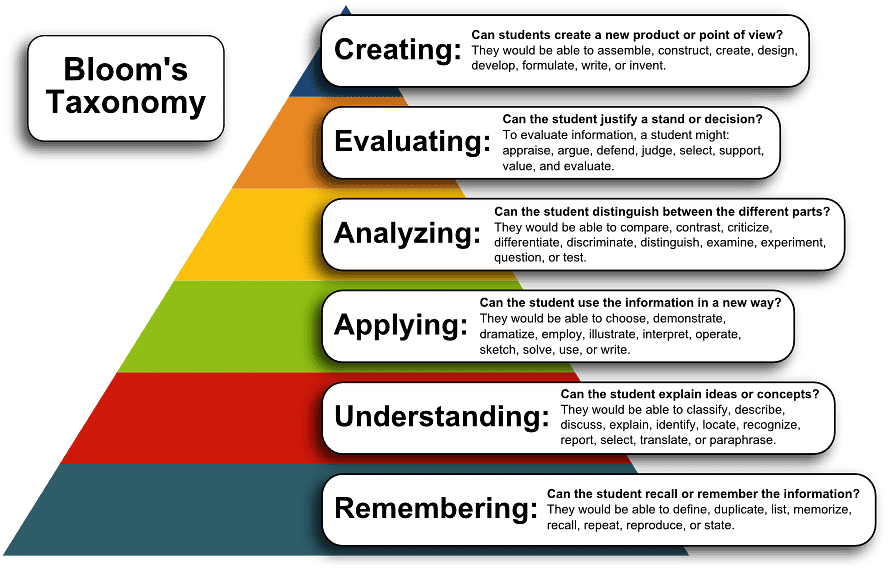
The Cognitive Domain
- Knowledge: Recognizing or remembering facts, terms, basic concepts, or answers without necessarily understanding their meaning.
- Comprehension: Demonstrating understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating the main ideas.
- Application: Using acquired knowledge to apply facts, techniques, and rules.
- Analysis: Examining and breaking information into component parts, determining how these parts relate to one another, and finding evidence to support generalizations.
- Synthesis: Building a structure or pattern from diverse elements.
- Evaluation: Presenting and defending opinions, making judgments about information, validity, or quality of work based on a set of criteria.
The Affective Domain
- Receiving: Involving student's memory and recognition.
- Responding: Involving student participation in the learning process.
- Valuing: Involving the value of knowledge acquired by students.
- Organizing: Involving accommodation of values, information, and ideas learned.
- Characterizing: Involving the building of abstract knowledge.
The Psychomotor Domain
- Observing: Actively attending to a physical event.
- Imitating: Attempting to copy a physical behavior.
- Practicing: Trying specific physical activities repeatedly.
- Adapting: Fine-tuning and making minor adjustments in physical activities to perfect them.
- Naturalization: Adapting, modifying, or designing new techniques, methods, or procedures according to the requirements of a situation.
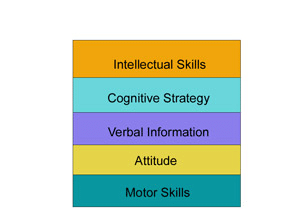
Gagne and Briggs Model
Also known as Gagne’s Nine Conditions of Learning or Gagne’s Taxonomy of Learning. - It categorizes educational learning objectives into specific areas.
 Gagne and Briggs Model
Gagne and Briggs Model
Categories of Educational Learning Objectives:
- Verbal Information: - Definition: Refers to the ability to articulate knowledge acquired by an individual. - Example: Reciting historical facts in a history class.
- Intellectual Skills: - Definition: Involves problem-solving using established rules. - Includes: Concept learning, rule learning, and problem-solving. - Example: Solving a math problem using learned formulas.
- Cognitive Skills: - Definition: Involves problem-solving by formulating rules. - Encompasses: Methods and techniques for self-learning, memory retention, and critical thinking. - Example: Developing a study strategy for memorizing vocabulary.
- Motor Skills: - Definition: Involves physical movements coordinated by the brain, nerves, and muscles. - Example: Playing a musical instrument or typing on a keyboard.
- Attitudes: - Definition: Refers to the internal state of an individual. - Example: Developing a positive attitude towards teamwork in a group project.
By understanding these categories in the Gagne and Briggs Model, educators can effectively structure learning objectives to enhance the overall learning experience for students.
Nature and Characteristics of Teaching
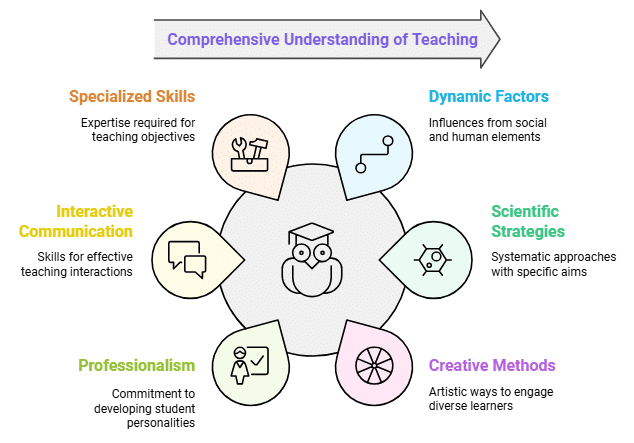
- Dynamic, Social, and Humane: Teaching is not a static concept; it is greatly influenced by dynamic social and human factors.
- Science: Teaching is systematic, with specific aims and the use of scientific strategies and techniques.
- Art: Teaching involves the creativity of teachers in explaining concepts to different types of learners.
- Diverse Application: Teaching can take various forms such as formal, informal, instructional, and more.
- System of Actions: Teaching involves a variety of actions related to content and pupil behavior under different conditions.
- Professional Activity: Teaching is a professional activity aimed at developing students' personalities.
- Interactive Process: Teaching heavily relies on communication skills and is carried out with specific purposes and objectives.
- Subjected to Analysis and Assessment: Teaching can be analyzed, assessed based on tasks, and provide feedback for improvement.
- Specialized Task: Teaching requires a set of specialized skills to achieve certain objectives.
- Collection of Various Modes: Teaching encompasses various modes like conditioning, training, instruction, and indoctrination which contribute to the overall teaching process.
- Continuous Process: Teaching is an evolving, continuous, and lifelong process emphasizing continuous learning and adaptation to change.
To understand the meaning of teaching, it is essential to understand the difference between teaching and other similar concepts like conditioning, training, instruction, and indoctrination. Here, a brief description is given below.
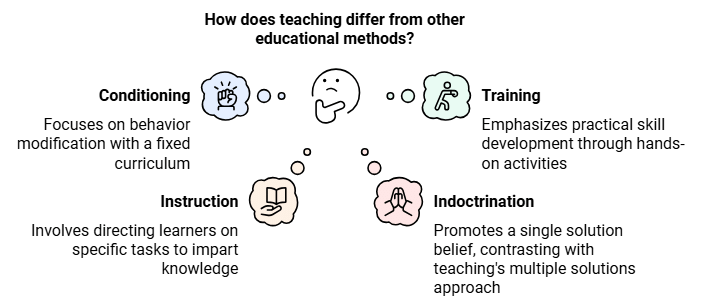
- Teaching is different from conditioning as it aims to develop intellect and has border scope with the vast curriculum while on the other hand conditioning is the modification of behaviour and learning habits. In conditioning, the curriculum is fixed and done by the repetition of the behaviour.
- Teaching is different from training as teaching is mostly theoretical and usually refers to classroom learning while training is practical oriented and it refers to workshops, seminars, role-plays, simulations, etc. skill development is a key aspect of the Training Process.
- Teaching and instruction are different as Instruction is the act of telling the learner what to do or what not to do to impart knowledge of specific subjects while teaching means the development of the potential of an individual.
- Teaching and Indoctrination are different as indoctrination poses the belief that there is only one solution to the problem while teaching points out that there are different solutions, often to the Same problem
The overall object of teaching is to build an overall personality of the learners and it evolves around the development of learner’s capability, thinking, and change in the behaviour of students.
Different Levels of Teaching
- Memory Level of Teaching
- Understanding Level of Teaching
- Reflective Level of Teaching
Memory Level Teaching (MLT)
- Memory-level teaching emphasis on presentation of facts and information and it’s all about CRAMMING.
- Knowledge or information is gained by the learner through memorization.
- It is the initial stage of teaching and induces the habit of ROTE Learning of facts and subject matters
- It covers only the knowledge-based objectives of Bloom’s Taxonomy. At this level, the student learns to identify, recall or remember the objects, events, and ideas and retain them in memory.
- The teacher plays a very dominating and authoritarian role while instructing. The role of the teacher is prominent (Primary & active) and that of the student is secondary (Secondary & Passive).
Key aspects:
- Learning
- Retention
- Reproduction
Objectives:
- Acquisition of factual knowledge through memorization and rote learning.
- Covers knowledge-based objectives of Bloom's Taxonomy.
- Subject-centered teaching.
- Teaches simple, memorable concepts.
- Delivers structured and observable knowledge.
Steps in Memory Level of Teaching by Herbert:
- Preparation: Testing previous knowledge.
- Statement of Aim: Introducing the topic.
- Presentation: Stimulating mental activity for self-learning.
- Association: Establishing relationships between facts.
- Generalization: Formulating principles for future situations.
- Application: Using new knowledge in various contexts.
Psychological Basis:
- According to Piaget, learners are at a pre-operational cognitive level.
- Pavlov and Skinner's conditioning theory supports reinforcement for longer retention.
Teaching Method:
- Subject-centered approach.
- Methods include drill, review, revision, and questioning.
- Drill involves practice, review forms new associations, revision solidifies concepts, questioning assesses objectives.
Evaluation System:
- Includes essay and objective questions.
- Oral tests evaluate memorization levels.
- Tests assess comprehension, analysis, synthesis, and discrimination.
Suggestions:
- Progress teaching material from simple to complex.
- Ensure teaching material is objective and useful.
- Use adequate teaching aids and integrate content well.
- Provide continuous reinforcement during instruction.
- Present subject matter systematically and organized.
The Herbartian theory of apperception supports that the young children’s mind is ready for perceiving themselves and the world around them. Their mind is ready for a great mass of factual information including concepts, elements, structures, models and theories. They can acquire and retain information about a large number of things, objects, and materials through memorization.
Classification of memory:
- Immediate memory: when a recall is immediate
- Permanent memory: the recalling of material for a longer time.
- Personal memory: while recalling the experience, we remember our personal experience.
- Impersonal memory: recalling from books, and companion.
- Active memory: make effort to recall past experiences, recalling answers in exams.
- Passive memory: recall experience without effort.
- Mechanical memory or physical memory: body becoming habitual of doing any task repeatedly.
- Rote memory: cramming facts without understanding.
- Logical memory: to learn something by using intellect and it’s recalling when needed.
Understanding Level of Teaching (ULT)
- Memory level teaching is the prerequisite for the understanding level of teaching as it talks about the generalization of principles, theory, and other key important facts.
- This helps to build the thinking level of students to make use of their acquired knowledge based on previously known facts and subjects.
- The teacher explains to the students the relationship between principles and facts and teaches them how these principles can be applied.
- It focuses on mastery of the subject.

Teaching at the Understanding Level
- Quality of Teaching: Teaching at the understanding level, as advocated by Morrison, is superior to memory-based teaching. It emphasizes mastering the subject, making it more valuable and thoughtful.
- Intellectual Development: At this level, teaching aims to develop intellectual behaviour. Students enhance their critical thinking skills, present information logically, analyze it effectively, and draw inferences.
- Motivation: Motivation at the understanding level involves both extrinsic and intrinsic factors.
- Teaching-Learning Approach: Focuses on connecting isolated facts with overarching principles. It includes exploration, presentation, assimilation, organization, and recitation through various means.
Objectives of Understanding Level Teaching
- Understanding Objectives: Interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, comparing, and inferring instructional messages.
- Application Objectives: Applying principles/rules in practical life situations using proper procedures.
Structure of Understanding Level Teaching
- Presentation: Content is presented, diagnosed, and recapitulated until students understand.
- Exploration: Testing previous knowledge and analyzing content.
- Assimilation: Generalization, individual activities, working in labs/libraries, and content tests.
- Organization: Providing opportunities for representation.
- Recitation: Students orally present the content.
Teaching Method at the Understanding Level
- Subject-Centered Approach: Teacher plans classroom proceedings, adopts a permissive role, and motivates learners.
- Teaching Methods: Include lecture, discussion, inductive-deductive, exemplification, etc.
- Evaluation System: Tests assess students' comprehension, synthesis, discrimination, generalization, and application of principles.
Suggestions
- Effective Classroom Interaction
- Organized Subject Matter
- Use of Teaching Aids
- Proper Classroom Environment and Teacher Motivation
Morrison has divided the understanding level of teaching into 5 steps;
- Exploration: testing previous knowledge, analyzing the content.
- Presentation: content is presented, diagnosis, and recapitulation till the students understand.
- Assimilation: generalization, individual activities, working in laboratory and library, the test of content.
- Organization: pupils are provided with the occasions for representation.
- Recitation: pupil presents the content orally.
Reflective Level of Teaching (RLT)
- Reflective level of teaching, also known as the introspective level, is advocated by Hunt as the highest and most practical level of teaching. It involves the application of scientific methods to comprehend problems. This level requires deep thought and is achievable only after the memory and understanding levels.
- At this stage, students cultivate curiosity, interest, inquiry, and persistence, leading to scientifically determined conclusions or solutions to problems. Teaching and learning at the reflective level necessitate a meticulous and critical examination of ideas or problems through a problem-solving approach.
Objective
- Develop insight into the learner to solve problems.
- Foster rational and critical thinking in students.
- Cultivate independent thinking and decision-making skills in students.
Structure
Hunt has segmented the reflective level of teaching into five steps:
- Creating a problematic situation.
- Formulating a hypothesis.
- Verifying the hypothesis.
- Collecting data.
- Testing the hypothesis.
Teaching Method
The teaching approach at this level is student-centered, emphasizing significant interaction between teachers and learners. The study material or classroom proceedings are not rigidly structured or pre-planned. Interactions are thoughtful, allowing learners to contribute their ideas to solve specific problems. Teachers assume a democratic role in this teaching level.
Evaluation System
Evaluation at the reflective level should assess higher-order cognitive abilities such as reasoning, creativity, original thinking, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
Suggestions
- Provide a conducive atmosphere for learning.
- Encourage independent learning and expression of thoughts.
- Offer proper guidance.
- Ensure fair evaluation.
|
27 videos|45 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Teaching Aptitude - Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance
| 1. What is the concept and definition of teaching? |  |
| 2. What are the main objectives of teaching? |  |
| 3. How does Bloom's Taxonomy classify educational objectives? |  |
| 4. What is the Gagne and Briggs Model in teaching? |  |
| 5. What are the different levels of teaching, and how do they differ? |  |





















