Types of Research - Research Aptitude Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Research |

|
| 1. Objective Based Research |

|
| 3. Logic-Based Research |

|
| 4. Formation/Interaction/Inquiry-Based Research |

|
| 6. Process-Based Research |

|
| 7. Nature Based Research |

|
Introduction
According to Redman and Mory (1923), research is a “systematized effort to gain new knowledge”. In simple terms research refers to a search for knowledge. It is a scientific and systematic search for information on a particular topic or issue. It is also known as the art of scientific investigation.

Key elements of Research:
- Research Question: Formulating a clear and focused inquiry to guide the investigation.
- Methodology: Selecting appropriate techniques and procedures for data collection and analysis.
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant information through various methods such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Data Analysis: Applying systematic procedures to interpret and make sense of the collected data.
- Results: Presenting findings accurately and objectively, often through statistical analysis or qualitative interpretation.
- Conclusion and Implications: Drawing conclusions based on the results and discussing their significance for the research field or real-world applications.

Types of Research
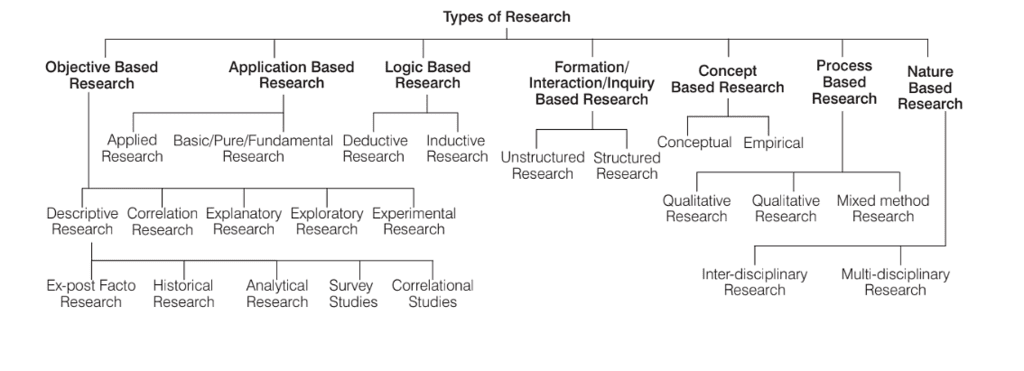
1. Objective Based Research
Objective-based research refers to a systematic inquiry conducted with specific goals or objectives in mind. These objectives serve as guiding principles for the research process, directing the selection of methodologies, data collection strategies, and analysis techniques
(i) Descriptive Research
- This type of research aims to systematically describe a situational problem or phenomenon.
- It provides information about various subjects such as the living conditions of a community.
- Includes surveys and fact-finding inquiries with interpretations.
- Main characteristic: researcher has no control over variables, only reports what has happened or is happening.
- Purpose: collecting information without disturbing the environment.
Types of Descriptive Research
- Ex-post Facto Research: Empirical inquiry based on scientific investigation of dependent and independent variables. Subjects are not randomly assigned but grouped based on specific characteristics or traits.
- Historical Research: Process of critical inquiry into past events to produce accurate descriptions and interpretations.
- Goal: discover past trends to understand the present and anticipate the future.
- Analytical Research: Focuses on cause-effect relationships, using available facts or information for critical evaluation. Researchers formulate hypotheses and specify interpretations.
- Survey Studies: Forms of questioning involving larger groups of people. Conducted to create authentic descriptions, diagnose problems, and plan for change.
- Correlational Studies: Measure two or more relevant variables to assess relationships among them.
(ii) Correlational Research
Correlational research measures the level of association or relationship between two or more variables. In correlational research, variables must be quantifiable and usually represent at least ordinal scale of measures.
A consistent relationship between variables is used to predict future events.
It aims to find out whether there is either:
- Positive Correlation: In this correlation, both variables change in the same direction. For instance, as height increases, weight also increases.
- Negative Correlation: In this correlation, the variables change in opposite directions. For example, as coffee consumption increases, tiredness decreases.
- Zero Correlation: In this correlation, there is no relationship between the variables. For example, coffee consumption is not correlated with height.
(iii) Explanatory Research
Explanatory research is conducted for problems that have not been researched before.
- The purpose of explanatory research is to explain why certain events occur and to build, elaborate, extend, or test theory.
- Explanatory research allows the researcher to test and verify specific theories and make amendments to those theories.
Example: To analyze the effects of re-branding initiatives on the levels of customer loyalty.
(iv) Exploratory Research
Exploratory research is conducted for problems that have not been clearly defined. It is a flexible approach that can address research questions of various types, such as what, why, and how.
This type of research is often utilized to generate formal hypotheses.
Example: Alcoholism, a significant issue in Indian society, lacks a clear definition due to its medical implications. Researchers, through exploratory research, delve into numerous reasons behind alcoholism. They may develop a hypothesis, such as alcohol consumption for body relaxation. Exploratory research remains open-ended, leaving room for further investigation and study on the issue.
(v) Experimental Research
Experimental research involves a methodical and scientific approach where the researcher manipulates one or more variables while controlling and altering other variables.
Primary Aim: To examine the cause-and-effect relationship between variables.
- For instance, in the realm of education, factors like the level of education, skill proficiency, industry sectors, and work experiences are considered independent variables. These variables can individually impact an individual's salary.
- If any of these variables increases, such as attaining a higher level of education or gaining more experience, the individual's salary is likely to increase as well.
2. Application Based Research
Application-based research seeks to solve practical problems. This type of research plays an important role in solving everyday problems that often have an impact on life, work, health, and overall well-being.
(i) Basic/Pure/Fundamental Research:
Basic research involves the process of collecting and analyzing data/information to develop or enhance theory. It is conducted solely for the purpose of theory development and refinement.

- Basic research advances fundamental knowledge about the human world.
- It focuses on refuting or supporting theories that explain how things operate, what makes things happen, why social relations are a certain way, and why society changes.
- It generates new ideas, principles, and theories, laying the foundations of modern progress and development in different fields.
Example: A study looking at how caffeine consumption impacts the brain.
(ii) Applied Research
Applied research aims to address specific practical problems faced by individuals, groups, or society. It is utilized in fields such as medicine, business, and education to discover solutions that can potentially cure illnesses, resolve scientific challenges, or advance technology.
- This type of research directly employs data from real-world applications to derive conclusions.
- The primary objective of applied research is to enhance the overall human condition.
Example: Identifying the most effective strategies for managing and treating conditions like anxiety, depression, and asthma falls under the realm of applied research.

3. Logic-Based Research
Logic based research is guided by the logical processes of induction and deduction. Logic-based research refers to a systematic investigation grounded in the principles of logic and reasoning
(i) Deductive Research
In deductive research, the researcher studies existing theories and tests hypotheses that emerge from those theories.
The deductive method involves:
- State the hypothesis based on the theory or research literature.
- Collect data to test the hypothesis.
- Make a proper decision on whether the hypothesis is supported or not.
Example: In a study analyzing the impact of classroom environment on a child's mental health, a researcher deduced that lack of orderliness and basic supplies are associated with the behavioral issues that children show in the classroom.

(ii) Inductive Research
In inductive research, a researcher collects data relevant to the topic of interest and identifies patterns.
The inductive approach involves:
- Observing different events or phenomena in the world.
- Identifying patterns between observations.
- Making a general view about what is occurring.
Example: A researcher collected data about depression and aggression among teenagers and found that a number of teenagers became depressed and aggressive after exam results were declared. The researcher theorized that overexpectation of parents from their child is the main reason for the depression and aggression.
4. Formation/Interaction/Inquiry-Based Research
Formation based research relies on the interaction of the researcher with a specific group of individuals. This interaction can take the form of direct or indirect engagement.
(i) Unstructured Research
- In unstructured research, the issue under investigation is not predetermined; instead, it arises spontaneously.
- Researchers have the freedom to explore the nature of a problem, issue, or phenomenon without quantifying it.
Example: A study on the diversity of food patterns in different regions of India.
(ii) Structured Research
- Structured research, also known as systematic observation, involves collecting data without direct involvement with the participants.
- This method relies on coding for data collection and is typically associated with quantitative research.
Example: If the Indian Standards Institution wishes to assess the popularity of a specific food product, it would employ structured research methods to analyze the data quantitatively.
5. Concept Based Research
Concept-based research involves exploring, analyzing, and understanding specific concepts or ideas within a particular field or discipline.
(i) Conceptual Research:
This type of research is generally used by philosophers and thinkers to develop new concepts or to reinterpret the existing concepts.
(ii) Empirical Research:
- The empirical research relies on experiences or observation alone.
- It is a data-based research coming up with conclusions that are capable of being verified by observation or experiment.
(iii) Research Aptitude
In this type of research, the researcher must formulate a working hypothesis. He collects data to prove or disprove his/her hypothesis.6. Process-Based Research
Process-based research involves studying the procedural aspects of a phenomenon, focusing on the sequence of steps, actions, or events involved. It aims to understand how processes unfold, evolve, and influence outcomes.
(i) Qualitative Research:
- Qualitative research is not merely a method but an approach, emphasizing induction and understanding human behavior or social phenomena.
- It focuses on processes rather than outcomes, employing holistic, naturalistic, and non-manipulative methods to grasp complex dynamics without reliance on statistical tests.
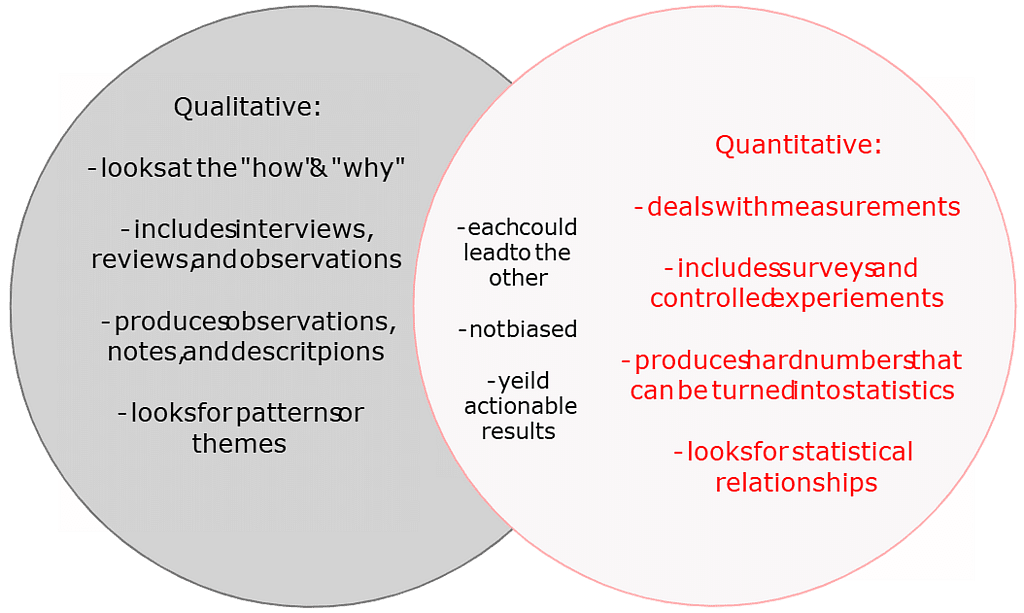
(ii) Quantitative Research:
- Quantitative research, primarily aligned with positivist paradigms, involves numerical data collection and experimentation.
- It employs deductive reasoning to test existing theories, utilizing sophisticated statistical analyses.
- Planned experiments and structured data collection ensure adherence to original plans, facilitating straightforward analysis and interpretation.
(iii) Mixed Research:
- Mixed-method research integrates quantitative and qualitative approaches, encompassing data collection and analysis from both paradigms.
- It combines methods such as experiments and surveys with qualitative techniques like focus groups and interviews, offering a comprehensive understanding of research phenomena.
7. Nature Based Research
(i) Inter-disciplinary Research
- Inter-disciplinary research involves integrating information, data, techniques, tools, perspectives, concepts, and theories from two or more disciplines to advance understanding or solve complex problems.
- It goes beyond the limitations of a single discipline or area of research practice.
(ii) Multi-disciplinary Research
- Multi-disciplinary research combines two or more subjects to delve into a topic in a way that wouldn't be achievable by discussing just one subject.
- In multi-disciplinary research, different disciplines independently address scientific and social challenges, each pursuing its own goals.
|
16 videos|24 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Research - Research Aptitude Notes
| 1. What are the main types of research based on objectives? |  |
| 2. How does Application Based Research differ from Objective Based Research? |  |
| 3. Can you explain what Process-Based Research entails? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Concept Based Research in academia? |  |
| 5. How does Nature Based Research contribute to environmental studies? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|













