Olympiad Notes: Angles | Math Olympiad for Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is an Angle? |

|
| Measuring Angles |

|
| Types of Angles |

|
| Angles in 2-D Shapes |

|
| Solved Examples: Angles |

|
Introduction
- Imagine you’re playing with a pair of scissors or flying a paper airplane. Did you know that every time you open the scissors or fold the plane’s wings, you’re creating angles?
- Angles are everywhere – in the corners of rooms, between the hands of a clock, and even when you stretch your arms wide!
- In this lesson, we will discover what angles are, the different types of angles, and how to spot them all around us.
- Get ready to explore the exciting world of angles and become an angle expert!
What is an Angle?
- An Angle is made when two lines meet at one point.
- Imagine a slice of pizza—each slice has an angle at the pointy end, as shown below.

Measuring Angles
An angle measure in geometry is the measurement of the angle created when two lines meet at one common point.
- The unit of measurement of an angle is degree.
- The sign '°' represents a degree.
- Angles with varying degrees include 30 degrees, 45 degrees, 90 degrees, and so on.
- This is written as 30°, 45°, 90°, and so on.
- Angles are measured using a simple geometric instrument called a Protractor.

Types of Angles
Angles are classified into three categories:

- Acute Angles: Angles less than 90 degrees.
- Right Angle: Angles equal to 90 degrees.

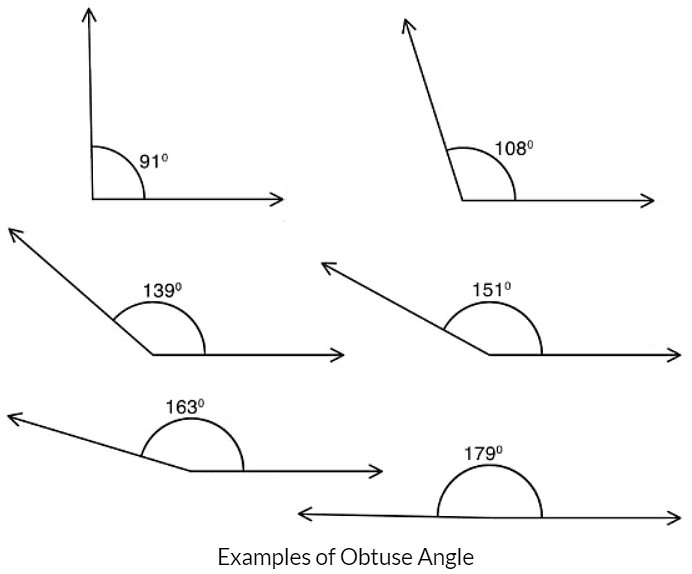
- Obtuse Angles: Angles greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.

Did You Know?
- If the angle is equal to 180 degrees, it is called a Straight Angle.
- It is called a straight angle because it measures 180 degrees, forming a straight line without any bends or curves.

Angles in 2-D Shapes
1. Triangle
- A triangle is a three-sided geometrical figure with three angles.
- The sum of angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.

2. Quadrilateral
- A Quadrilateral is a four-sided geometrical figure with four angles.
- The sum of angles of a quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
- Examples of quadrilaterals are given below, where each of them has the sum of all angles equal to 360 degrees.
3. Pentagon
- A Pentagon is a five-sided geometrical figure with five angles.
- The sum of angles of a pentagon is 540 degrees.
- A Regular Pentagon has all angles equal to 108 degrees.

4. Hexagon
- A Hexagon is a six-sided geometrical figure with six angles.
- The sum of angles of a hexagon is 720 degrees.
- A Regular Hexagon has all angles equal to 120 degrees.

Angles Made by a Clock at Different Times

On a clock, we may see various angles based on their amplitude: acute, straight, obtuse, flat angles, and even complete angles.
- The full circumference of the clock is 360 degrees.
- The distance between each number on the clock is similar to 30 degrees.
- Example: The angle created between 1 o’clock and 2 o’clock is 30 degrees.
Solved Examples: Angles
Example 1: Look at the following pictures and answer the questions given below:

a) Are the angles marked in yellow equal and why?
b) Are the angles marked in green equal and why?
c) Are the angles marked in blue equal and why?
Answer:
a) Yes, the angles marked in yellow are equal.
Solution:
As both the yellow angles are of a Regular Pentagon (a shape having 5 sides), all angles will be equal to 108 degrees. Hence, the angles are equal.b) Yes, the angles marked in green are equal.
Solution:
As both the green angles are of a Regular Pentagon (a shape having 5 sides), all angles will be equal to 108 degrees. Hence, the angles are equal.c) Yes, the angles marked in blue are equal.
Solution:
As both the blue angles are of a Regular Octagon (a shape having 8 sides), all angles will be equal to 135 degrees. Hence, the angles are equal.
Example 2: What kind of angles are made by the hands of the clock given below?

Solution:
Example 3: What kind of angles are made by the given yogic poses below?

Solution:
- In figure (a), the angle made by the arm is Acute Angle.
- In figure (b), the angle shown is Obtuse Angle.
- In figure (c), the angle shown is Right Angle.
Example 4: Find out how many angles are made by joining the following matchsticks:

Solution:
- In fig (a), we can make 4 angles.
- In fig (b), we can make 5 angles.
- In fig (c), we can make 6 angles.
|
32 videos|57 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Angles - Math Olympiad for Class 5
| 1. What is an angle and how is it formed? |  |
| 2. How do you measure angles accurately? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of angles? |  |
| 4. How do angles relate to 2-D shapes? |  |
| 5. Can you provide a simple example of calculating angles in a triangle? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|