Operating Costs Definition: Formula, Types, and Real-World Examples | Cost and Management Accounting for CA Intermediate PDF Download
What are Operating Costs?
Operating costs refer to the expenses involved in the regular maintenance and management of a business on a day-to-day basis. These costs encompass the direct costs of goods sold (COGS) along with other operational expenditures, commonly known as selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses. SG&A costs typically cover items such as rent, payroll, overhead expenses, raw materials, and maintenance costs. It's important to note that operating costs do not include non-operational expenses related to financing activities like interest payments, investments, or foreign currency conversions.
When calculating a company's financial performance, operating costs are subtracted from revenue to determine the operating income. This figure is then reflected in the company's income statement.
Key Takeaways
- Operating costs represent the continuous expenses incurred in the day-to-day operations of a business.
- These costs encompass both the costs of goods sold (COGS) and other operational expenses, including SG&A expenditures.
- In addition to COGS, typical operating costs may involve expenses such as rent, equipment maintenance, inventory expenditures, marketing efforts, employee payroll, insurance premiums, and resources allocated for research and development.
- Analyzing a company's income statement provides insights into its operating costs and financial performance.
Understanding Operating Costs
Businesses need to carefully monitor their operating costs along with expenses related to non-operational activities like interest payments on loans. These costs are recorded differently in a company's financial records, enabling analysts to assess how costs align with revenue-generating operations and if the business can be managed more efficiently.
In general, a company's management aims to maximize its profits. Profitability is influenced by both the revenue generated by the company and its operational expenditures. Increasing profits involves boosting revenue and reducing operating costs. Since cutting costs appears to be a simpler way to enhance profits, managers often opt for this approach.
However, excessively reducing operating costs can hamper a company's productivity and consequently its profitability. Although reducing a specific operating cost typically leads to short-term profit gains, it may also impact the company's long-term earnings.
For instance, if a company slashes its advertising expenditure, short-term profits are likely to rise due to lower operating costs. Nonetheless, by reducing advertising expenses, the company might compromise its ability to attract new customers, potentially affecting future earnings.
Impact of Operating Costs on Profitability
- Profitability is influenced by revenue and operational expenses.
- Increasing profits involves boosting revenue and cutting operating costs.
- Managers often opt for cost reduction to enhance profitability.
Long-Term Effects of Cost-Cutting Measures
- Excessive cost reductions can hinder a company's productivity.
- Short-term profit gains may lead to long-term earnings decline.
- Example: Cutting advertising costs may impact future revenue generation.
How to Calculate Operating Costs
Calculating a business's operating costs involves extracting key details from the income statement to assess financial performance over a specific period.
Operating cost=Cost of goods sold+Operating expenses
- Retrieve the total Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) or Cost of Sales from the income statement.
- Identify the total Operating Expenses located further down the income statement.
- Add the total Operating Expenses to the COGS to determine the overall operating costs for that period.
Types of Operating Costs
Operating costs encompass various expenses necessary for the day-to-day functioning of a business. These costs do not involve capital investments but cover several crucial aspects of operational expenditures, including:
- Accounting and legal fees
- Bank charges
- Sales and marketing costs
- Travel expenses
- Entertainment costs
- Non-capitalized research and development expenses
- Office supply costs
- Rent
- Repair and maintenance costs
- Utility expenses
- Salary and wage expenses
Furthermore, operating costs also encompass the cost of goods sold, which directly relate to the production of goods and services. These costs include:
- Direct material costs
- Direct labor expenses
- Rent for the plant or production facility
- Benefits and wages for production workers
- Equipment repair costs
- Utility expenses and taxes for production facilities
Business operating costs consist of fixed costs and variable costs, each playing distinct roles within a company's financial framework.
Fixed Costs
Definition of Fixed Costs:
- A fixed cost remains constant regardless of the level of sales or production activities within a company. These expenses must be paid irrespective of the company's performance.
Examples of Fixed Costs:
- For instance, consider a manufacturing firm that pays a fixed amount as rent for its factory space, regardless of the production output or revenue generated. Even if the company reduces its production, these costs persist.
Components of Fixed Costs:
- Fixed costs typically encompass overhead expenses, insurance premiums, security costs, and equipment maintenance charges.
Role of Fixed Costs in Economies of Scale:
- Fixed costs play a crucial role in achieving economies of scale. When a significant portion of a company's costs are fixed, it can enhance profitability per unit with increasing production volumes.
Impact on Production Efficiency:
- By spreading fixed costs across a higher number of units produced, companies can lower the average per-unit production cost, thereby improving production efficiency.
Limitations of Economies of Scale:
- However, the principle of economies of scale has its limitations. For instance, as production levels increase, companies may need to expand facilities to accommodate the growth, leading to higher fixed costs.
Variable Costs
Variable costs, as the name suggests, consist of expenses that fluctuate with production levels. Unlike fixed costs, which remain constant, variable costs rise with increased production and fall with decreased production. Examples of variable costs include raw materials and electricity expenses. To boost french fry sales, a fast-food chain may need to up its potato orders from suppliers.
Companies can sometimes secure volume discounts when buying supplies in bulk. This arrangement involves the seller reducing the per-unit cost in return for the buyer committing to large-scale purchases regularly. Consequently, this agreement can somewhat weaken the direct correlation between production changes and operating cost fluctuations.
For instance, a fast-food chain might buy potatoes for $0.50 per pound for purchases under 200 pounds. However, if they purchase in bulk, say 200 to 500 pounds, the supplier may offer a discounted price of $0.45 per pound. While volume discounts can slightly alter the relationship between production and variable costs, the overall trend remains consistent.
Semi-Variable Costs
Semi-variable costs are a combination of fixed and variable costs, falling between the two in terms of characteristics.
While variable costs fluctuate with production levels and fixed costs remain constant regardless of production, semi-variable costs exhibit properties of both.
These costs partially increase or decrease based on production changes, akin to variable costs, yet they persist even when production is at zero, similar to fixed costs.
An illustrative example of a semi-variable cost is overtime labor within a company's operations.
Regular wages are typically fixed costs, as a minimum workforce is needed for operations, but overtime wages can vary based on productivity levels.
Overtime payments demonstrate both fixed (base salary) and variable (additional hours worked) elements, making them semi-variable costs.
Real-World Example of Operating Costs
Below is the income statement for Apple Inc. (AAPL) for the year ending Sept. 25, 2021, according to its annual 10-K report:
- Apple reported total revenue or net sales of $365.8 billion for the 12-month period.
- The total cost of sales (or cost of goods sold) was $213 billion, while total operating expenses were $43.9 billion.
- We calculate operating costs as $213 billion + $43.9 billion.
- Operating costs (cost of sales + operating expenses) were $256.9 billion for the period.
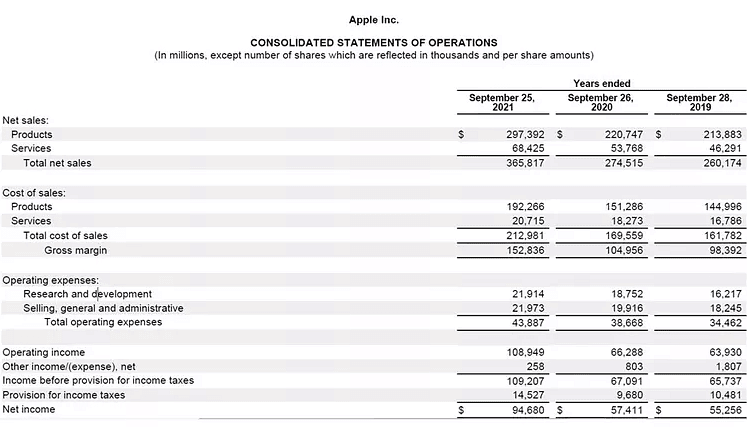
It's crucial to analyze Apple's total operating costs across multiple quarters to gauge the company's efficiency in managing these costs effectively. Investors can also track operating expenses and the cost of goods sold separately to assess whether these costs are on the rise or decline over time.
SG&A vs. Operating Costs
Selling, general, and administrative expense (SG&A) is detailed in the income statement as the total of all direct and indirect selling expenses along with all general and administrative expenses (G&A) incurred by a company. SG&A encompasses all expenses not directly linked to the production of goods or provision of services—this includes costs associated with selling and delivering products or services, as well as managing the company.
SG&A essentially covers everything that is not part of the cost of goods sold (COGS). On the other hand, operating costs encompass COGS in addition to all operating expenses, which includes SG&A.
Limitations of Operating Costs
Similar to any financial measure, operating costs should be assessed across various reporting periods to identify trends effectively. At times, companies might reduce costs for a specific quarter, leading to a temporary boost in their earnings. It is crucial for investors to consistently monitor costs to understand whether they are increasing or decreasing over time. They should also compare these findings with revenue and profit performance.
What is the Total Cost Formula?
- The total cost formula represents a combination of a company's fixed and variable expenses to determine the overall cost of producing a specific quantity of goods or services.
- To compute the total cost, you sum the average fixed cost per unit with the average variable cost per unit and then multiply this sum by the total number of units manufactured.
- This formula holds significant importance for management as it aids in evaluating the profitability of the business.
- By utilizing the total cost formula, managers can identify areas where fixed or variable costs might be reduced to enhance profit margins effectively.
- Furthermore, this calculation assists managers in establishing the optimal pricing strategy for their products and facilitates comparisons between the profitability of different product lines.
How are Profits Affected by Operating Costs?
High or increasing operating costs can diminish a company's net profit. Management typically seeks ways to stabilize or reduce these costs while ensuring the production of goods that satisfy consumer demand. Should operating costs escalate significantly, management might need to raise product prices to sustain profitability, risking customer migration to competitors offering similar goods at lower prices.
What Sets Apart Operating Costs from Startup Costs?
Operating costs are the ongoing expenses a business faces in its regular operations, while startup costs are the expenses associated with initiating a new business. Before a business commences operations or introduces a new product, it incurs expenses such as research and development, equipment acquisition, office space leasing, and employee salaries. Typically, these startup costs are financed through business loans or private investments, contrasting with operating costs that are covered by revenue from sales.
|
24 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Operating Costs Definition: Formula, Types, and Real-World Examples - Cost and Management Accounting for CA Intermediate
| 1. What is the formula to calculate operating costs? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of fixed costs in a company's operating costs? |  |
| 3. How do variable costs differ from fixed costs in terms of operating costs? |  |
| 4. How do operating costs impact a company's profitability and risk? |  |
| 5. What are semi-variable costs and how do they fit into a company's operating costs? |  |
|
24 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CA Intermediate exam
|

|
















