Overview: Sustainable Management of Natural Resources - 1 | Science for Super TET PDF Download
Indian culture and traditions have always integrated living in harmony with nature. Our Mahaupanishad has famous phrase ‘Vasudhaiv Kutumbakam’ i.e., entire earth is one family. Hence, sustainable living has always been an integral part of our culture.
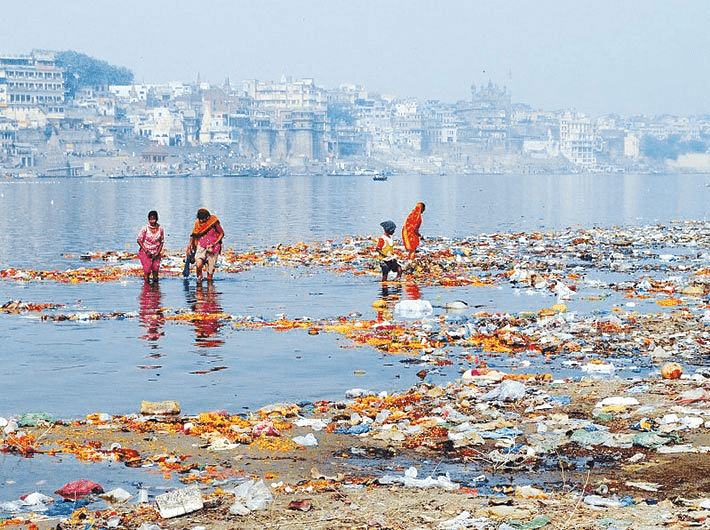
- Ganga Action Plan: The multi-crore Ganga Action Plan came about in 1985 because the quality of water in the Ganga was very poor. Coliform is a group of bacteria, found in human intestines whose presence in water indicates contamination by a disease-causing microorganism.
- Pollution in Ganga: The Ganga flows from Gangotri in the Himalayas to Ganga Sagar in the Bay of Bengal through a distance of over 2500 km. More than a hundred towns and cities in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal pour their garbage and excreta into it. Untreated sewage is pushed into the Ganges every day. Additionally, bathing, washing of clothes and immersion of ashes or unburnt corpses further adds to the woes. Industrial units dump the effluents into the Ganges which further adds to pollution and toxicity which kills fish in a large portion of the river. To conserve and rejuvenate River Ganga, the Union Government launched Namami Gauge Programme in June 2014.
 Pollution in Ganga
Pollution in Ganga - To check the quality of water: There are measurable factors which are used to quantify pollution or the quality of water that we use for various activities. pH of water is something that can be easily checked using a universal indicator.
- Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose and Recycle. There are five mantras to save our environment.
(i) Refuse: To say no to things one doesn’t need.
(ii) Reduce: To use less, for e.g., by switching off unnecessary lights and fans, repairing leaky taps etc.
(iii) Reuse: Reuse’ means, we use the articles again and again. Plastic bottles in which pickles and jams are supplied can be used again for storing kitchen articles. Used envelopes can be reversed and used again.
(iv) Repurpose: When a product cannot be used for its original purpose, then it should be put to use for some other purpose. For example, old crockery can be used for growing plants.
(v) Recycle: ‘Recycle’ means that we collect plastic, paper, glass and metal items and recycle them to make articles of our need instead of making them from fresh materials. To achieve this, we have to segregate the waste so that the material that can be recycled does not mix with the other waste. - Preservation of resources: We should make environment-friendly decisions encouraging forms of growth that meet present basic needs while preserving the resources for future generations.
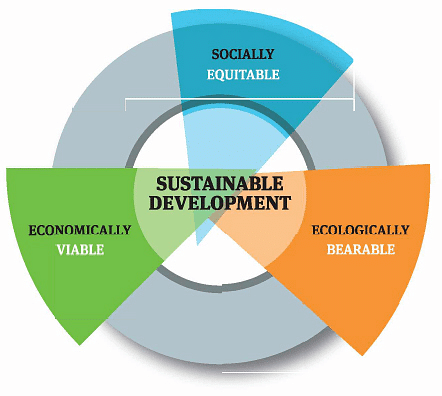
- Sustainable development: It implies a change in all aspects of life. People should be willing to change their perceptions of socio-economic and environmental conditions around them and be ready to change their strategy to use natural resources.
 Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development
Why do we need to Manage our Resources?
- Management of resources: Everything that we use and consume is obtained from resources on this earth. We need to use the resources carefully because these are not unlimited. With the increase of population, the demand for these resources is increasing. We have to ensure that these resources last for the generations to come and are not exploited for short term gains. We should also ensure that there should be equitable distribution of resources to all — rich and poor.
- During the Vedic period, agriculture was the main economic activity in our country. People were aware of the productive and protective aspect of forests. In pre-historic India, we were already practising conservation and sustainable management of natural resources, in contrast with present-day global concerns.
Hence, there were sacred corridors and groves which ensured the protection and conservation of nature and natural resources. - Exploitation of natural resources: We cause damage to the environment while exploiting natural resources. For example, mining causes pollution because of the large amount of slag which is discarded for every tonne of metal extracted.
Forests and Wildlife
Preservation of biodiversity: We need to preserve diversity. Forests are hot spots of diversity. We measure diversity in terms of the number of species and the range of different life forms. We must preserve the biodiversity that we have inherited from previous generations. Loss of diversity leads to loss of ecological stability.
 Forests and Wildlife
Forests and Wildlife
Stakeholders
Stakeholders to the forests are:
- People who are dependent on the forest produce for various needs.
- Forest department of the government which owns the land and controls the resources from the forests.
- Industrialists who get the raw materials for the products from the forests.
- The wildlife and nature enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
Sustainable Practices:
People living in forest areas need large quantities of firewood, small timber and bamboo. Implements for agriculture, fishing and hunting are largely made of wood. People also gather fruits, nuts and medicines from the forests. Their cattle also graze in forest areas. Before the Britishers came, people had been living in those areas for centuries and had developed practices that ensured that the resources were available in a sustainable manner.
Mindless Exploitation of Resources:
Britishers exploited the forests ruthlessly. Forest people were forced to live in smaller areas making life difficult for them. Even after the Forest Department in independent India took over from the British, local knowledge and local needs were ignored. Vast tracts of forests were planted with pine, teak or eucalyptus trees. Huge areas were cleared of vegetation. This destroyed a great amount of biodiversity in the area. This was done to earn revenue for the forest department and to provide inputs to the timber, paper, lac and sports industries at the cost of people living there.
|
59 videos|118 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Sustainable Management of Natural Resources - 1 - Science for Super TET
| 1. Why is it important to manage our resources? |  |
| 2. How does sustainable management of natural resources benefit forests and wildlife? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of not managing our resources effectively? |  |
| 4. How can individuals contribute to the sustainable management of natural resources? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of sustainable management practices for forests and wildlife? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Super TET exam
|

|