Overview of Refinery Processes (Part - 2) | Chemical Technology - Chemical Engineering PDF Download
4.2 Technical questions:
1. How to remember the refinery process flow sheet in a simple way?
Ans: Well, visualize the refinery into four blocks namely the separation block, the treating block, the reactive transformation block and the rest.
The separation block consists of CDU, VDU, naphtha splitters, C4, C3 and other separators
The treating block consists of all hydrotreaters and gas treating unit
The reactive transformation block consists of thermal cracker (termed as cracking), alkylator, isomerizer and reformer
The last block consists of other units such as blending units, kerosene splitter, n-butane splitter.
This way the refinery can be easily remembered after thoroughly understanding the functional role of each process.
(a) Crude distillation Unit |
(b) Vacuum distillation unit |
(c)Thermal Cracker |
(d) Naphtha HDS |
(e) LGO Hydrotreater |
(f) HGO Hydrotreater |
(g) C4 Separator |
(h) Kerosene Splitter |
(i)FCC Unit |
(j)C3 Separator |
(k) C2 Separator Unit |
(m) Gas treating Unit
|
(n) Naphtha Splitter |
(o) Catalytic Reformer
|
(p) n-Butane Splitter |
(q) Isomerization Unit |
(r)Alkylation Unit |
(s) LVGO Splitter |
(t) LPG Pool Unit |
(u) Gasoline Pool |
(v) Gasoil Pool |
(w) Fuel Oil Pool |
Figure 4.1: Summary of prominent sub-process units in a typical petroleum refinery complex








Table 4.1: Summary of streams and their functional role as presented in Figures 1 and 2.
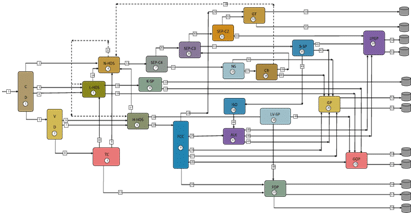
Figure 4.2: Overall refinery process block diagram (Dotted lines are for H2 stream).
|
69 videos|121 docs
|
FAQs on Overview of Refinery Processes (Part - 2) - Chemical Technology - Chemical Engineering
| 1. What is a refinery process? |  |
| 2. How does distillation work in a refinery process? |  |
| 3. What is cracking in a refinery process? |  |
| 4. What is reforming in a refinery process? |  |
| 5. What is hydrotreating in a refinery process? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|

















