Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > PPC & Economic Growth
PPC & Economic Growth | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Production Possibility Curves (PPC)
- The Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is an economic model that examines the maximum potential output a country can achieve by utilizing all its production factors to create only two goods or services.
- Any pair of goods or services can be employed to illustrate this model.
- Most PPC graphs depict capital goods and consumer goods on the axes. Capital goods, such as machinery in a factory, aid in production, while consumer goods, like a finished product, serve immediate needs.
- Capital goods are assets that aid in the production of output, particularly in manufacturing sectors. For instance, a robotic arm used in a car manufacturing plant qualifies as a capital good.
- Consumer goods, on the other hand, are end products with no further productive utility. A simple example of a consumer good is a wristwatch.
Production Possibility Frontier (PPC) Diagram

Diagram Explanation
The Use of Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
- The PPC illustrates the maximum potential output of an economy by showing various combinations attainable with all available resources.
- Point A on the curve signifies the production of only consumer goods (300 units).
- Point B represents the production of only capital goods (200 units).
- Points C & D indicate the efficient utilization of resources, with C yielding 150 capital goods and 120 consumer goods.
Opportunity Cost in Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
- Opportunity cost is demonstrated in the PPC as the trade-off required to produce additional units of a specific good.
- For instance, moving from point C (120 consumer goods, 150 capital goods) to D (100 consumer goods, 225 capital goods) incurs an opportunity cost of 50 capital goods for 105 consumer goods.
- Changes in the allocation of resources within an economy, like the shift from point C to D, lead to movements along the PPC.
Efficiency and Production Potential
- Production at any point on the PPC signifies efficiency, while points inside the curve, like point E, represent inefficiency.
- Attainable production levels are those on or inside the curve, such as point F, while points outside the curve are unattainable.
Question for PPC & Economic GrowthTry yourself: What does the Production Possibility Curve (PPC) represent?View Solution
Shifts in a PPC
- Unlike moving along the PPC, the entire PPC can shift inward or outward
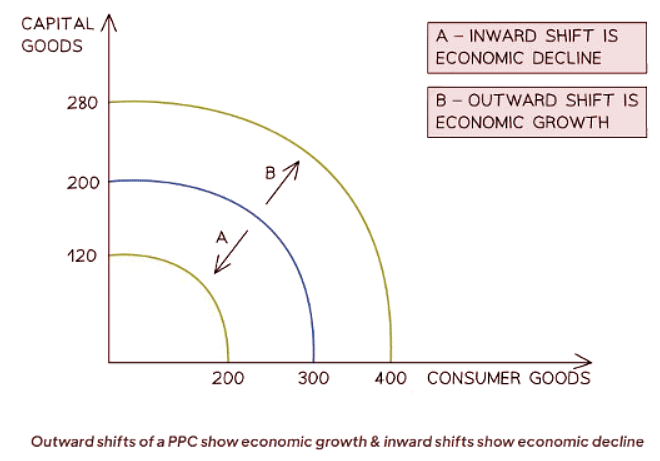
Diagram Explanation
Economic Growth and Decline
- Economic growth signifies a rise in an economy's productive capacity, leading to an outward shift of its production possibilities curve. This shift enables the production of more consumer and capital goods using the available resources. It is typically driven by enhancements in the quality or quantity of factors of production.
- Improving the quality of factors of production, such as through training and education, can boost productivity. For example, a well-educated workforce tends to be more efficient, thereby expanding production possibilities.
- Increasing the quantity of factors of production, like through changes in migration policies to attract foreign workers, can also elevate production possibilities.
- Economic decline, on the other hand, occurs when there is a detrimental impact on an economy's factors of production, leading to a reduction in either their quality or quantity.
- For instance, the Japanese tsunami of 2011 significantly impaired Japan's production capabilities for several years, inwardly shifting its production possibilities curve and resulting in economic decline.
The document PPC & Economic Growth | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
71 videos|82 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on PPC & Economic Growth - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is a Production Possibility Curve (PPC) and how does it relate to economic growth? |  |
Ans. A Production Possibility Curve (PPC) shows the maximum possible production combinations of two goods or services that an economy can achieve given its resources and technology. Economic growth is represented by an outward shift of the PPC, indicating an increase in a country's ability to produce more goods and services over time.
| 2. How does efficiency play a role in the PPC and production potential? |  |
Ans. Efficiency refers to the ability of an economy to utilize its resources in the most productive way possible. When an economy operates efficiently, it can produce at its maximum potential along the PPC curve. Any point inside the curve represents underutilization of resources, while any point outside the curve is unattainable given current resources.
| 3. What factors can cause a shift in a PPC and how does it affect economic growth? |  |
Ans. Factors such as technological advancements, increases in labor productivity, or improvements in resource allocation can cause a shift in a PPC. An outward shift signifies economic growth as the economy can produce more goods and services with the same amount of resources.
| 4. How does a country achieve economic growth based on the concepts of PPC? |  |
Ans. To achieve economic growth, a country must focus on increasing its resources, improving technology, enhancing productivity, and allocating resources efficiently. By constantly striving to operate at or near the PPC curve, a country can maximize its production potential and experience economic growth.
| 5. Can a country operate beyond its PPC and what are the implications of doing so? |  |
Ans. Operating beyond the PPC represents a scenario where a country is producing more goods and services than its resources allow. This is unsustainable in the long run and can lead to inefficiency, resource depletion, and ultimately a decrease in overall production. It is essential for a country to operate along or near its PPC to achieve sustainable economic growth.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















