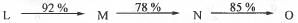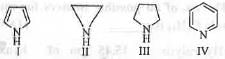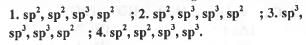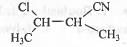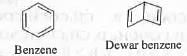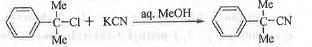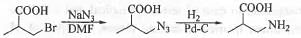Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The CORRECT order of stability for the following carbocations is
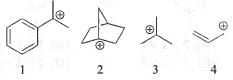
[2018]
Explanation
I, II and III are tertiary carbocation. But, II being non-planar is very unstable.
III is stabilised by +1 effect of three methyl groups and 9-hyperconjugable a-H atom.
I is stabilised by +1 effect of two methyl groups and 6- hyperconjugable α-H atom. Moreover, it is further stabilized by resonance involving phenyl ring. Hence, it is more stable than III.
IV is stabilized by two degenerate resonance.
Hence, it is more stable than II but less stable than I and III.
Hence, the correct order of the stability of carbocations : I > III > IV > II.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Consider the following four xenon compounds: XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 and XeO3
The pair of xenon compounds expected to have non-zero dipole moment is
[2018]
Explanation
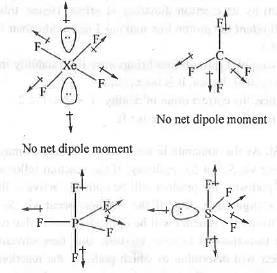
From the concept of hybridization theory, we know that the shapes of XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 and XeO3 are Linear, Square planar, Distorted octahedral and Pyramidal respectively. The structures are shown below
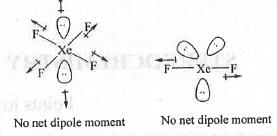
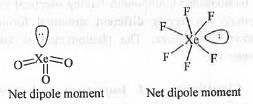
In case of XeF4, two l.p. moments will cancels out each other and four Xe-F bond moments will cancels out each other making it non-polar.
Similarly, in case of XeF2, two Xe-F bond moments will cancels out each other and the two l.p. moments will cancel out the other l.p. moment making XeF2 nonpolar.
But, in case of XeF6 and XeO3, there exist a net dipole moment making these polar.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The compound that contains the most acidic hydrogen is
[2018]
Explanation
Among annulene, ethane, ethene and ethyne, ethyne is most acidic in nature.
The acidity of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base, higher will be acidity of the compound. The conjugate bases of ethane, ethene and ethyne are :
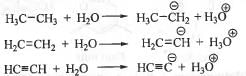
In case of the conjugate bases of ethane, ethene and ethyne, the negative charge are present sp3, sp2 and sp hybridized orbitals respectively.
The order of electronegativity of various hybridized orbitals runs as : sp > sp2 > sp3.
Greater is the electronegativity of the orbital in which negative charge is present, higher will be the stability of the anion i.e. conjugate base. Hence, the conjugate base obtained from ethyne will be most stable while the conjugate base derived from ethane will be least stable. Hence, the stability order of the conjugate bases runs as : C2H'> C2H3‘ > C2H5'.
Acidity of allene is similar to that of ethene.
Hence, the order of the acidity of the given compounds runs as : C2H2 > C2H4 > C2H6.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:In the following sequence of the reactions, the overall yield (%) of O is
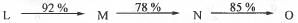
[2017]
Explanation
Let the amount of the starting material L is : 100 gm.
The yield for the first step i.e. conversion of L to M is 92 %. Hence, the amount of M obtained = (100).(92/100) = 92 gm. The conversion of the second step i.e. M to N is 78 %. Hence, the amount of N obtained = (92).(78/100) = 71.76 gm. The conversion of N to O is 85 %. Hence, the amount of O obtained = (71.76).(85/100) = 61 gm.
Hence, the overall yield (%) of O is : 61.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
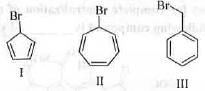
Try yourself:The correct order of rate of solvolysis for the following compounds is
[2017]
Explanation
Benzylic carbocations (Compound I) are highly stabilized by resonance with the benzene ring.
Tertiary allylic carbocations (Compound II) are also highly stabilized by resonance, and tertiary carbocations are more stable than primary and secondary ones.
Tertiary carbocations (Compound III) are highly stable due to the inductive and hyperconjugation effects from the surrounding alkyl groups.
The general order of stability for carbocations is: benzylic > tertiary allylic > tertiary. This means Compound II (tertiary allylic) will have the fastest solvolysis rate due to the combination of allylic and tertiary stability, followed by Compound III (tertiary), and finally Compound I (benzylic).
Therefore, the correct order of the rate of solvolysis for the given compounds is:
II > III > I
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The correct statement(s) about the following species is(are)
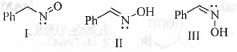
1. I and II are resonance structure ;
2. II and III are resonance structure ;
3. II and III are diastereomers ;
4. Ill is a tautomer of I.
[2016]
Explanation
Here, I and II are termed as tautomers as these differs from each other by not only the position of electrons but also by the position of the atoms. Similarly, I and III are also tautomers as these are also differs from each other by both the position of electrons and position of atoms.
But, II and III are the geometrical isomers (E and Z). Hence, these are diastereomers.
Hence, the correct statements are : 3 and 4.
Hence, the correct answers are : (C, D).
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The correct order of pKa for the following compound is
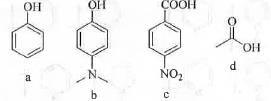
[2016]
Explanation
Acidity of a compound depends on the stability of its conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base, higher will be the acidity of the acid. Lower is the value of pKa, higher will be the acidity. Phenolic compounds are weakly acidic. This is due to that phenoxide ion become stabilize by four canonicals. But, carboxylic acid compounds are much more acidic than phenolic compounds. This is due to the greater stability of the conjugate base obtained from carboxylic acid. Carbonyl group has very strong electron withdrawing (-1, -R) effect. Hence, it will stabilize the conjugate base of carboxylic acid effectively. Hence, c and d are more acidic than a and b.
As conjugate base is anionic in nature, presence of EWG and EDG will stabilize and destabilize the conjugate bases respectively. - NO2 group is a strong electron withdrawing group (-1 and -R effect). Hence, it will stabilize the conjugate base to a greater extent making c more acidic than d. -NMe2 group is a strong electron donating group (+R > -I). Hence, it will destabilize the conjugate base to a greater extent making b less acidic than a.
Hence, the order of acidity : c > d > a > b.
Hence, the order of pKa is : b > a > d > c.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The correct order of the pKa values for the conjugate acids of heterocyclic compounds given below is
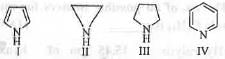
(1) II > III > I > IV ;
(2) IV > II > III > I ;
(3) III > II> IV > I ;
(4) III > IV > II > I.
[2015]
Explanation
All of the given compounds are basic in nature. Hence, the conjugate acids of these compounds will be positively charged species. Lesser is the stability of the conjugate acid, more easily it will get deprotonated and hence, higher will be its acidity and hence, lower will be its pKa.
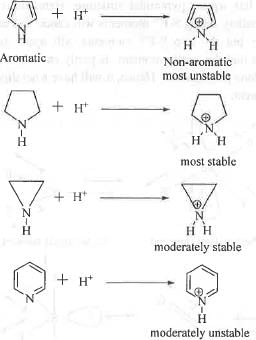
The conjugate acid of I is very unstable. Upon deprotonation, the l.p. present on nitrogen atom will undergo resonance in the ring and will become an aromatic compound. Hence, the conjugate acid will readily give up the proton to attain stability due to aromaticity. Hence, the conjugate acid of I is highly acidic. Hence, its pKa will be very low.
Similarly, the conjugate acid of IV will also become destabilize due to the higher electronegativity of the nitrogen atom. Hence, it will also readily give up the proton. Hence, the conjugate acid is also acidic in nature and will have low pKa value. But, pKa is somewhat higher than the pKa of the conjugate acid of I.
The conjugate acids of II and III will be stabilized by the +1 effect of two methylene and ethylene groups respectively. As ethylene groups has greater +1 effects, the conjugate acid of III is more stable than the conjugate acid of II. Hence, the conjugate acid of III will have less tendency to give up the proton than the conjugate acid of II. Hence, the conjugate acid of III is less acidic than the conjugate acid of II. Hence, the pKa of the conjugate acid of III is more than the pKa of the conjugate acid of II.
Hence, the correct order of pKa is : III > II > IV > I. Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The major product formed in the following reaction is
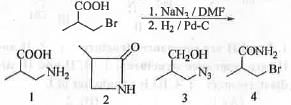
[2015]
Explanation
Bromide is a good leaving group while azide is a good nucleophile. In aprotic solvent like DMF, SN2 type of reaction become favoured. Hence, when the given reactant is treated with sodium azide in DMF solvent, simple substitution will occur via Sn2 pathway. When this substituted product is treated with H2/Pd-C, azide will get reduce to primary amine. The reaction schemes is shown below :
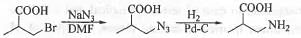
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The Volhard method is used for the estimation of
(1) Chloride ion by titration with silver nitrate ;
(2) Silver ion directly ;
(3) Oxygen in water ;
(4) Glucose in blood.
[2015]
Explanation
Volhard method is used to determine chloride ions present in sample. At first sample is treated with measured excess of AgNO3 solution whose concentration is known. Then, the excess AgNO3 solution is back titrated with ammonium thiocyanate and excess SCN- is titrated with ferric ammonium sulphate. The reactions are shown below :
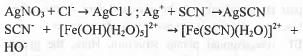
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The correct orientation of dipoles in Pyrrole and Pyridine are :
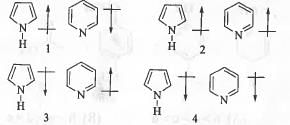
[2014]
Explanation
In case of Pyrrole, to maintain aromaticity the l.p. of electrons are heavily delocalized in the ring. Hence, the ring carbons become negatively charged while the nitrogen atom become positively charged. Hence, the dipole will orient from positive pole to negative pole i.e. from nitrogen to ring carbons.
But, Pyridine is an aromatic compound and l.p. of electrons are present in sp2 hybrid orbital. Hence, here no need of delocalization of l.p. on nitrogen atom in the ring is required to maintain the aromaticity of the compound. As nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon, dipole will orient from ring carbon to nitrogen.

Hence, orientation of dipoles in Pyrrole and Pyridine are towards the ring and away from the ring respectively.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The homolytic breaking of Ca-Cb bond is easiest in :
1. CaH3-CbH3 ;
2. CH3CaH2CbH2CH3 ;
3. Me2CaHCbHMe2 ;
4. Me3CaCbMe3.
[2014]
Explanation
The Ca-Cb carbons in compounds 1, 2, 3 and 4 are 1°, 1°, 2° and 3° respectively. Homolytic breaking of a bond leads to the formation of radicals. Greater is the stability of the radicals, higher will be the chance of breaking of the bond. Radicals are stabilized by electron donating as well as electron withdrawing groups. The radicals produced after the homolytic breaking of Ca-Cb bonds in 1, 2, 3 and 4 are as follows :
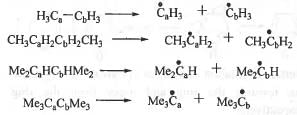
The radicals generated after cleavage of compounds 1, 2, 3 and 4 are l°(methyl), 1 “(ethyl), 2° and 3° respectively. The stability order of various radicals are as follows : 3° > 2° > 1°. This can be explained in terms of +1 effect and hyperconjugative effect of -Me groups.
The no. of electron donating (+ I effect) -Me groups present in methyl, ethyl, iso-propyl and tert-butyl radicals are 0, 1, 2, 3 respectively. Hence, electron donation by the substituent -Me groups will be maximum in case of tert-butyl radical and it will be minimum in methyl radical. Hence, in terms of +1 effect , the order of stability of radicals : 3° > 2° > 1°(ethyl) > 1°(methyl).
The no. of hyperconjugable alpha-H atoms in tert- butyl, iso-propyl, ethyl and methyl radicals are 9, 6, 3 and 0 respectively. Hence, the no. of hyperconjugated structures can be drawn are : 10, 7, 4 and 1 respectively. Hence, in terms of hyper-conjugation, the order of stability of radicals : 3° > 2° > l°(ethyl) > 1 “(methyl).
Hence, on combing both the effect the order of stability of radicals : 3° > 2° > 1“(ethyl) > 1“(methyl). Hence, tert-butyl radicals produced by Ca.Cb bond of compound 4 will have maximum stability. Hence, the homolytic breaking of Ca-Cb bond is easiest in compound 4.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The CORRECT order of stability of the following carbonium ions is
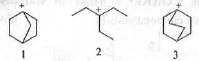
[2013]
Explanation
All these carbocations are tertiary. Hence, these will be approximately same stable with respect to electron donating inductive effect. But, carbocation 2 become more stable due to hyperconjugation. 2 has six hyperconjugable a-H atoms. Hence, it will have total seven hyper conjugated structures. But, in case of 1 and 3, as the positive charge is located on bridgehead carbons, these are non-planar. Hence, no such hyperconjugation is possible. Hyperconjugation in carbocations 1 and 3 will introduce double bond at the bridge-head position which will violate Bredts rule which states that it is impossible to introduce a double bond at the bridge-head position of a bicyclic system. But, in case of 3 the ring is somewhat less strained due to its some flexibility. Hence, in case of 3 the carbocation will be somewhat stabilized by hyperconjugation. Hence, the order of stability is as follows : 2 > 3 > 1.
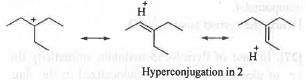
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The most polar compound among the following is
[2013]
Explanation
A compound will be polar if it has a net dipole moment. Hence, the most polar compound will be one which has highest dipole moment. Now, let us examine the dipole moment of the following compounds : XeF4 has square planar structure. Hence, here the bond moments due to the two X-F bonds are exactly equal and opposite to the bond moment of the other two X-F bonds. Also, the moment due to one lone- pair is cancelled out the moment due to the other lone-pair. Hence, it has no net dipole moment.
BF3 has trigonal planar structure. Here, the group moment of the -BF2 group is exactly equal and opposite to the bond moment of the third B-F bond. Hence, it has also no net dipole moment.
SO3 has trigonal planar structure. Here, the group moment of the -SO2 group is exactly equal and opposite to the bond moment of the remaining S=0 bond. Hence, they will cancel out each other. Hence, it has no net dipole moment.
SF4 has square pyramidal structure. Here, the two oppositely acting S-Fax moments will cancel out each other but the two S-Feq moments will assist each other and the vector moment is partly cancel out by the lone pair moment. Hence, it will have a net dipole moment.
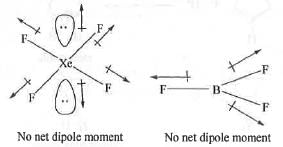
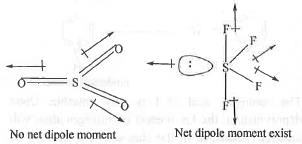
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The compounds those would not respond to tests of both nitrogen and sulphur with sodium fusion extracts are
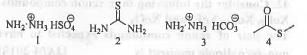
[2012]
Explanation
Only those nitrogenous compounds will respond Laggaines test for nitrogen which contain nitrogen directly attached to carbon atom. As, in case of 1 and 3, no carbon directly attached to carbon is present, these compounds will not give positive test for nitrogen atom.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
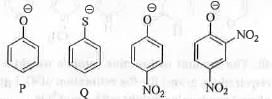
Try yourself:The order of nucleophilicity of the following anions in a SN2 reaction is
[2012]
Explanation
In case of a SN2 reaction, higher is the negative charge density on the anion greater will be the nucleophilicity of the anion. S atom being more polarisable and less electronegative than O atom, S is more nucleophilic than O atom. Presence of strong electron withdrawing group like -N02 will decrease the electron density on oxygen atom by conjugation through its ( - 1 and - R ) effect. Hence, thiophenolate anion is most nucleophilic followed by phenolate anion. Due to the presence of two E.W.G. -NO2 group S will be least nucleophilic.
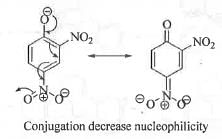
Hence, the order of nucleophilicity of the given anions is a s : Q > P > R > S .
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself: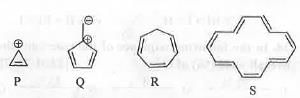
The species/compounds that are aromatic among the following are
[2012]
Explanation
This can be explained in terms of Huckel s rule of aromaticity.
In case of P : It is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains (4n + 2)π e- [when n = 0]. Hence, it is an aromatic species.
In case of Q : It is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains 4nπ e- [when n = 1], Hence, it is an antiaromatic species.
In case of R : It is non-planar due to the presence of a sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Hence, it is nonaromatic species.
In case of S : It is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains (4n + 2)π e-[when n = 3]. Hence, it is an aromatic species.
Hence, P and S are the aromatic species.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Hybridization of the atoms indicated with the asterisk (*) in the following compounds sequentially are
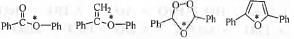
[2011]
Explanation
In case of 1, the following canonicals can be drawn.

Hence, the O atom is sp2 hybridized.
In case of 2, the following canonicals can be drawn

Hence, the O atom is sp2 hybridized.
In case of 3, the l.p. of electron present on the asterisk oxygen atom does not involve in conjugation. Hence, O atom is sp3 hybridized.
In case of 1, the following canonicals can be drawn

Hence, the O atom is sp2 hybridized.
Hence, the hybridization of the atoms indicated with the asterisk(*) in the following compounds sequentially are : sp2, sp2, sp3, sp2.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself: The 1UPAC name of the following compound is
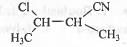
1. 2-cyano-3-chlorobutane ;
2. 2-chloro-3-cyanobutane ;
3 . 2-methyl-3-chIorobutancnitrile ;
4. 3-chloro-2-methylbutanenitrile.
[2010]
Explanation
In the longest chain four carbon atoms are present. Hence, the partial name of the compound is butane. -CN group is the main functional group. Hence, the name of the compound should end with nitrile. Substituents are present at C-2 and C-3 positions respectively. Numbering should start from -CN carbon. Hence, methyl and chloro groups are present at the C-2 and C-3 position respectively as the Substituents.
Alphabetically, chloro group should come before methyl group. Hence, the complete IUPAC name of the compound is : 3-chloro-2-methylbutanenitrile.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself: Benzene and Dewar benzene are
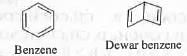
1. canonical forms ;
2. structural isomers ;
3. tautomers ;
4. conformational isomers.
[2010]
Explanation
Two structures are termed as resonance if two differs only in the position of electrons while two structures are termed as tautomer if they differs by not only the position of electrons but also by the position of the atoms.
As Benzene and Dewar benzene differs from each other only in the position of electrons, these can be termed as canonicals.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Which of the following are aromatic?
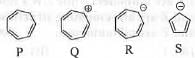
[2009]
Explanation
The aromatic species are Q and S respectively. According to Huckel a system will be aromatic if it is 1. cyclic, 2. planar, 3. fully-conjugated and 4. contains (4n + 2)π electrons.
In case of P : Here, one carbon atom is sp3 hybridized. Hence, it is neither planar nor fully- conjugated. Hence, it is not aromatic.

In case of Q : It is 1. cyclic, 2. planar, 3. fully- conjugated and 4. contains (4n + 2)π electrons (when n = 1). Hence, it is aromatic in nature.
In case of R : It is 1. cyclic, 2. planar, 3. fully- conjugated and 4. contains 4nn electrons (when n = 2). Hence, it is anti-aromatic in nature.
In case of S : It is 1. cyclic, 2. planar, 3. fully- conjugated and 4. contains (4n + 2)π electrons (when n = 1). Hence, it is aromatic in nature.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Arrange the following in the correct order of acidity of the hydrogen indicated in the bold.
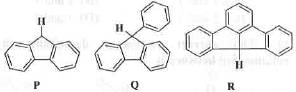
Explanation
Acidity of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base, higher will be the acidity of the acid. The conjugate base obtained from the compounds P and Q are stabilized by the resonance involves two and three phenyl rings respectively. Hence, the conjugate base of Q is more stable than the conjugate base of P. Hence, Q is more acidic than P. Similarly, the conjugate base of R is stabilized by the three phenyl rings through resonance. Moreover, the whole system is fully planar due to locked ring system. Hence, here resonance is much more important than the previous two. Hence, the conjugate base of R is most stable making R most acidic. Hence, the correct order of acidity of the compounds are : R > Q > P.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The major product obtained in the following reaction:
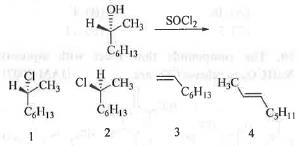
[2009]
Explanation
When a secondary alcohol is treated with SOCl2, -OH group will get convert into -Cl group producing alkyl halide type compound. The reaction mechanism follows internal nucleophilic substitution (SNi) pathway. Hence, the stereochemistry of the product remains intact. Here, actually when C-O bond cleaved, -Cl atom attack the carbon atom internally from the same side. Thats why the stereochemistry of the product remain intact. The reaction mechanism is shown below :
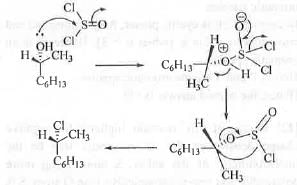
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:R-(-)-2-Bromooctane on treatment with aqueous KOH mainly gives 2-octanol that is
1. Optically active with R configuration ;
2. Optically active with S configuration ;
3. A racemic mixture ;
4. A meso compound.
[2008]
Explanation
As the substrate is secondary, the reaction may occur via SN2 or SN1 pathway. If the reaction follows Sn pathway, the product will be optically active with S configuration. But, if the reaction occur via Sn pathway, the product will be optically inactive due to the formation of race micmixture. But, he resolvent effect will determine in which pathway the reaction actually occur. Here, the solvent is water which is a polar protic solvent. Hence, the reaction will follow SN1 pathway and leads to the formation of race micmixture.
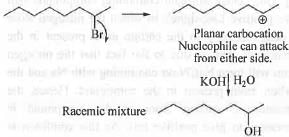
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself: The correct order of acidity among is
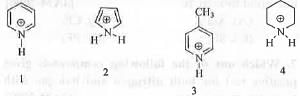
1.1 < 2 < 3 < 4 ;
2. 4 < 3 < 1 < 2;
3. 2 < 1 < 3 < 4 ;
4. 2 < 4 < 1 < 3 .
[2008]
Explanation
Acidity of a compound depends on the easiness with which it will lose its proton. Also, acidity of a compound can be explained interms of the stability of the conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base higher will be the acidity of the compound. In case of 2 after proton loss it will become aromatic. As aromatic system is very stable, it will lose its proton readily. Hence, compound 2 is most acidic.
In case of 1, the positive charge on nitrogen atom will cause the loss of proton and that is why it will have sufficient acidity.
But, in case of 3 , the methyl group at the C-4 position will decrease the positive charge on the nitrogen atom by its electron donating +1 effect. Hence, this will retard the proton loss making 3 less acidic than 1 and 2.
In case of 4, proton loss brings very little stability in the system. Hence, it is least acidic.
Hence, the correct order of acidity 4 < 3 < 1 < 2.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The correct statement describing the relationship between is
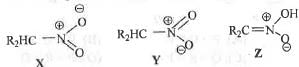
1. X and Y are resonance structure while Z is a tautomer.
2. X and Y are tautomers while Z is a resonance.
3. X, Y and Z are all resonating structures.
4. X, Y and Z are all tautomers.
[2008]
Explanation
Here, X and Y are termed as resonance as these two differs only in the position of electrons while Z is a tautomer as it differs from X and Y by not only the position of electrons but also by the position of the atoms.
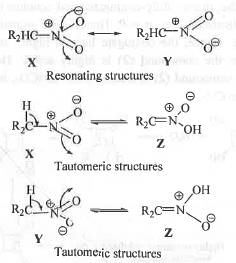
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
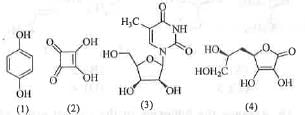
Try yourself:The compounds that react with aqueous NaHCO3 to release CO2 are
[2007]
Explanation
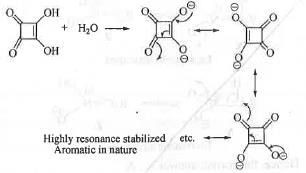
The strong acid will react with aqueous NaHCO3 to release CO2. The acidity of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base. Higher is the stability of the conjugate base, greater will be the acidity of the compound.
The conjugate base obtained from the compound (2) is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains (4n + 2)π electrons when n = 0. Hence, it is aromatic in nature. Hence, the conjugate base is highly stable.
Hence, the compound (2) is highly acidic. Hence, when compound (2) is treated with NaHCO3, it will release CO 2.
The conjugate base obtained from the compound (3) is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains (4n + 2)π electrons, when n = 1. Hence, it is aromatic in nature. Hence, the conjugate base is highly stable. Hence, the compound (3) is highly acidic. Hence, when compound (3) is treated with NaHCO3, it will release CO2.
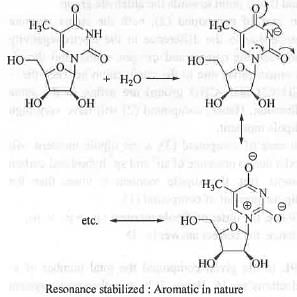
Hence, both compounds (2) and (3) on reaction with NaHCO3 will release CO2.
Hence, the correct answer is : C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The value of n for the following molecule according to Huckel's rule is
[2007]
Explanation
In the given compound the total number of nelectrons are 16. Hence, it is an anti-aromatic system as it satisfy the 4nπ electron rule when n = 4.
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The correct order of dipole moment (p) of the following compounds is
1. CH3CH2CH2CHO,
2. CH3CH=CHCHO,
3. CH3CH2CH=CH2
[2007]
Explanation
Aldehyde group is highly polar group due to the presence of highly electron egative oxygen atom.
Hence, compound (1) will have a net dipole moment and it will point towards the aldehyde group.
In case of compound (2), both the sigmamoment (arise due to the difference in the electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen atoms) and the pimoment (arise due to the conjugation between the -CH=CH and -CHO group) are acting in the same direction. Hence, compound (2) will have very high dipole moment.
In case of compound (3), a net dipole moment will exist due to presence of sp3 and sp2 hybridized carbon atoms. But, this dipole moment is lower than the dipolemoment of compound (1).
Hence, the order of dipole moment : μ2 > μ1 > μ3. Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Which one of the following compounds gives positive test for both nitrogen and halogen with Lassaigne's extract?
[2007]
Explanation
Only those nitrogen containing compounds will give positive Lassaigne's in which the nitrogen atom is attach directly to the carbon atom present in the compound. This is due to the fact that the nitrogen atom will form NaCN on combining with Na and the carbon atom present in the compound. Hence, the presence of carbon atom in the com pound is necessary to give positive test. As this condition is only full-filled in case of it will give positive test for both nitrogen and halogen with Lassaigne's extract.
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:The fluorides, whose value of dipole moment is not equal to zero, is
[2006]
Explanation
To answer this question, we have to draw the structures of the given compounds. XeF4 has square planer structure. Hence, here the bond moments due to the two fluorine atoms are exactly equal and opposite to the bond moment of the other fluorine atoms. Also, the moment due to one lone-pair is cancelled out the moment due to the other lone-pair.
Hence, it has no dipole moment. CF4 has tetrahedral structure. Here, the group moment of the -CF3 group is exactly equal and opposite to the bond moment of the C-F bond. Hence, it also has no dipole moment.
PF5 has TBP structure. Here, the group mom ent o f the -PF2eq group is exactly equal and opposite to the bond moment of the -PFeq bond. Also, the two axial fluorine atoms are oppositely acting. Hence, they will cancel out each other. Hence, it has no net dipole moment. SF4 has square pyramidal structure. Here, the two oppositely acting S-Fax moments will cancels out each other but the two S-Feq moments will assist each other and it is partly cancel out by the lone pair.
Hence, it will have a net dipole moment.
Hence, the correct answer is : C:
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
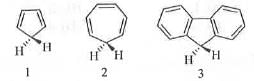
Try yourself:The increasing order of the acidity of the hydrogen marked in bold italics among the following is
[2006]
Explanation
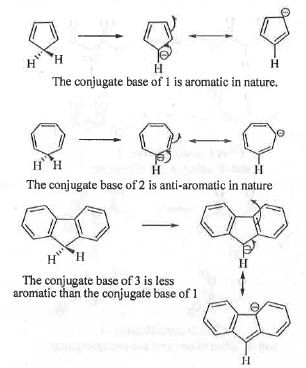
The acidity of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base, higher will be the acidity. The conjugate base obtained from 1 is cyclic, planar, fully conjugated and contains (4n + 2)π electrons, where n = 1. Hence, the conjugate base is aromatic in nature and it is very stable. Hence, 1 will have very strong tendency to lose proton. Hence, 1 is highly acidic. In case of 2, the conjugate base is cyclic, planar, fully conjugated and contains (4n)π electrons, where n = 2. Hence, the conjugate base is anti-aromatic in nature and very unstable. Hence, 2 will have no tendency to lose proton. Hence, 2 is much less acidic than 1. In case of the conjugate base of 3, the negative charge is not only delocalized in the five member ring but also it is delocalized in two phenyl rings. Hence, the availability of the negative charge in the five member ring decrease. Hence, the five member ring in the conjugate base of 3 is less aromatic than the five member ring in the conjugate base 1. Hence, 3 will have moderate tendency to lose proton. Hence, 3 is more acidic than 2, but less acidic than 1. Hence, the correct order of acidity of the given compounds is: 2 < 3 < 1.
Hence, the correct answer is : D.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself: The reaction of (+) 2-iodobutane and Nal* in acetone was studied by measuring the rate of incorporation of I*(ki) and the rate of racemisation(kr)
(+) CH3CH(I)CH2CH3 + Nal* → CH3CH(I*)CH2CH3 + Nal
For this reaction ,the relationship between kr and ki is
[2005]
Explanation
The given reaction is : (+)CH3CH(l)CH2CH3 + NaI*→ (-) CH3CH(I*)CH2CH3 + NaI
This is an example of SN2 type reaction. SN2 reaction involves the product formation with inversion of configuration. When one molecule of the original substance undergo inversion, one molecule of product is formed with inversion of configuration. This means that when one original optically active molecule undergo inversion, the inverted product and another origians, optically active molecule lose their optical activity due to the occurrence of racemisation i.e. when one moleofie is inverted, actually two molecules are racemised. Hence, it can be concluded that the rate of racemisation is double to the rate of inversion. Hence, mathematically, 2ki = kr
Hence, the correct answer is : B.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Benzyl chloride is reacted with different nucleophiles shown below. Arrange them in the decreasing order of reactivity.
Nucleophiles : HO-, AcO-, PhO- MeO-
1. MeO- > HO- > PhO- > AcO- ;
2. HO- > MeO- > PhO- > AcO- ;
3. HO- > PhO- > MeO- > AcO-;
4. AcO- > MeO- > HO- > PhO-
[2005]
Explanation
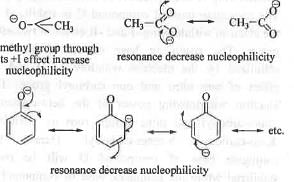
Nucleophilicity of a species means the availability of electronic charge density at a particular point of the species. Greater is the availability of the charge density, higher will be the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile. In case of acetate anion, two degenerate canonicals can be drawn. Hence, the average negative charge on an oxygen atom is half. Hence, it is very weak nucleophile. In case of phenoxide anion four canonicals can be drawn. But, here canonicals are less important as less electronegative carbon atom bears the negative charge. Hence, the availability of negative charge on oxygen atom is slightly more. Hence, it is stronger nucleophile than the acetate anion. In case of hydroxide anion the availability of negative charge on oxygen atom is very high. Hence, it is much stronger nucleophile than the previous two. In case of methoxide anion, the methyl group attached to the oxygen atom increase the availability of negative charge on oxygen atom through electron donation to the oxygen atom. Hence, it is strongest nucleophile among the four. Hence, the nucleophilicity order : MeO->HO->PhO-> AcO-
Hence, the correct answer is : A.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:For the reaction shown below if the concentration of the KCN is increased four times, the rate of the
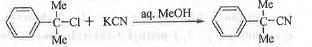
1. Doubled ;
2. Increased four times ;
3. Unaffected ;
4. Halved.
[2005]
Explanation
In the aqueous methanolic medium substitution reaction will be favoured. As the substrate is tertian Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution reaction will be preferred i.e. SN1 reaction will occur. In case of SN1 reaction, the rate of the reaction is independent of the nucleophile concentration. That is why the rate will remain unaffected if the con centration of the KCN is increased four times.
In case of SN1 reaction rate = k[Substrate]. Hence, the correct answer is C.
Report a problem
Question for Past Year Question: Some Basic Concept Of Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Arrange the following in the decreasing order of acidity of the hydrogens indicated as bold.
A. CH3COCH3,
B. CH3COCH2COCH3,
C. CH3OOCH2COOCH3,
D. CH3COCH2NO2.
1. B > C > A > D ;
2. D > B > C > A ;
3. D > C > B > A ;
4. B > D > C > A
[2005]
Explanation
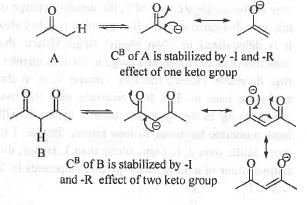
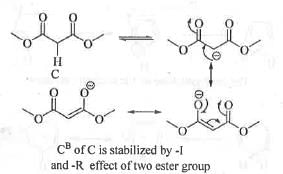
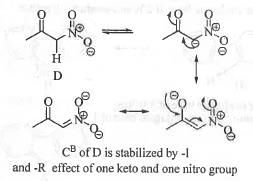
Acidity of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base, higher will be acidity of the compound. The conjugate base of compound A is stabilized by the electron withdrawing -I and -Reffect of one carbonyl group. The conjugate base of compound B is stabilized by the electron with drawing - I and - Reffect of two carbony l group. The conjugate base of compound C is stabilized by the electron with drawing - I and - Reffect of two ester group. The conjugate base of compound D is stabilized by the electron withdrawing -I and -Reffect of one nitro and one carbonyl group. The electron with drawing power of the ke to -carbonyl, ester-carbonyl and nitro groups runs as : Nitro > Keto-carbonyl > Ester-carbonyl. Hence, the conjugate base of compound D will be most stabilized while the conjugate base of compound A will be least stabilized. Hence, the acid ty of these compounds runs as : D > B > C >A.
Hence, the correct answer is : B
Report a problem