Past Year Questions: Tacheometric, Curve, Hydrographic and Plane Table Surveying & Theory of Errors | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A delivery agent is at a location R. To deliver the order, she is instructed to travel to location P along straight-line paths of RC, CA, AB and BP of 5 km each. The direction of each path is given in the table below as whole circle bearings. Assume that the latitude (L) and departure (D) of R is (0, 0)km. What is the latitude and departure of P (in km, rounded off to one decimal place)? [2023, Set-II]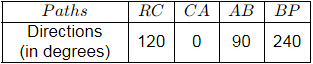
(a) L = 2.5 ; D = 5.0
(b) L = 0.0 ; D = 5.0
(c) L = 5.0 ; D = 2.5
(d) L = 0.0 ; D = 0.0
Ans: (b)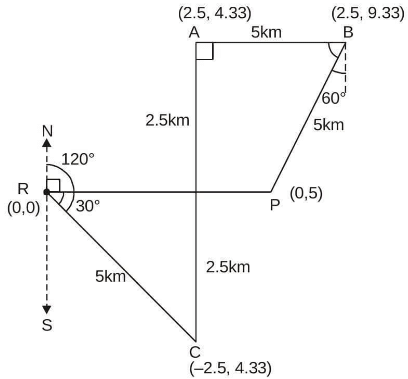

Q2: The direct and reversed zenith angles observed by a theodolite are 56∘00′ 00′′ and 303∘ 00′ 00′′, respectively. What is the vertical collimation correction? [2023, Set-I]
(a) +1∘ 00′ 00′′
(b) −1∘ 00′ 00′′
(c) −0∘ 30′ 00′′
(d) +0∘ 30′ 00′′
Ans: (d)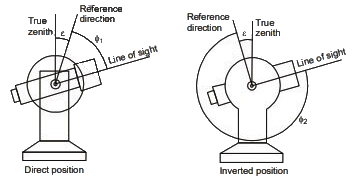 In above example of both direct zenith angle and reversed zerwith angle are smaller than true value.
In above example of both direct zenith angle and reversed zerwith angle are smaller than true value.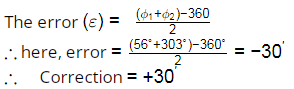
Q3: The diameter and height of a right circular cylinder are 3 cm and 4 cm, respectively. The absolute error in each of these two measurements is 0.2 cm. The absolute error in the computed volume (in cm3 , round off to three decimal places), is _______. [2020, Set-II]
(a) 1.65
(b) 7.52
(c) 3.25
(d) 5.18
Ans: (d)
Let diameter, x = 3 and height = y = 4 and error = ±0.2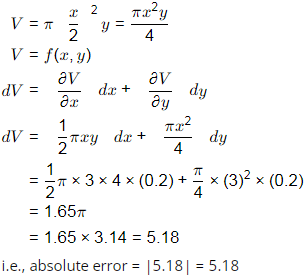
Q4: A series of perpendicular offsets taken from a curved boundary wall to a straight survey line at an interval of 6m are 1.22, 1.67, 2.04, 2.34, 2.14, 1.87, and 1.15 m. The area (in m2 , round off to 2 decimal places) bounded by the survey line, curved boundary wall, the first and the last offsets, determined using Simpson's rule, is _______ [2019, Set-II]
(a) 35.50
(b) 45.25
(c) 68.50
(d) 75.45
Ans: (c)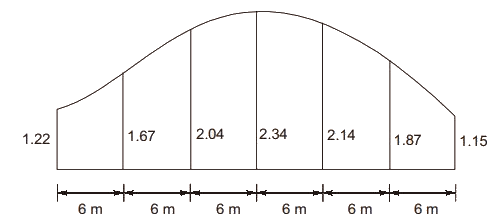 Area by Simpson's rule
Area by Simpson's rule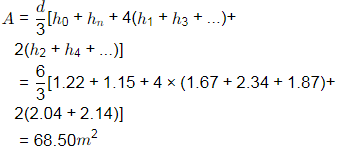
Q5: Consider the hemi-spherical tank of radius 13 m as shown in the figure. What is the volume of water (in m3) when the depth of water at the centre of the tank is 6 m? [2019, Set-II]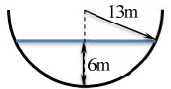 (a) 78π
(a) 78π
(b) 156π
(c) 396π
(d) 468π
Ans: (c)
Volume of water
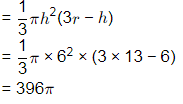
Q6: The method of orientation used, when the plane table occupies a position not yet located on the map, is called as [2017 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
(a) traversing
(b) radiation
(c) levelling
(d) resection
Ans: (d)
1. Traversing: 'Traverse’ means to pass across. Traversing refer to the framework of series of lines forming an open or closed polygon.
2. Radiation: It is a method of locating a point by drawing a radial line from the plane table station to the station under consideration.
3. Levelling: It is the method of determining the difference of elevations or levels of different points on the earth’s surface.
4. Resection:It is the method of locating a station occupied by the plane table when the position of that station has not been plotted earlier on the sheet when the plane table occupied other station
Q7: The VPI (vertical point of intersection) is 100 m away (when measured the horizontal) from the VPC (vertical point of curvature). If the vertical curve parabolic, the length of the curve (in meters and measured along the horizontal) is ________. [2017 :1 Mark, Set-II]
Ans:
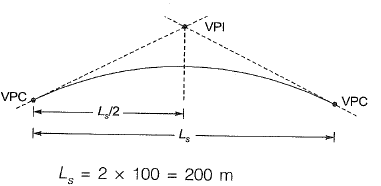
Q8: A circular curve of radius R connects two straights with a deflection angle of 60°. The tangent length is [2016 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
(a) 0.577 R
(b) 1.155 R
(c) 1.732 R
(d) 3.464 R
Ans: (a)
Tangent length
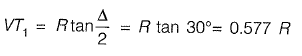
Q9: In a survey work, three independent angles, X, Y and Z were observed with weights Wx, WY, Wz, respectively. The weight of the sum of angles X, Y and Z is given by [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-T]
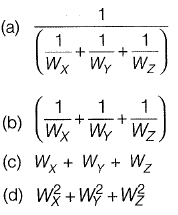
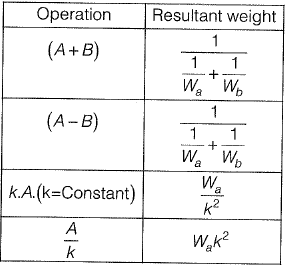
Ans: (a)
Various laws of weight
Let there be quantities A and B with weight Wa and Wb respectively
Q10: The chainage of the intersection point of two straights is 1585.60 m and the angle of intersection is 140°. If the radius of a circular curve is 600.00 m, the tangent distance (in m) and length of the curve (in m), respectively are [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
(a) 418.88 and 1466.08
(b) 218.38 and 1648.49
(c) 218.88 and 418.82
(d) 418.88 and 218.38
Ans: (c)
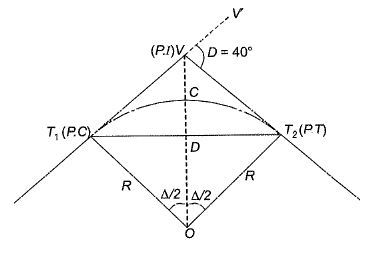
Δ = 180° - 140° = 40°
Length of the curve
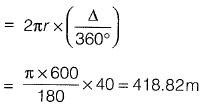
Tangent distance (7) is the distance between
P-C to P.I (also the distance from P.I to P. T)
⇒ T = T1V
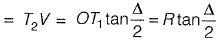
= 600 tan 20° = 218.88 m
Q11: A tacheometer was placed at point P to estimate the horizontal distances PQ and PR. The corresponding stadia intercepts with the telescope kept horizontal, are 0.320 m and 0.210 m, respectively. The ∠QPR is measured to be 61° 30' 30". If the stadia multiplication constant = 100 and stadia addition constant = 0.10 m, the horizontal distance (in m) between the points Q and R is ______. [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans:
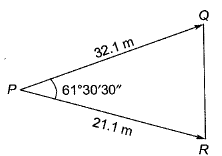
PQ = ks + C
= 100(0.32) + 0.1 = 32.1 m
PR = ks + C
= 100(0.21) + 0.1 = 21.1 m
Applying the cosine rule
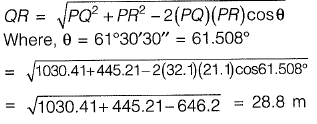
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Tacheometric, Curve, Hydrographic and Plane Table Surveying & Theory of Errors - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is tacheometric surveying and how is it different from traditional surveying methods? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of curve surveying in civil engineering? |  |
| 3. How does hydrographic surveying differ from other types of surveying? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the theory of errors in surveying? |  |
| 5. What are the common applications of plane table surveying in modern engineering projects? |  |
















