Patterns Class 5 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Pattern? |

|
| Understanding Number Patterns |

|
| Border Patterns |

|
| What are Tiling Patterns? |

|
What is a Pattern?
- Have you ever noticed the cool designs on your clothes, the way tiles fit perfectly on a floor, or the way numbers follow a special order in a puzzle?
- These are all examples of patterns!
- Patterns are like puzzles that repeat in a smart way, making things look neat, fun, and organized.
A pattern is formed by repeating a unit, which may be a set of numbers or shapes, according to a rule.
Understanding Number Patterns
1. Square Numbers
Patterns of squares using dots can be made in two different ways.
I. Rita uses coloured dots to make patterns of squares as follows:
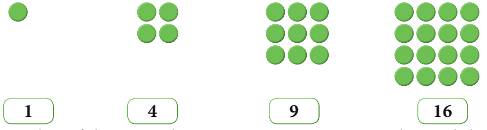
- 1 x 1 = 1
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 3 x 3 = 9
- 4 x 4 = 12
The number of dots in each square contains a square number and this is so called because the dots are arranged in a square shape.
A square number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself.
Now, can you name the next two square numbers and draw the square patterns?

II. Abhinav makes the square patterns as:
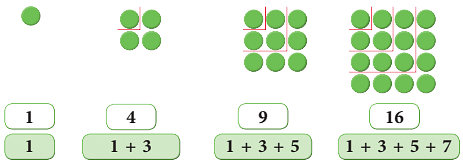
- 1 × 1 = 1
- 2 × 2 = 4 = 1 + 3
- 3 × 3 = 9 = 1 + 3 + 5
- 4 × 4 = 16 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7
Thus, we observe that,
First square number = 1 = First odd number
Second square number = 4 = 1 + 3 = Sum of first two odd numbers
Third square number = 9 = 1 + 3 + 5 = Sum of first three odd numbers
Fourth square number = 16 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = Sum of first four odd numbers
2. Triangular Numbers
- Triangular patterns using dots can be made as given below.
- The number of dots in each triangle is known as a triangular number.
- Look at the following triangular pattern by using dots.
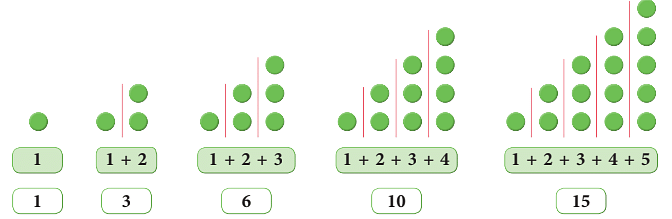
Thus, we observe the pattern as:
First triangular number = 1 = First natural number.
Second triangular number = 3 = 1 + 2 = Sum of first two natural numbers.
Third triangular number = 6 = 1 + 2 + 3 = Sum of first three natural numbers and so on.
Now, see what happens if you add two consecutive triangular numbers?
1 + 3 = 4
3 + 6 = 9
6 + 10 = 16
10 + 15 = 25
Square numbers
EduRev Tips: We get a square number by adding two consecutive triangular numbers. The square numbers are shown in a multiplication square as given alongside. They lie on a diagonal line.
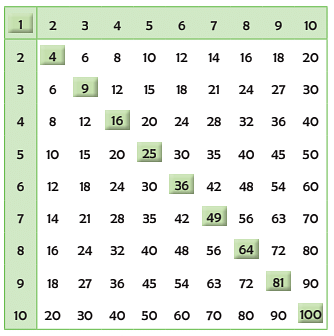
Border Patterns
- Observe the following patterns around you. Patterns in the border of dupatta, bedsheets, floors, etc.

- These are called border patterns. We see that border patterns enhance the original beauty.
- These border patterns are formed by repeating a certain shape or unit in one direction.
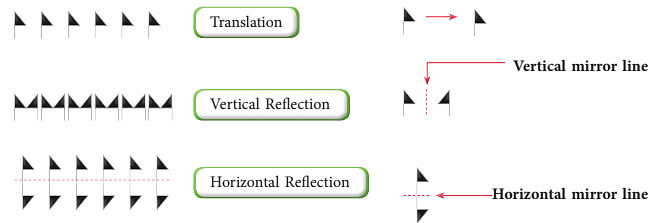
- Following a basic symmetry repetition, maybe of translation, vertical reflection or horizontal reflection.
To understand better, let us take an example.
Consider the symbol  as the basic unit or shape in the border pattern. We can get the following patterns when
as the basic unit or shape in the border pattern. We can get the following patterns when  follows the different symmetries as shown below.
follows the different symmetries as shown below.
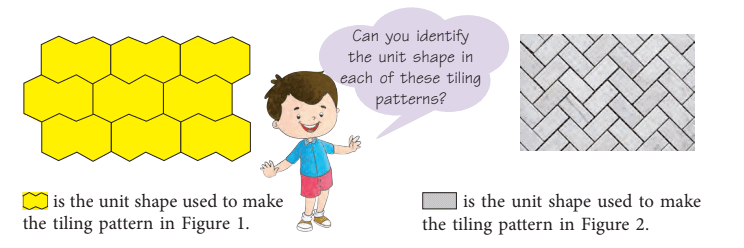
What are Tiling Patterns?
The most familiar examples of translations are the patterns formed by pairing stones or bricks and the cross-section of beehives.
A tiling pattern is formed by the repetition of a single unit or shape which when repeated, fills the plane with no gaps and no overlaps.
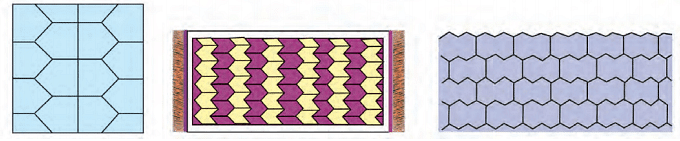
Look at the following patterns.
Now, observe these patterns. Are they tiling patterns? If not, then why not?

Thus, the above patterns are not tiling patterns.
Tiling Patterns Around Us
Tiling patterns are found in things around us.

Multiple tiling patterns can be made using a single shape as shown.
|
58 videos|122 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Patterns Class 5 Notes Maths
| 1. What is a pattern in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How can we identify number patterns? |  |
| 3. What are border patterns and how are they used? |  |
| 4. What is tiling pattern and how can it be created? |  |
| 5. Why are patterns important in mathematics? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|

















