Person, Income, Agricultural Income- Definitions and Basic Concepts of Income Tax, Income Tax Laws | Income Tax Laws - B Com PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Agricultural Income |

|
| Concept of Casual Income |

|
| Capital and Revenue Receipts |

|
Introduction
You have studied several terms related to the Indian Income Tax Act. Among them, agricultural income and casual income require more detailed discussion, as they are considered exempt under the Act, though certain conditions apply. This unit also covers the concepts of capital and revenue incomes and highlights the significance of distinguishing between the two when deciding whether a specific income should be included in a person’s total income.
Agricultural Income
- Agricultural income is not subject to tax under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- The reason for this is that agriculture falls under the authority of the State Government, which means only they can tax income generated from agriculture.
- The exemption for this kind of income is outlined in Section 10 (1) of the Act.
- Since agricultural income is not taxed, the definition of what constitutes agricultural income is very important.
- Taxpayers, or assessees, are often interested in classifying their income as agricultural, even if it is only loosely connected to agriculture.
- Conversely, tax authorities tend to interpret the definition of agricultural income more strictly, which can lead to disagreements between taxpayers and the tax officials.
- The Income Tax Act, 1961 provides a detailed definition of agricultural income in Section 2 (1A).
Definition of Agricultural Income
- Agricultural income is defined under Section 2(1A) as any rent or money earned from land located in India that is used for farming activities.
- The definition clearly states that any rent or income (whether in cash or kind) is considered agricultural only if the following conditions are fully met:
- Rent or revenue must come from land.
- The land must be located in India.
- The land must be used for agricultural purposes.
- To understand what agriculture is, it is important to note that income is considered to be generated from land when that land is worked on using human labor and skills.
- While tilling (the act of preparing soil for planting) is not a mandatory part of agriculture, it is essential that human effort and capability are applied directly to the land rather than just on the products grown from the land.
The Supreme Court has in CIT v. Raja Benoy Kumar Sahas Roy expounded on the terms’ Agriculture’ and’ Agricultural Purposes’. The relevant portion of the judgment is given below:
(i) Agriculture in its most primary sense denotes the cultivation of the field and is restricted to the cultivation of the land in the strict sense of the term, meaning thereby tilling of land, sowing of seeds, planting, and similar operations on the land. It also includes in its scope all the operations which foster the growth and preservation of the produce along with the operations required to make the produce ‘marketable’. The term comprises within its scope all types of produce regardless of its nature.
(ii) To decide whether a particular piece of land has been used for agricultural purpose, there has to be some measure of cultivation of land and some expenditure of skill and labour upon it. Consequently, income from the sale of forest trees growing naturally and without any human intervention cannot be treated as agricultural income.
Kinds of Agricultural Income
Agricultural Income is of five kinds:
(i) Any rent or revenue derived from land
(ii) Income derived from Agriculture
(iii) Any income derived from marketing process performed by cultivator or receiver of rent in kind
(iv) Any income derived from the sale of product
(v) Income from farm building
(ii), (iii) and (iv) can be combined under one heading and explained.
Let us now discuss the different kinds of income in detail.
(i) Any rent or revenue derived from land (Section 2(1A) (a))
- Agricultural income refers to the money earned from land in India that is used for farming.
- Rent is the payment one person receives from another for allowing them to use the land. This payment can be made in either cash or goods.
- The person receiving the rent may not necessarily own the land.
- If the land is rented out and the payment is made in the form of crops or produce, the person receiving this type of rent is called a receiver of rent in kind.
- When the receiver of rent in kind processes the produce to make it ready for sale, or if they earn money from selling such produce, this income is also considered agricultural income for them.
- Additionally, any income earned by the cultivator from farming activities is also regarded as agricultural income.
(ii) Income derived from such land by agriculture or from manufacturing process [Section 2(1A)(b)]
The words ‘such land’ are of significance here. These words limit agricultural income to the land situated in India which is used for agricultural purposes; the income generated by the following activities is considered agricultural income:
(a) Agriculture
(b) Process ordinarily employed by a cultivator to render the produce marketable
(c) Sale by cultivator of the produce without any further processing except the one mentioned in (b) above.
It is, thus, clear that the cultivator may need to make the produce marketable as the produce as such may not be sold. He is allowed the use of a process which is generally employed by all the cultivators to make the produce marketable. Tobacco leaves are generally dried before being sold, and therefore, the income from the sale of dried tobacco leaves will be agricultural in nature. However, the income from the sale of beedies made out of the same tobacco will not be treated as agricultural income, because marketable produce has been further processed and made more valuable.
(iii) Income from agricultural house property or farm buildings [Section (2 (1A) (c]
Income derived from any building in the following cases will be agricultural income:
- The building is owned and used by the person receiving rent or income from the land.
- The building is located on or near agricultural land in India.
- The farmer requires the building due to their connection to the land and uses it as a home, storage space, or additional building.
- The land where the building is located must be subject to land revenue in India or a local tax collected by government officials.
- If the land does not have land revenue, it must be outside of urban areas, which include places like cantonment boards, municipal boards, or any area with a population of 10,000 or more.
- If the land is designated by the Central Government in the Official Gazette, it must not be within 8 kilometers or within the area defined by lower limits from the jurisdiction of such municipal boards as notified by the Central Government.
Instances of Non-agricultural Income
The following incomes though connected with land are not agricultural in nature:
- Annuity payable to vendor of agricultural land or to a person giving up his claim to a piece of agricultural land.
- Commission for selling agricultural produce.
- Income from Dairy Farm.
- Forest produce resulting from wild growth.
- Fisheries
- Ginning of cotton.
- Harvesting of crop on purchased land.
- Letting out of land for stocking timber or crops.
- Dividend paid out of agricultural income.
- Commission earned by the landlord for selling agricultural produce.
- Profit earned on purchase of standing crop.
- Rearing of silkworms.
- Income from stone quarries.
- Royalty income of mines.
- Income from poultry farming.
- Income from land used for brick making.
- Income from producing water fruits in a tank.
- Compensation for requisition of land for military use.
- Remuneration of mutawalli or trustee out of agricultural income of Wakf.
- Income from sale of tender forms by the assessee engaged in the cultivation of sugarcane.
- Income from maintaining or running nurseries.
Partly Agricultural Income
There are certain instances where it becomes extremely difficult to classify an income as agricultural or non-agricultural. These are cases where the said income satisfies some characteristics of agricultural income and a few characteristics of business income. Such incomes are said to be partly agricultural in nature. Profit of a sugar mill which grows its own sugarcane is cited as one of the examples of partly agricultural income. In this case, income earned till harvesting of sugarcane is agricultural in nature whereas income accruing from the manufacture of sugar is taxable income. Hence, 60% income is agricultural income and remaining 40% is commercial income. Similarly, income from growing and selling of tea is partly agricultural income. These cases have been dealt with under rules 7 and 8 of the Income Tax Rules, 1962.
Example of Partly Agricultural Income
- Income from Growing and Manufacturing Products (Rule 7): This rule applies to factories producing goods like oil, vegetable ghee, flour, and sugar. It is relevant for manufacturers who create and sell products using their own agricultural goods as raw materials. This includes both types of income: agricultural and non-agricultural. When selling agricultural produce, part of the revenue is considered agricultural income, and the market value is counted as such. To calculate business income, the market value of agricultural goods that are grown or received as rent in kind and used as raw materials will be deducted. For agricultural income calculations, the market value of the produce is treated as earnings, and costs for cultivation and other expenses are deducted from it.
- Income from Tea Gardens (Rule 8): The total income from the manufacture and sale of tea is not fully considered agricultural income. Instead, 60% of the total income is classified as agricultural income, while the remaining 40% is classified as non-agricultural or business income.
- Income from Manufacturing Latex or Canex (Rule 7A): For income derived from the sale of latex, canex, or block rubber, 65% of the total income is regarded as agricultural income, and 35% is viewed as non-agricultural income. Costs related to replacing dead plants with new ones will be included in production costs. Any subsidy received from the rubber board will be deducted from production costs.
- Income from Coffee Manufacturing (Rule 7B): If coffee is sold immediately after curing, then 75% of the income from that sale is considered agricultural income, while 25% is non-agricultural income. However, if the coffee is sold after curing, roasting, grinding, and adding flavors, then 60% of that income is considered agricultural income and 40% as business income or non-agricultural income. For this calculation, costs related to plants will be included in production expenses, which replace dead plants, but any subsidy received from coffee boards will not be deducted from the production costs.
Integration of Agricultural income with the Non– Agricultural income
As discussed, that there is no tax on agricultural income, but if an assessee earns both agricultural as well as non–agricultural income, then such agricultural income is added in his total income for computation of income tax on non–agricultural income. This concept is called as ‘partial integration of agricultural income with non–agricultural income’. The partial integration is done only when the following two conditions are satisfied: –
- The Net agricultural income is over Rs. 5,000.
- The non-agricultural income of the taxpayer is more than the exemption limit of Rs. 2,50,000 for individuals (except for those aged 60 years or older), as well as for HUF, AOP/BOI, etc.
- The partial integration rule applies only to:
- Individuals
- HUF
- AOP/BOI
- Artificial juridical persons
- Firms
- Companies
- Cooperative societies
- Local authorities
- An individual (male or female) who is a resident in India and is aged 60 years or older but less than 80 years at any time during the previous year has a maximum exemption limit of Rs. 3,00,000 instead of Rs. 2,50,000. If the individual is 80 years or older, the maximum exemption limit is Rs. 5,00,000 instead of Rs. 2,50,000.
- If an individual chooses to pay tax under section 115 BAC, the exemption limit is Rs. 2,50,000 for all age groups.
Steps of computation of tax when there is agricultural income along with non-aricultural income
The given below are the steps to calculate the tax:
- Add agricultural income and non–agricultural income and calculate tax on the aggregate as if such aggregate is the total income.
- Add agricultural income to the maximum exemption limit available and compute tax on such amount as if it in the total income.
- Deduct the amount of income tax computed under step 2 from the tax computed under step 1.
The amount so calculated shall be total income tax payable by the assesse - Claim rebate u/s 87A, if applicable.
- Add surcharge, if applicable and health and education cess @ 4%
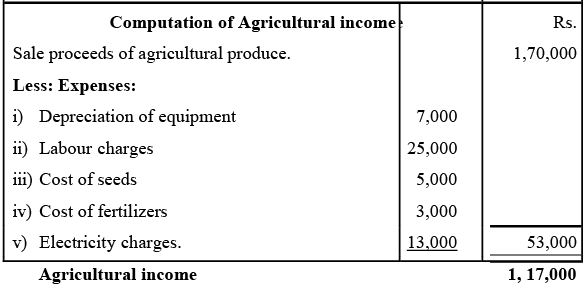
Illustration:
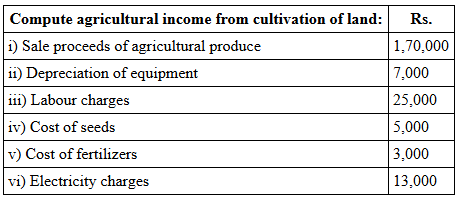
Sol:
Concept of Casual Income
You will remember from earlier unit that one of the important characteristics of the term ‘income’ is its regularity or at least expected regularity. However, there may be certain Incomes which are not regular and which do not arise from any source of income. They are known as ‘casual incomes’.
Definition and Chargeability of Casual Income
If an assessee, accidentally or without any pre–expectation, gets any income of non-recurring nature, it is treated as casual income. It includes income from betting, lottery winnings, playing cards, income from horse race, cross word puzzles etc. The maximum amount of casual income upto Rs.10,000 in case of winnings from lotteries, crossword puzzles, card games, other games, horse race is not subjected to tax deduction at source.
Following point should be kept in mind regarding casual income:
(i) Casual income shall be taxable @ 30%
(ii) Any expenses, if paid, in receiving casual income, shall not be deducted from any income.
(iii) Any casual loss shall not be set off against any income.
(iv) Personal gift such as birthday gift are given on account of family affection, hence, will not be included in income. For example–gift to wife by her husband, gift to son by his father, gift to a relative by another relative etc.
Some Examples of Casual Income
- Accidently or fortuitous receipt of money or precious article in the way.
- Money won in lotteries.
- Crossword puzzles, card games, betting, or gambling of any nature.
- Receipt of remuneration for acting as an arbitrator in any disputes (without any prior provision or stipulation).
- Receipt of reward to a person for tracing out any lost child (Prior to declaration of reward or without any stipulation).
- Winnings from horse race or any other race.
- Prize awarded for coin collection or stamp collection or gardening. Anyone or all the following winnings will be taxable:
- Winning from lotteries
- Winning from crossword puzzles
- Races (including horse races)
- Winning from gambling or betting of any form or nature
Following Incomes shall not be Treated as Casual Income
(i) Any amount paid under an agreement like payments by husband to his wife under an agreement to live apart as maintenance allowance, will not be covered in casual income, hence, it will be taxable.
(ii) Capital gain or receipt accrued in any business or profession.
(iii) Receipts like bonus, gratuity, or perquisites, received by a salaried person.
(iv) Voluntary payments are not casual income like tips to maids, servants’ tips to waiter, excess money than prescribed fee for any services given to the client (either in money or in kind).
Capital and Revenue Receipts
- It is important to understand the difference between capital and revenue.
- This difference matters for both accounting and tax purposes.
- Generally, when we buy something that lasts a long time, we consider it as capital expenditure.
- For instance, purchasing furniture is seen as capital expenditure and is listed on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
- In contrast, money spent on repairs is viewed as regular or routine spending.
- Therefore, such expenses are recorded on the debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
- Similarly, when we receive money from selling a capital asset, it is called a capital receipt.
- For example, if we sell a piece of land and receive Rs. 2,00,000, this amount is considered a capital receipt.
- On the other hand, money received by an advocate for providing professional services is classified as revenue.
- It is interesting to note that the Income Tax Act of 1961 does not specifically define what capital and revenue are.
- Thus, we rely on accounting conventions and decisions made by courts for guidance in this area.
- Besides accounting, understanding the difference between capital and revenue receipts is crucial for tax matters and figuring out tax liabilities.
- In general, revenue receipts are subject to tax, while capital receipts typically are not.
- However, if the sale of an asset results in a profit (more than what it cost), this profit is called a capital gain and is handled under special provisions of the law.
- Therefore, accurate tax liability cannot be determined unless receipts are properly classified.
Determine the Nature of a Receipt
Based on the judicial pronouncements, a few guidelines have been laid down for the purpose of determining the nature of a receipt. Some important guidelines are discussed below:
- A receipt by way of price or compensation on the disposal of circulating capital or stock in trade is a revenue receipt whereas a receipt on the disposal of a capital asset is capital in nature. A capital asset is used to manufacture items or generate income e.g., machines.
- Receipt in substitution of a source of income is of capital nature while the amount that substitutes income itself shall be the income chargeable to tax For example, compensation for the loss of an agency is a capital receipt while the amount received for the breach of a business contract is a revenue receipt.
- In the case of an isolated transaction of purchase and sale of property, the motive of the seller is a deciding factor in determining the nature of receipt. Sale proceeds of securities (where they are held as investment) will be capital receipt whereas it will be of revenue nature if the securities are held as stock in trade.
- When a sum is received for the surrender of certain rights under an agreement, it is a capital receipt because a certain capital asset in the form of those rights are being given up. If, however, the sum is received in the nature of compensation for the loss of future profits, it will be treated as a revenue receipt.
It would also help, if the following are also taken into consideration when trying to distinguish between capital and revenue receipts:
- Nature of receipt at the initial stage: If the receipt at the beginning appears to be a trading receipt, it will be taxed as such. However, if it seems like a capital receipt at the start, it cannot be taxed, regardless of how much it is or how the taxpayer uses it.
- Nomenclature not decisive: No matter what the parties involved in a contract label the transaction or the resulting receipt, the actual nature of the receipt must be determined based on established principles and the specific situation.
- Nature of receipt in the hands of the receiver: It is crucial to understand that when evaluating a receipt, its nature from the receiver's perspective matters. This means that even if an expense is considered capital for the giver, it can still be seen as a revenue receipt for the receiver. Thus, the important factor is how the receipt is viewed by the receiver, not how the expenditure is viewed by the giver.
- Nature under company law not important: The Supreme Court has stated that a receipt can be classified as a capital receipt under Company Law while also being considered a revenue receipt under the Income Tax Act, 1961, without any conflict.
- Lack of assessment in earlier years immaterial: The fact that the Income Tax Authorities did not impose tax on the interest portion of the annual receipt does not alter the nature of the receipt. It remains part capital and part revenue, and thus the revenue portion is subject to tax.
- Income from consumable assets: Profits generated from consumable assets are regarded as revenue, even if those capital assets appear to be diminishing or getting used up.
- Exchange rate fluctuation: Any extra income that the taxpayer gains due to changes in exchange rates will be taxed as a revenue receipt. However, if the profit arises not from the taxpayer's business activities but as a return on an investment, it will be classified as a capital receipt.
- Perpetual annuity: An annuity received in exchange for a capital asset is considered taxable income. However, if the annuity is referred to as an installment of a capital sum received for the capital asset, it will not be taxed.
Examples of Capital and Revenue Receipts
The following are a few examples of capital receipts:
- Receipt to meet the capital expenditure is a capital receipt.
- Compensation received for the suspension of an export license.
- Pagdee received as consideration for grant of monthly tenancies.
- Profit due to fluctuations in the rate of exchange of foreign currency.
- Profit from the sale of foreign exchange when the purchase of capital goods in foreign country became impossible.
- Entrance fee collected by a company in respect of new shares.
- Sale of assets of a firm at the time of its conversion to a company to the extent the consideration is attributable to sale of land.
- Compensation received for relinquishing the rights of a partnership.
The following are a few examples of revenue receipts:
- Receipt of annuity for transfer of a capital asset.
- Income from compensation received by the Government for compulsory acquisition of land.
- Damages received in respect of repairs not carried out in time.
- Cash assistance received under an export promotion scheme.
- Lump sum amount received for waiver of royalty.
- Subsidy received by a cooperative society from Government.
- Surplus left with the seller due to a reduction in export duty.
- Damages received by a company for breach of contract.
- Sale of import entitlement received under an export promotion scheme against export.
Illustration: State whether the following receipts are casual income:
(i) Mr. A received Rs 6,000 for acting as an arbitrator without any stipulations as to remuneration.
(ii) Mr. B received Rs 10,000 for acting as an arbitrator with a clear and definite stipulation for the said remuneration.
(iii) Mr. C, a decree holder received interest of Rs 1,000 under an order of court granting stay of execution of the decree on judgment debtor Mr. D.
(iv) Mr. E is in service of Mr. F. Mr. F’s sons was lost and Mr. E traced him out without any stipulations of rewards, but Mr. F gave him a rewards of Rs 1,000.
Solution:
(i) This receipt is casual income; it is of non–recurring nature as there was no stipulation for remuneration.
(ii) There was an offer of definite remuneration to Mr. B for acting as an arbitrator. He accepted the work. Hence, this is not a casual income. (iii) It is not a casual income
(iv) It is of non–recurring nature. There was no stipulation of reward, hence, it is casual income of Mr. E
Let's Sum Up
- Agricultural income is not taxed, so it's important to understand what it means. According to Section 2(1A) of the Income Tax Act, it refers to any rent or money made from land in India that is used for farming.
- Income from properties, like houses near farmland, is also considered agricultural income if the house is used by the farmer for purposes like storing farm products, tools, or animals.
- This income is exempt from tax under Section 10(1) of the Income Tax Act of 1961, since agriculture is managed by the states, and the central government cannot tax income from it.
- If a sugar mill grows its own sugarcane, part of the income it makes from sugar is agricultural. Similarly, if a tea company grows its own tea, part of its income is also considered agricultural.
- Rules 7 and 8 of the Income Tax Rules explain how to figure out which parts of this income are exempt and which are taxable.
- Casual income, which is unexpected money received as a surprise, is subject to tax. This type of income is not the same as capital gains or money from business activities.
- It's essential to understand the difference between capital income and revenue income. Only revenue income is taxable, not capital receipts.
- Revenue income includes money received from selling goods or providing services, while money received from selling a capital asset, like a house, is considered a capital receipt.
- However, any gain from selling a house is classified as a capital gain and is taxable.
- Some principles have been established, based on accounting rules and court decisions, to help differentiate between capital and revenue incomes.
|
33 videos|41 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Person, Income, Agricultural Income- Definitions and Basic Concepts of Income Tax, Income Tax Laws - Income Tax Laws - B Com
| 1. What is the definition of income tax? |  |
| 2. What is agricultural income? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between income and agricultural income? |  |
| 4. What is the basic concept of income tax laws? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of income tax returns that an individual can file in India? |  |





















