Physical Properties of Metals & Non-metals | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9 PDF Download
There are more than 115 elements known, at present 80% of these elements are metals and rest are non-metals. On the basis of their characteristic properties, all of these elements are divided into two main groups: Metals and non-metals.
Position of Metals and Non-metals in the Periodic Table
- The elements which are placed on the left-hand side (except hydrogen) and in the centre of the periodic table are called metals. Such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, iron, copper-zinc etc.
- The elements which are placed on the right-hand side of the periodic table are called non-metals such as oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, fluorine etc.
- These metals and non-metals are separated from each other in the periodic table by a zig-zag line.
- The elements placed in the zig-zag line show some properties of metals and some properties of non-metals are called metalloids.
- Such as boron(B), silicon(Si), germanium(Ge), arsenic(As), antimony(Sb), tellurium(Te) and polonium(Po).
The position of metals, non-metals and metalloids are shown in a simple form in figure.
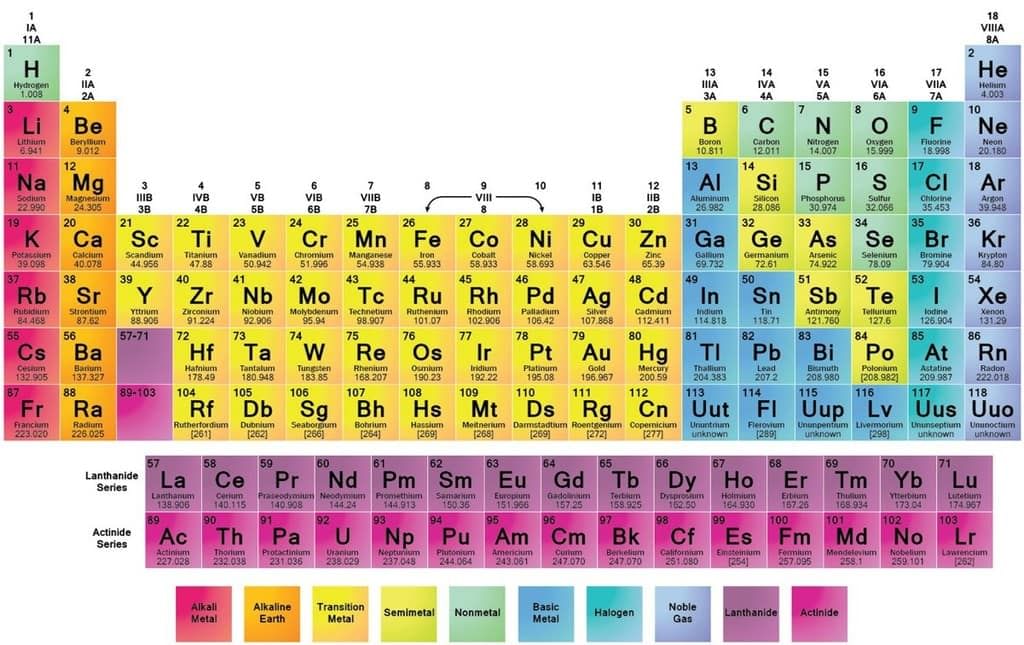
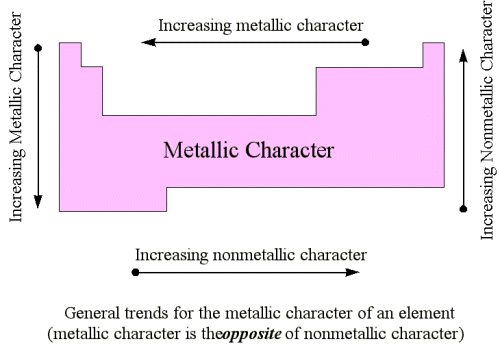
- Metals present at the extreme left are known as light metals, while those present in the centre of the periodic table are called heavy metals or transition metals.
- The elements at the extreme left of the periodic table are most metallic and those on the right are least metallic or non-metallic.
- Thus, the metallic character decreases on going from left to right side in the periodic table.
- For example, sodium is more metallic than aluminium because sodium is on the left-hand side of the aluminium.
- However on going down in a group the metallic character increases. For example, carbon is non-metal while lead is metal because metallic character increases down in a group.
Metals
The elements which can be polished, drawn into wires (ductile), hammered into sheets (malleable) and a good conductor of heat and electricity are called metals. Such as gold, silver and aluminium. Al is the most abundant metal in the earth's crust.
Electronic View of Metal
An element is called metal, which forms positive ions (or cations) by losing an electron.
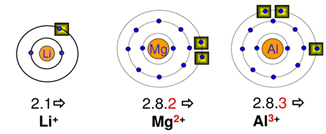 Electronic View of Metal
Electronic View of Metal
- Sodium is a metal that forms sodium ion (Na+) by losing one electron.
- Similarly, magnesium metal forms Mg2+ by losing two electrons, Al metal forms Al3+ by loss of three electrons.
- Thus, metals are also known as electropositive elements.
- The atoms of metals have 1 to 3 electrons in their outermost shell. For example, all alkali metals have one electron in their outermost shell. (Lithium-2, 1, sodium 2, 8, 1, potassium-2, 8, 8, 1, ... etc).
- Sodium(11) (2,8,1) magnesium(12) (2,8,2) and aluminium(13) (2, 8, 3) are metals having 1, 2 and 3 electrons respectively in their outermost shell, which lose these electrons easily.
- The number of electrons lost by an atom of a metal is called its valency.
- Thus metals have 1 to 3 electrons in their valence shell of their atoms.
Exceptions: Hydrogen and Helium. Hydrogen is a non-metal having 1 electron in its outermost shell of its atom. Helium ha 2 electrons in its outermost shell of its atom.
Physical Properties of Metals
The important physical properties of metals are given below:
Physical State of Metals
Most of the metals are solid under normal conditions of temperature and pressure (Except mercury which exists in a liquid state at room temperature). For example, Iron, Copper, Aluminium, Zinc, Sodium are solid at room temperature.
 Physical state different properties to the original metal
Physical state different properties to the original metal
Hardness of Metals
Most of the metals are hard, but all metals are not equally hard. The hardness of metals varies from metal to metal.
Example: Iron, Copper, Aluminium, Sodium and Potassium.
Malleability of Metals
The property in which metals can be beaten with a hammer into very thin sheets without breaking is called malleability. Gold and silver are the best malleable metals.
 Malleable Metal Gold
Malleable Metal Gold
Aluminium and copper are also highly malleable metals. All of these metals can be beaten with a hammer to form very thin sheets, called a foil.
Activity-1.1
Aim:
Aim:
To show that the metals are malleable.
Procedure:
Take an iron nail, a piece of zinc, copper, coal, aluminium, place all of the above one by one on a block of iron and strike it 4 and 5 times with a hammer.
Observation:
1. Iron nail, aluminium, copper & zinc metals change their shape into thin sheets.2. Coal is broken into small pieces. i.e. it is not a metal, because it does not show the property of malleability.
Conclusion:
1. Zinc, Fe, Al, Cu, are malleable i.e. they are metals.2. Coal is non-metal.
Lustre of Metals
Most of the metals, in their pure state, have a shining surface. This property is called metallic lustre. Example, gold is shining yellow and copper is brown, iron, aluminium and zinc are lustrous grey.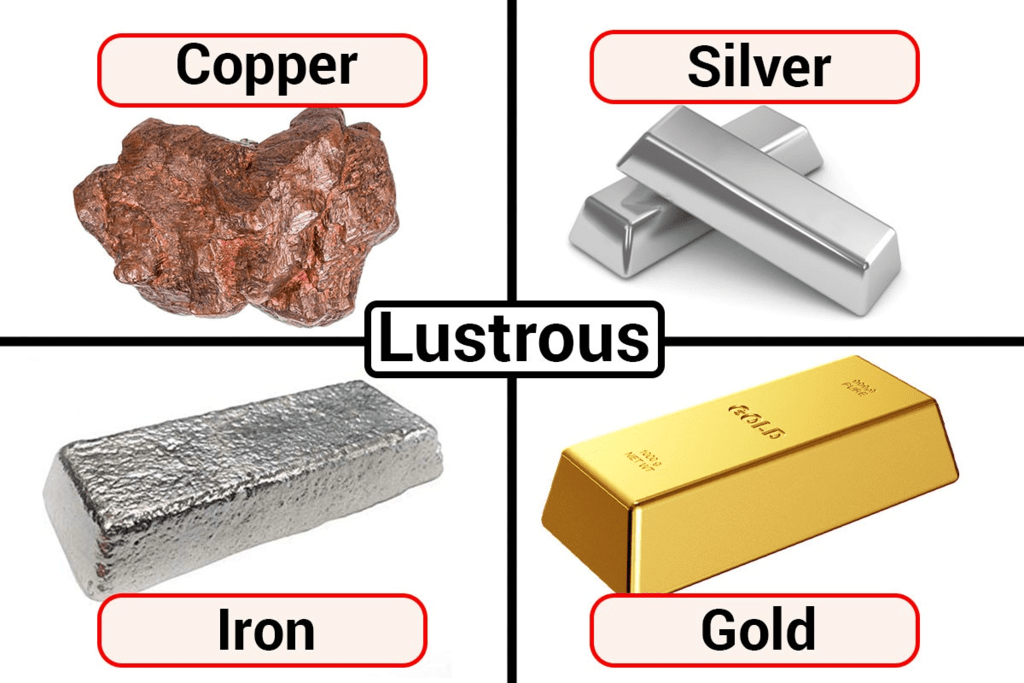
Activity-1.2
Aim:
To show that metals have shine or brightness. Take a small piece of iron, copper, aluminium and magnesium. Now clean their surface by rubbing them with a sand paper.
Observation:
Iron is shining grey in colour, magnesium and aluminium appear white, gold is yellow in colour and copper is reddish in colour.
Result:
Thus metals have shine or brightness.
Ductility of Metals
Ductility is also an important property of metals. The ability of metals to be drawn (stretched) into thin wires is termed as ductility.  Ductility
Ductility
- Examples of ductile metals are wires made up of iron, copper and aluminium. Gold and silver are the most ductile metals.
- For example, 100 mg of silver can be drawn into a thin wire of about 200 metres long.
- Similarly we can draw a wire of about 2 kilometre from only 1 gm of gold. Copper and aluminium are also very ductile, and therefore, they can be drawn into thin wires which are used in electrical wiring.
- We are familiar with silver foil used for decorating sweets and aluminium foil are used for wrapping food.
Thermal Conductivity of Metals
The process in which a metal allows the flow of heat through it is called its thermal conductivity. Most of metals are good conductors of heat, such as silver, gold, iron, copper and aluminium. Silver and copper are the best conductor of heat.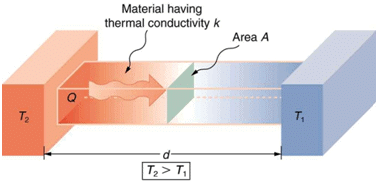 Thermal conductivity of metals
Thermal conductivity of metals
Activity-1.3
Aim:
To show that metals are good conductor of heat.
Procedure:
Take a metal rod and place its one end in hot water.
Observation:
The other end also gets heated soon.
Result:
This shows that metals are good conductors of heat.
Activity-1.4
Procedure:
Take a small wire and clamp it on a stand as shown in the figure below. Then fix a pin to the free end of the wire with the help of wax. Now heat the copper wire with a candle or burner near its clamped end.
Observation:
After some time the other end will also become hot and wax will melt and nail will fall down.
Result:
This shows that metals are good conductors of heat. This experiment also shows that metal wire does not melt. i.e. metals have high melting points. Repeat this activity with aluminium & iron metal.
Metals conduct heat when a portion of an object made of metal is heated, its atoms gain energy. The energetic atoms vibrate vigorously and transfer energy to the other adjacent atoms. In this way the entire object and anything in its contact also become hot.
Electrical Conductivity of Metals
The property in which metal facilitates the flow of electric current through it is called electrical conductivity. All metals are good conductors of electricity because they contain free or mobile electrons. These free electrons conduct electric current. Silver is the best conductor of electricity. Since silver is expensive, therefore, copper and aluminium are commonly used for making electric wires. These metals are next best conductor of electricity.
However, iron and mercury offer greater resistance to the flow of current. Therefore, they have low electrical conductivities.
Activity-1.5
Aim:
To show that metal is a good conductor of electricity.
Procedure:
Take a dry cell, a bulb fitted in a holder, connecting wires (copper wire), crocodile clips and a switch. Set up all apparatus an electric circuit as shown in figure.
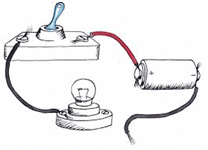 Apparatus for the experiment
Apparatus for the experiment
Observation:
The bulb glows at once when switch is on
.
Result:
This shows that copper metal conducts electric current, i.e. it is a good conductor of electricity.
Sonorous
The property of metals in which metals produce sound when they strike a hard object or other surface are called sonorous. Some metals like copper, silver, gold, aluminium give musical sound when they are struck by themselves or any other object. Uses of Some Metals
Many metals and their compounds are useful in our daily life. These are as follows:
- Aluminium is used to prepare utensils and household equipment like a vacuum cleaner. Aluminium is extensively used in making bodies of rail, cars, automobiles, trucks and aircraft. Aluminium wires are widely used in electrical work. Aluminium foil is used to wrap chocolate and medicines and to seal milk bottles.
- The major use of copper is in making electrical wires. Copper is also used in making utensils, steam pipes, coin and electroplating.
- Steel is an alloy of iron which is used for making parts of machines, as a building material and in the construction of fridges. As a matter of fact, steel is said to be the backbone of the industry.
- Gold and silver called noble metals (or coinage metals) are used in jewellery.
- Mercury is used in thermometers barometers and to prepare amalgams.
- Platinum is used to make crucibles and electrodes.
- Zinc is used to galvanize iron, to prepare roofing material, a container of dry cells and to make brass when mixed with copper.
- Metal like sodium, titanium and zirconium find their applications in atomic energy and space science projects.
- Titanium (Ti) and its alloys are used in aerospace, marine equipments, aircraft frames, chemical industries and chemical reactors. The wide application of titanium is attributed to its resistance to corrosion, high melting points and high strength.
- The metals such as titanium, chromium, manganese and zirconium are called strategic metals because these metals play an important role in the country's economy and defence. These metals and their alloys are used in high grade steels, jet engines, space science projects and atomic energy.
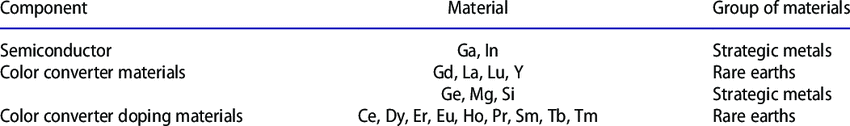 Rare earth and strategic metal
Rare earth and strategic metal
Non-metals and their General Properties
Non-metals are present on the right-hand side of the periodic table (exception: Hydrogen). Among the total known elements, there are only 22 non-metals, out of which 11 are gases like oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen one is a liquid (Bromine) and the rest 10 are solids such as sulphur, phosphorus and the allotropes of carbon (Diamond and graphite).
Electronic View of Non-metals
An element is called a non-metal which form ions by gaining electrons. For example, oxygen is a non-metal that form O2- ions by gaining two electrons. Similarly, nitrogen form N3– ions by gaining three electrons.
Thus, non-metals also known as electronegative elements. The atoms of non-metals have usually 4 to 8 electrons in their outer most shell. For example, Carbon (At No. 6), Nitrogen (At. No. 7), Oxygen (At. No. 8), Fluorine (At. No. 9) and Neon (At. No. 10), have respectively 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 electrons in their outermost shell. However, there are two exceptions namely hydrogen and helium which have one and two electrons in their valence shell or outer most shell, but they are non-metals.
Physical Properties of Non-metals
The important physical properties of non-metals are given below :
1. Non-metals may be solids, (such as sulphur, phosphorus and diamond), liquid (Bromine), or gases (such as oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, neon, argon, etc.) at room temperature.
2. Non-metals are usually brittle and cannot be used to make sheets and wires.
3. Non-metals are non lustrous and cannot be polished. (Exception: Graphite and iodine are lustrous nonmetals).
4. Non-metals are generally bad conductor of heat and electricity.
Exception: Graphite which is a good conductor of electricity. Non-metals do not conduct the electric current due to absent of free or mobile electrons.
 Graphite, a good conductor of electricity 5. Non-metals can be easily broken due to its low tensile strength.
Graphite, a good conductor of electricity 5. Non-metals can be easily broken due to its low tensile strength.
6. Non-metals are generally light and have low densities.
7. Unlike metals, non-metals do not produce any sound when struck with an object.
8. Non-metals are soft (Exception: Diamond)
9. Non-metals have low melting and boiling points. (Exception: Graphite has very high melting point (3730°C))
Exceptions in Physical Properties
On the basis of the above discussion of the physical properties of metals and non-metals, we have concluded that elements can not be grouped according to the physical properties alone, as there are many exceptions. - All metals except mercury are solids at room temperature.
- Lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat.
- Mercury expands significantly for the slightest change in temperature.
- We know that metals have very high melting points but gallium (Ga) and caesium (Cs) have very low melting points. These two metals will melt if we keep them on our palm.
- Iodine is a non-metals but it is lustrous.
- Alkali metals such as Lithium, Sodium and Potassium are soft, so, that they can be easily cut with a knife. i.e., they have low densities and low melting points.
- Carbon is a non-metal that can exist in different forms. Each form is called an allotrope Diamond, an allotrope of carbon is the hardest natural substance. which has very high melting and boiling point.
- Graphite is another allotrope of carbon which is good conductor of electricity.
|
12 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Physical Properties of Metals & Non-metals - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9
| 1. What are the physical properties of metals? |  |
| 2. What is the aim of Activity-1.1? |  |
| 3. What are some common uses of metals? |  |
| 4. What are the general properties of non-metals? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the position of metals and non-metals in the periodic table? |  |

















