Points to Remember: Biomolecules | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
1. Classification of Carbohydrates: Depending upon the no. of simple carbohydrates obtained on hydrolysis of a carbohydrate, saccharides are classified into four categories:
➤ Monosaccharide: If a carbohydrate does not undergo further hydrolysis to produce simple carbohydrate then it is called monosaccharide. Example - Glucose, Fructose etc.
➤ Disaccharide: If a carbohydrate undergo hydrolysis to produce two simple monosaccharides then it is called disaccharide.
Example - Sucrose etc.
➤ Oligosaccharide: If a carbohydrate undergo hydrolysis to produce 3-10 no. of simple monosaccharides then it is called oligosaccharide. Example - Raffmose etc. ➤ Polysaccharide: If a carbohydrate undergo hydrolysis to produce a large no. of simple carbohydrates then it is called polysaccharide. Example - Starch etc.
2. Structure Elucidation of D-(+)-Glucose:
1. Open Chain Structure:
➤ Elemental studies and molecular weight determination studies reveal that it has formula C6H12O6.
➤ When it is treated with acetic anhydride in presence of pyridine then penta acetate is formed. This proved that it has five free -OH groups.
➤ When it is treated with hydroxylamine then oxime is formed. Also, on treatment with HCN results in the formation of cyanohydrin. These proved that it contains carbonyl group.
➤ When treated with Tollen's reagent silver mirror is formed on the sides of test tube indicating that the carbonyl group is aldehyde in nature.
➤ When it is treated with cone. HI and red P and heated then n-Hexane is formed. This proved that all six carbons are present in a straight chain.
➤ All these informations supports the open chain structure of D-(+)-Glucose.
II. Cyclic Hemi-acetal Structure:
➤ When D-(+)-Glucose is treated with sodium bisulphite then no crystal of addition compound is formed. It is against the presence of free -CHO group.
➤ It cannot restore the pink colour of Schiffs base.
➤ It exist in two forms - α and (β-D-(+)-glucose.
➤ When it is treated with one mole of MeOH in presence of HCl then hemi-acetal is formed. But, the reaction is not proceed anymore. But, usually acetal formation need two mole of alcohol.
➤ The specific rotation of D-(+)-Glucose is +112°. But, when a solution of it keep at RT then specific rotation start to decrease and finally become 52.5°. This is called mutarotation. This phenomenon is against open chain structure of D-(+)-Glucose.
3. Oxidation and Reduction of D-(+)-Glucose: When D-(+)-Glucose is reduced with NaBH4 then sorbitol is formed.
➤ When D-(+)-GIucose is oxidized with Br2/H2O and HNO3 then gluconic and glucaric acids are formed.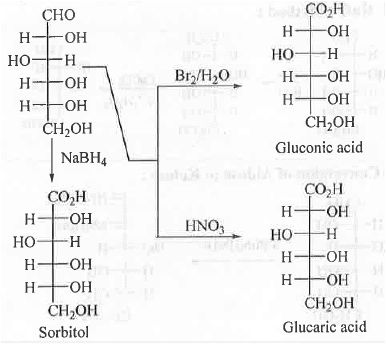
4. Stepping up of carbohydrate: Fisher - killini method: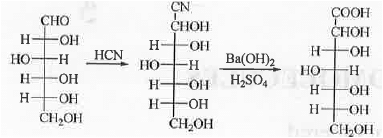
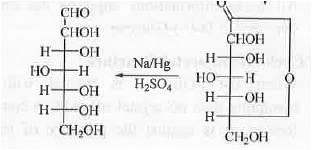
5. Stepping Down of carbohydrate:
1. Wohl's Method: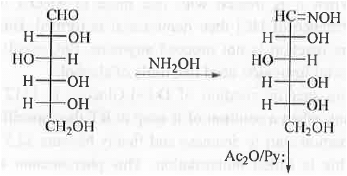
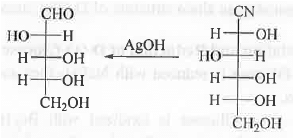
II. Ruff's Method: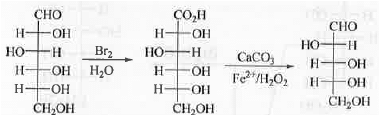
6. Conversion of aldose to ketose: 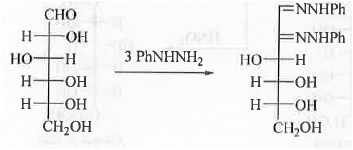
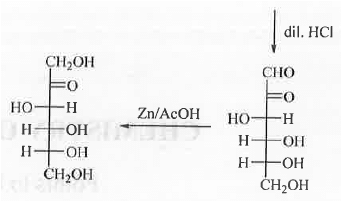
7. Conversion of ketose to aldose: 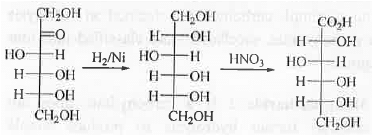
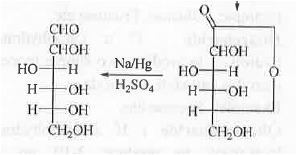
8. Osazone Formation: In case of carbohydrates, osazone formation will occur if it contains the following unit. CHO-CH(OH)- and CH2OH-CO-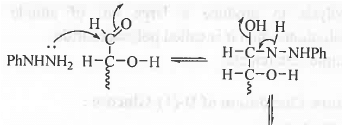

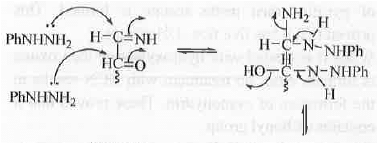

The structures of glucose and mannose are shown below: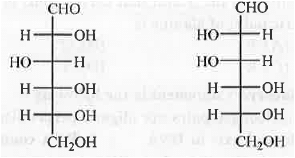
Both of them contains CHO-CH(OH)-moiety. Hence, these will lead to the formation of same osazone.
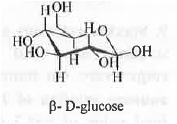
7. Mutarotation: In solution, the rapid interconversion of a-D-glucose and (3-D-glucose in presence of both acid and base is called mutarotation. Rate of the reaction is dependent on the concentrations of substrate, acid and base. Hence, 2-Hydroxypyridine is used which can act as acid as well as base.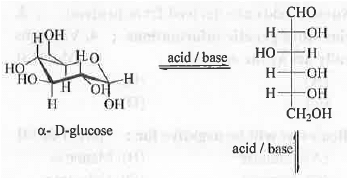
8. Zwitter-ion: Amino acids like Glycine contains one acidic group either -COOH and one basic group like - NH2. Hence, one proton will release by the acidic functional group which is readily pick up by the basic amine group. Hence, all these will exist as dipolar ion which is known as Zwitter-ion.
Evidence - Due to the existence of Zwitter-ion, amino acid has very high dipole moment and very high melting point.
|
44 videos|102 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Biomolecules - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What are biomolecules? |  |
| 2. How are biomolecules classified? |  |
| 3. What are the functions of biomolecules in living organisms? |  |
| 4. How do biomolecules contribute to maintaining homeostasis in the body? |  |
| 5. Why are biomolecules important for overall health and well-being? |  |





















