Points to Remember: Organic Spectroscopy | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
1. UV Spectroscopy:
A. Some Important Terms:
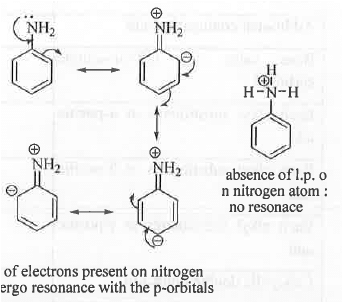
➤ Chromophore: It is the electronic species that is responsible for the absorption of a molecule in UV/VIS region.
Example -
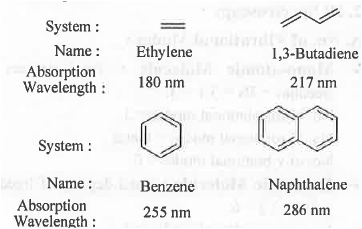
➤ Auxochrome: It is substituent on the Chromophore which will increase the wavelength for absorption to a higher wavelength.
Example -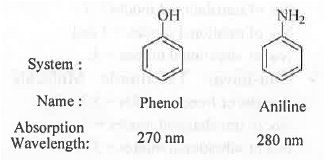
➤ Bathochromic Shift (Red Shift): A shift in absorption wavelength towards higher value Example -
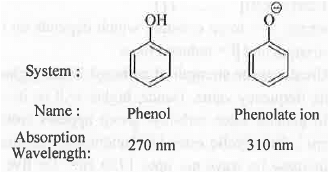
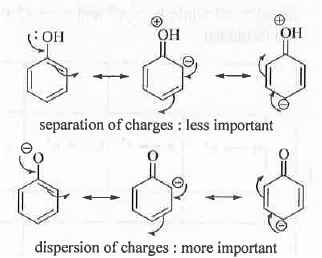
➤ Hypsochromic Shift (Blue Red): A shift in absorption wavelength towards lower value Example -
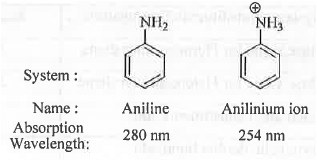
➤ Hyperchromic Shift: A shift in molar absorptivity(e) towards higher value. Molar absorptivity will be very high for an quantum mechanically allowed transition. Higher is the value of e, greater will be the intensity of the transition, π →π*.
➤ Hypochromic Shift: A shift in molar absorptivity towards lower value. Molar absorptivity will be very low for an quantum mechanically forbidden transition. Lower is the value of ε, lower will be the intensity of the transition.
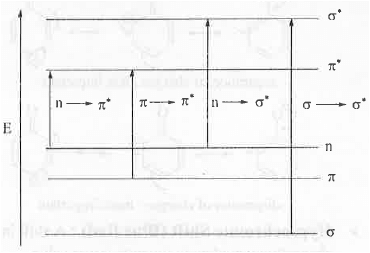
➤ Selection Rules: σ —*• σ* and π → π* transitions are allowed while n → π* and n → π* transitions are forbidden.
B. Woodward's Rule for Calculating  :
: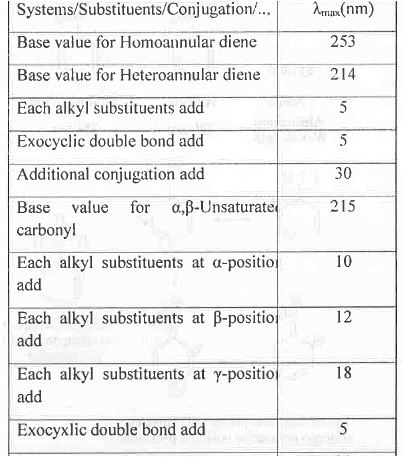

Example - Let us calculate the 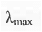 value of the following system:
value of the following system: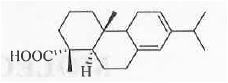
Homo-annular diene has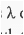 of 253 nm. Now, the system has four additional alkyl substituents, one exo-cyclic double bond.
of 253 nm. Now, the system has four additional alkyl substituents, one exo-cyclic double bond.
Hence, the final absorption wavelength will be : 253 + 4(5) +1(5) = 278 nm. These are shown below :
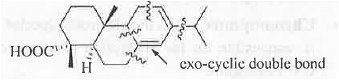
2. IR Spectroscopy:
A. No. of Vibrational Modes:
➤ Mono-atomic Molecule: Total degrees of freedom = 3N = 3.1 =3.
No. of translational modes = 3.
No. of rotational modes = 0 and No. of vibrational modes = 0.
➤ Di-atomic Molecule: Total degrees of freedom = 3N = 3.2 = 6.
No. of translational modes = 3.
No. of rotational modes = 2 and No. of vibrational modes = 1.
➤ Linear Tri-atomic Molecule: Total degrees of freedom = 3N = 3.3 = 9.
No. of translational modes = 3.
No. of rotational modes = 2 and No. of vibrational modes = 4.
➤ Non-linear Tri-atomic Molecule: Total degrees of freedom = 3N = 3.3 = 9.
No. of translational modes = 3.
No. of vibrational modes = 3.
B. Stretching Frequency:
The mathematical expression of frequency is: v = l/2π[√(k/β)] ..........(1)
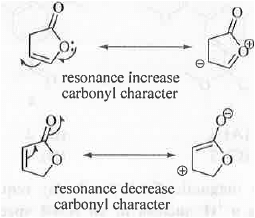
where, k = force constant which depends on the bond strength and p = reduced mass Greater is the strength of carbonyl bond, higher will be its frequency value. Hence, higher will be its wave no. In general ester carbonyl group appears around 1750 cm-1. But, cyclic ester i.e. lactones are strained which increase its wave no. up to 1770 cm-1 for five member system. But, in case of R, the double bond will undergo resonance with the carbonyl group decreasing the carbonyl character of the ester group. Hence, wave no. of the ester carbonyl decrease and it will become 1750 cm-1.
In case of Q, ester oxygen undergo resonance with the double bond. Hence, the oxygen lone-pair will become less available to the carbonyl group for resonance increasing the carbonyl character of the ester carbonyl group. Hence, the wave no. of the ester carbonyl group will become 1800 c m-1.
3. 'H and ,3C NMR :
Chemical Shift Value: Two compounds can be differentiated and identified by using their NMR spectrum. Any two protons having different chemical environment will have different chemical shift values.Chemical shift value is denoted by 8- symbol. Chemical shift value depends on the electronic environment around the concerned proton/carbon. Higher is the electronic deficiency around a concerned proton/carbon, higher will be chemical shift value. Let us analyze the structure of 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid:
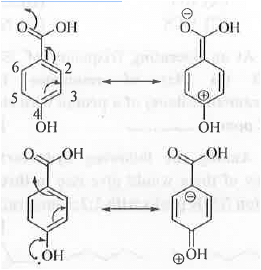
-COOH group containing carbon is most electron deficient as it is attached with two highly electronegative oxygen atom. Hence, it will appear at highest  -value (171 ppm). The C-4 carbon is also attached with one electronegative oxygen atom. Hence, it will also appear at a higher
-value (171 ppm). The C-4 carbon is also attached with one electronegative oxygen atom. Hence, it will also appear at a higher  value (162 ppm). We know that -COOH group has very strong electron withdrawing (-1 and -R effects) and -OH group has electron donating (+R > -1 effects). Hence, due to the resonance C-2, C-4 and C-6 positions b eco m e electron deficient while C - l , C-3 and C-5 positions become electron rich. Hence, the C-2 and C-6 carbons become deshielded while C-3 and C-5 carbons become shielded.
value (162 ppm). We know that -COOH group has very strong electron withdrawing (-1 and -R effects) and -OH group has electron donating (+R > -1 effects). Hence, due to the resonance C-2, C-4 and C-6 positions b eco m e electron deficient while C - l , C-3 and C-5 positions become electron rich. Hence, the C-2 and C-6 carbons become deshielded while C-3 and C-5 carbons become shielded.
Hence, C-2 and C-6 carbons will appear at a 8-value (133 ppm) than the C-3 and C-5 (116). As C-l carbon contains one strong electron withdrawing group -COOH, it will have moderate 8-value (122 ppm).
➤ Ring Current: Let us explain the phenomena by taking the example of [18]-annulene. The structure of [18]-annulene is shown below: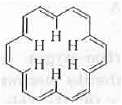
It is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains [4n + 2]n e's where n = 4. Hence, it is aromatic in nature.
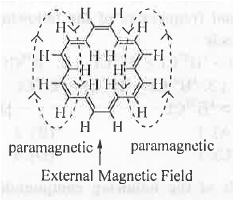
Now, when it is placed in an external magnetic field, due to the circulation of the rc-e's, electric ring current is generated which is paramagnetic i.e. parallel to the external magnetic field outside the ring while it is diamagnetic i.e. opposite to the external magnetic field within the ring. Hence, the six protons present inside the [18]-annulene become highly shielded and hence, these will appear at upfield region. But, the protons present outside the ring become highly deshielded and hence, will appear at the downfield region. Hence, the outer protons resonate at 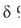 9.28 in its 'H NMR spectrum.
9.28 in its 'H NMR spectrum.
|
44 videos|102 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Organic Spectroscopy - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What are the common spectroscopic techniques used in organic chemistry? |  |
| 2. How is IR spectroscopy used in organic chemistry? |  |
| 3. What information can be obtained from NMR spectroscopy in organic chemistry? |  |
| 4. How is mass spectrometry helpful in organic chemistry? |  |
| 5. Why is UV-Vis spectroscopy important in organic chemistry? |  |

















