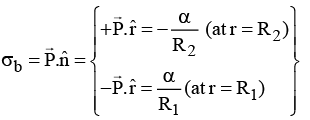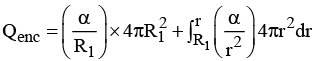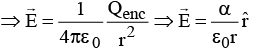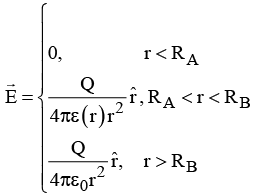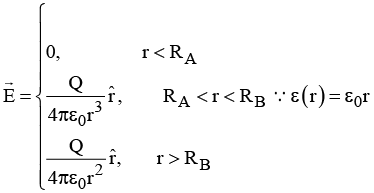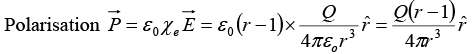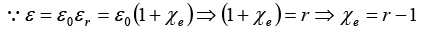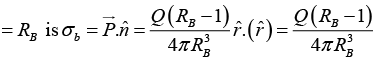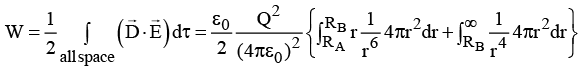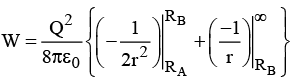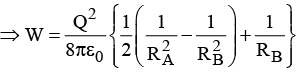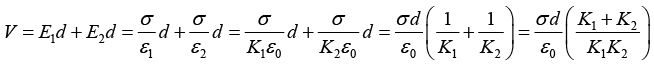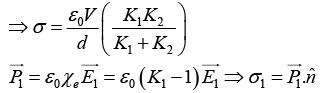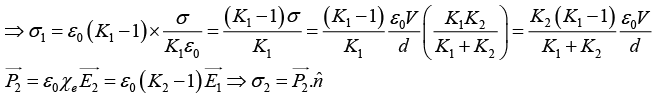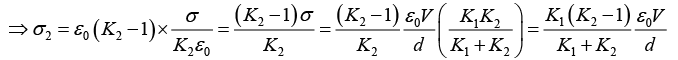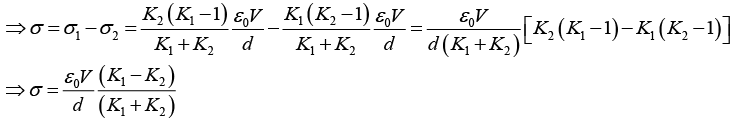Polarisation & Boundary Condition: Assignment | Electricity & Magnetism - Physics PDF Download
Q.1. Assume that z = 0 plane is the interface between two linear and homogenous dielectrics (see figure). The relative permittivities are εr = 5 for z > 0 and εr = 4 for z<0. The electric field in the region 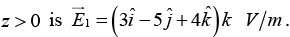 Assume that there are no free charges on the interface.
Assume that there are no free charges on the interface.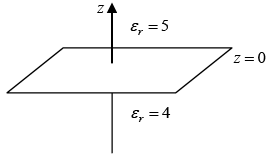
(a) Find the electric field 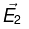 in the region z < 0.
in the region z < 0.
(b) Find the electric field 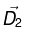 in the region z < 0.
in the region z < 0.
(a)
and
(b)
Q.2. A unit cube made of a dielectric material has a polarization 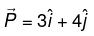 units. The edges of the cube are parallel to the Cartesian axes. Find
units. The edges of the cube are parallel to the Cartesian axes. Find
(a) the volume bound charge.
(b) the bound charge on both the surfaces parallel to the y - z plane.
(c) the bound charge on both the surfaces parallel to the x - z plane.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Q.3. The half space region x>0 and x<0 are filled with dielectric media of dielectric constants ε1 and ε2 respectively. There is a uniform electric field in each part. In the right half, the electric field makes an angle θ1 to the interface and the corresponding angle to the left half θ2. Show that ε1 tan θ1 = ε2 tan θ2 .
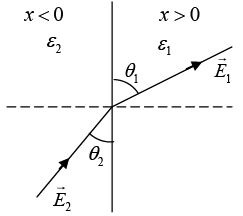
Q.4. A spherical conductor of radius a is placed in a uniform electric field 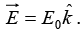 The potential at a point P(r ,q ) for r>a, is given by
The potential at a point P(r ,q ) for r>a, is given by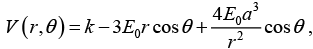
where k is some constant.
Where r is the distance of P from the centre O of the sphere and θ is the angle OP makes with the z -axis. Find the charge density on the sphere at θ = 60º.
Q.5. A conducting spherical shell of radius R1 carries a total charge Q. A spherical layer of a linear, homogeneous and isotropic dielectric of dielectric constant K and outer radius R2 (>R1) covers the shell as shown in figure.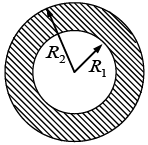 (a) Find the electric field and the polarization vector
(a) Find the electric field and the polarization vector 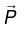 inside the dielectric. From this
inside the dielectric. From this 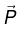 , calculate the surface bound charge density, σb, on the outer surface of the dielectric layer and the volume bound charge density ρb, inside the dielectric.
, calculate the surface bound charge density, σb, on the outer surface of the dielectric layer and the volume bound charge density ρb, inside the dielectric.
(b) Calculate the electrostatic energy of the system
(a)
The surface bound charge density at r
(b)
Q.6. A polarized dielectric cube of side ℓ is kept on the x -y plane as shown. If the polarization in the cube is 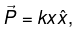 where k is a positive constant, and then finds all the bound surface charge densities and volume charge density.
where k is a positive constant, and then finds all the bound surface charge densities and volume charge density.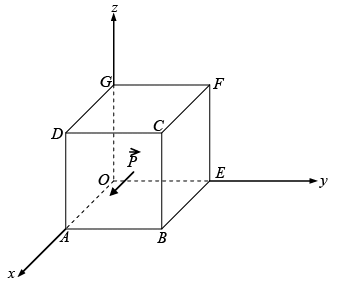
Volume charge density
Bound surface charge density on the surface OADGO (y = 0 plane)
Bound surface charge density on the surface EBCFE (y = l plane)
Bound surface charge density on the surface OGFEO (x = 0 plane)
Bound surface charge density on the surface ADCBA (x = l plane);
Bound surface charge density on the surface OABEO (z = 0 plane)
Bound surface charge density on the surface GFCDG ( z = l plane)
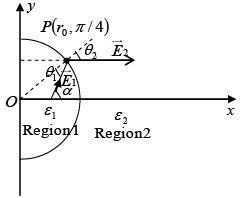
Q.7. A ray of light inside Region 1 in the xy -plane is incident at the semicircular boundary that carries no free charges. The electric field at the point 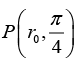 in plane polar coordinates is
in plane polar coordinates is 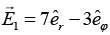 where
where 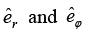 are the unit vectors. The emerging ray in Region 2 has the electric field
are the unit vectors. The emerging ray in Region 2 has the electric field 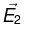 parallel to x -axis. If ε1 and ε2 are the dielectric constants of Region-1 and Region-2 respectively then find ε2/ε1.
parallel to x -axis. If ε1 and ε2 are the dielectric constants of Region-1 and Region-2 respectively then find ε2/ε1.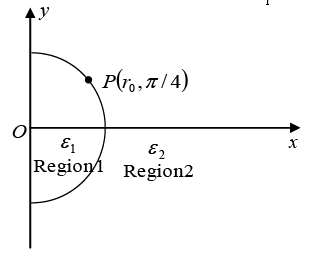

Thusmakes an angle
Q.8. A spherical shell of inner and outer radii R1 and R2, respectively, is made of a dielectric material with frozen polarization 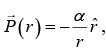 where a is a constant and r is the distance from its centre. Find the electric field in the region R1 < r< R2.
where a is a constant and r is the distance from its centre. Find the electric field in the region R1 < r< R2.
and
For, R1 < r< R2 ;
⇒ Qenc = 4παR1 + 4πα(r - R1) = 4παr
Q.9. A conducting sphere of radius RA has a charge Q. It is surrounded by a dielectric spherical shell of inner radius RA and outer radius RB (as shown in the figure below) having electrical permittivity ε(r ) = ε0r.
(a) Find the surface bound charge density at r =RB.
(b) Find the electrostatic energy of the system.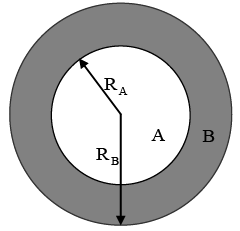
or
(a)
The surface bound charge density at r
(b)
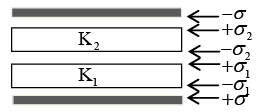
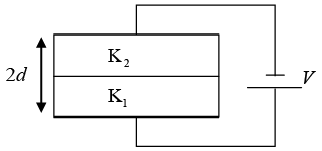
Q.10. In a parallel plate capacitor the distance between the plates is 2d. Two dielectric slabs of thickness d each and dielectric constants K1 and K2 respectively, are inserted between the plates. A potential of V is applied across the capacitor as shown in the figure. Show that the value of the net bound surface charge density at the interface of the two dielectrics is 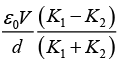
|
82 videos|32 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Polarisation & Boundary Condition: Assignment - Electricity & Magnetism - Physics
| 1. What is polarization in the context of electromagnetic waves? |  |
| 2. How does polarization affect the transmission of light through materials? |  |
| 3. What are the boundary conditions for the reflection and transmission of polarized light at an interface? |  |
| 4. Can the polarization of light be changed after reflection or transmission through a material? |  |
| 5. How is the concept of polarization applied in various fields and technologies? |  |

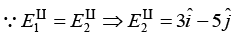
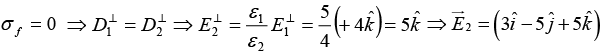
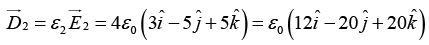
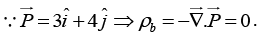
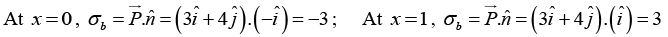
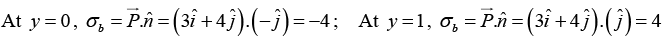
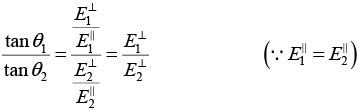
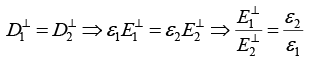
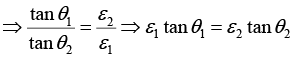
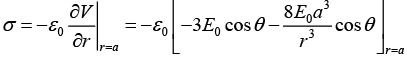
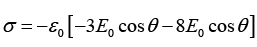
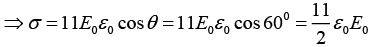
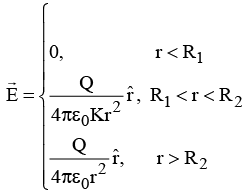
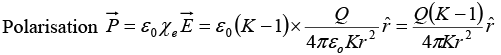
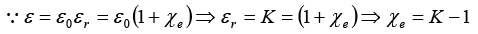
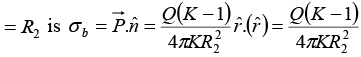
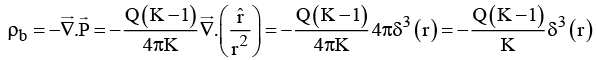
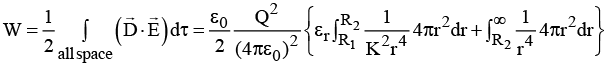
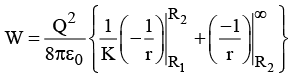
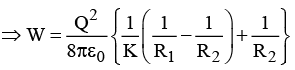
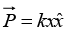
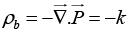
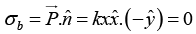
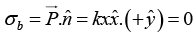
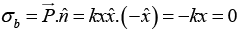
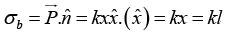
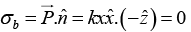
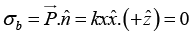
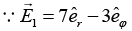
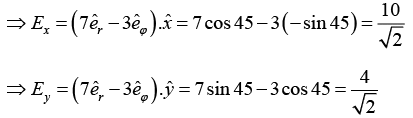
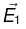 makes an angle
makes an angle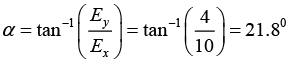
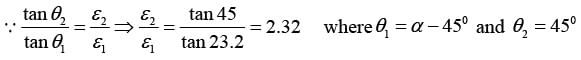
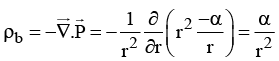 and
and