Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Policies to Control Inflation & Deflation
Policies to Control Inflation & Deflation | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Policies To Tackle Inflation
- Demand-pull inflation is effectively mitigated through contractionary demand-side policies.
- Contractionary fiscal policy and contractionary monetary policy are designed to diminish total (aggregate) demand within an economy.
- A reduction in the total demand for goods and services leads to a decline in the general price level, thereby alleviating inflation.
- The reduction in total demand can be achieved through any policy that diminishes one of the components of real Gross Domestic Product (rGDP).
Examples of Demand-side Policies Which Are Likely To Reduce Demand Pull Inflation
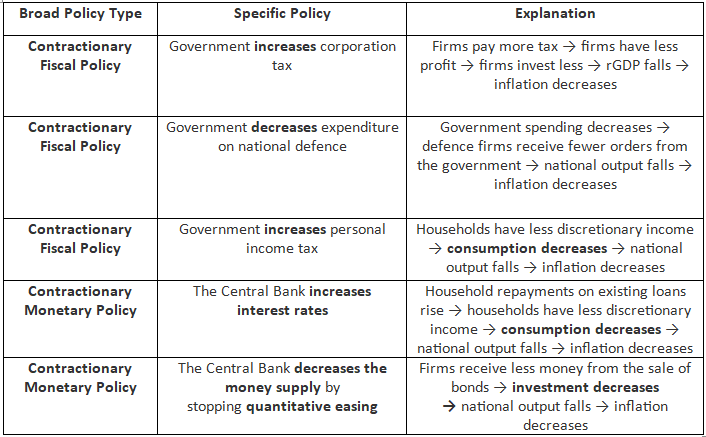
- Demand-side strategies prove more efficient in the short run in addressing inflation induced by an increase in total (aggregate) demand.
- However, they exhibit lower efficacy in combating cost-push inflation.
- A challenge associated with contractionary policies is that while they diminish demand-pull inflation, they also decrease output and employment.
Examples of Supply-side Policies Which Are Likely To Reduce Cost Push Inflation

- Supply-side policies, though typically long-term in nature, are highly effective in curbing price levels.
- However, they do not assist in addressing inflation resulting from demand-side factors.
Policies To Tackle Deflation
- Deflation triggered by a decline in total demand (e.g., during a recession) is effectively tackled through expansionary demand-side policies.
- Expansionary fiscal policy and expansionary monetary policy are geared towards amplifying total (aggregate) demand within an economy.
- As total demand rises, general price levels also increase, thereby mitigating or eradicating the deflation.
- Any policy that augments one of the components of real Gross Domestic Product (rGDP) can bolster total demand.
Examples of Demand-side Policies Which Are Likely To Reduce Deflation

- Demand-side policies can prove highly effective in addressing deflationary pressures.
- Expansionary monetary policy often exacerbates income inequality, as the poorest households typically do not benefit from it, given that banks may not necessarily extend loans to them.
Question for Policies to Control Inflation & DeflationTry yourself: Which type of inflation can be effectively addressed through contractionary demand-side policies?View Solution
The document Policies to Control Inflation & Deflation | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
71 videos|82 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Policies to Control Inflation & Deflation - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How can central banks use monetary policy to tackle inflation and deflation? |  |
Ans. Central banks can use monetary policy tools such as adjusting interest rates, open market operations, and reserve requirements to control inflation and deflation. By raising interest rates, central banks can reduce borrowing and spending to combat inflation, while lowering rates can stimulate spending to fight deflation.
| 2. What are some examples of supply-side policies that can help tackle inflation? |  |
Ans. Supply-side policies to tackle inflation include promoting competition, investing in infrastructure to boost productivity, reducing regulations to encourage business growth, and encouraging innovation and technology advancements.
| 3. How can fiscal policy be used to control inflation and deflation? |  |
Ans. Fiscal policy tools, such as adjusting government spending and taxation, can be used to control inflation and deflation. For example, reducing government spending during times of high inflation can help reduce demand and stabilize prices, while increasing spending during deflation can stimulate economic activity.
| 4. What are the potential drawbacks of using expansionary monetary policy to tackle deflation? |  |
Ans. One potential drawback of using expansionary monetary policy to tackle deflation is the risk of causing inflation to rise too quickly. Additionally, lowering interest rates too much can lead to asset bubbles and financial instability in the long run.
| 5. How do expectations of inflation and deflation play a role in the effectiveness of policy measures? |  |
Ans. Expectations of inflation and deflation can impact consumer and business behavior, affecting the effectiveness of policy measures. If individuals expect prices to rise, they may spend more now, fueling inflation. Conversely, if deflation is expected, consumers may delay purchases, leading to further economic slowdown. Central banks and governments must consider and manage these expectations when implementing policy measures.
Related Searches

















