Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Population
Population | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Population Increase |

|
| Overpopulation & Underpopulation |

|
| Case Study: Nigeria |

|
| Case Study: Canada |

|
Population Increase
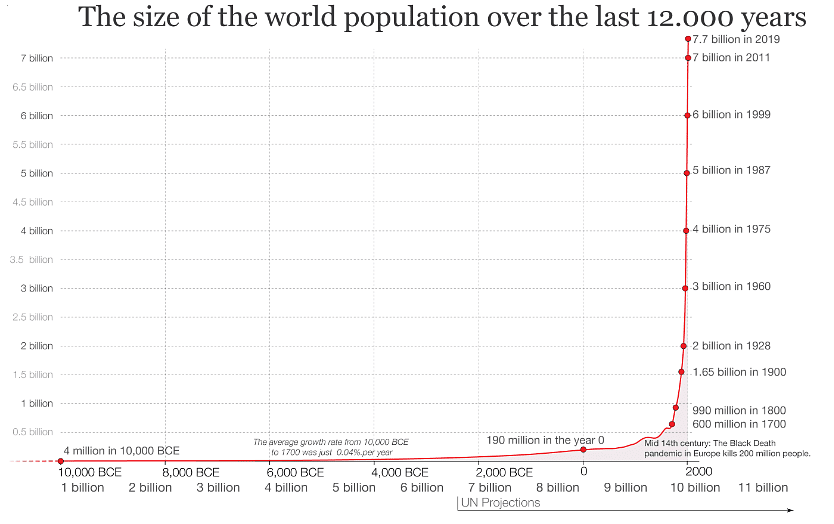
- The global population is currently growing by around 80 million individuals annually.
- The global population is currently growing by around 80 million individuals annually.
- In the year 1804, the global population stood at 1 billion with a gradual and modest growth rate.
- Population growth remained stable and slow.
- Population growth remained stable and slow.
- It took slightly over a century for the global population to double to 2 billion.

Population Growth Overview
- Following 1930, the population growth rate escalated, leading to a significant population surge.
- The most rapid population increase occurred in the 1980s and 1990s.
- Population growth rate denotes the average yearly variation in population size over a specified period, typically a year.
- While the population is still expanding, the pace of growth has decelerated.
Factors Affecting Population Growth
- The pace of population rise significantly accelerated post-1930, resulting in a population explosion.
- Notable population expansion transpired during the 1980s and 1990s.
- Population growth rate, signifying the average annual population size alteration, notably decreased from 2% in 1970 to under 1% in 2022.
- UN projections estimate a population stabilization at approximately 11 billion by 2100.

Overpopulation & Underpopulation
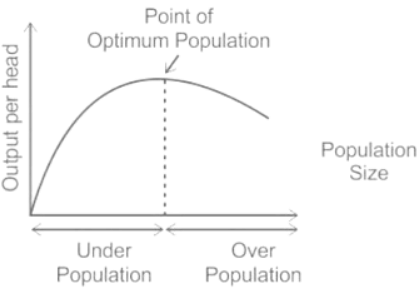
- Every region possesses a carrying capacity, which signifies the maximum population an area can sustain.
- Overpopulation arises when a locality exceeds its capacity to support the populace with available resources and technology. This can lead to:
- Escalation in levels of pollution, impacting the environment and health of inhabitants.
- Rise in crime rates due to increased competition for limited resources.
- Higher rates of unemployment or underemployment, straining the economy.
- Shortages of food and water, intensifying hunger and thirst among residents.
- Pressure on essential services like hospitals and schools, affecting quality and accessibility.
- On the contrary, underpopulation occurs when available resources surpass the needs of the population, resulting in:
- Decreased tax revenue due to fewer individuals contributing, potentially leading to increased tax burdens.
- Underutilization of resources, which may result in wastage and inefficiency.
- Scarcity of skilled workers, affecting productivity and growth.
- Lower levels of exports and production, impacting the economic prosperity of a region.
- Reduced demand for goods and services, affecting businesses and economic growth.
- The ideal scenario is achieved when there is a balance between population size and available resources/technology.
- Optimal population levels result in the highest standard of living because:
- There is a sustainable balance ensuring that the standard of living remains stable.
- The population is sufficient to develop and utilize the resources effectively.
Question for PopulationTry yourself: What is the definition of overpopulation?View Solution
Case Study: Nigeria
- Nigeria's population exceeds 217 million currently and is projected to grow to 400 million by 2050 and 1 billion by 2100.
- Lagos is anticipated to emerge as the world's largest city by the year 2100.
Population Statistics
- Approximately 30% of Nigeria's population lives in poverty, earning less than $515 annually.
- The urban population has surged from 18% in 1960 to nearly 53% in 2021.
- Nigeria is undergoing rapid population expansion at a rate of 2.5%.
Population Density
- Nigeria's population density stands at 226 individuals per square kilometer. In Lagos, this figure escalates significantly to 6871 people per square kilometer.
Resources
- Nigeria possesses abundant resources such as oil, gas, iron ore, coal, zinc, and arable land.
- The distribution of resources does not lead to overall prosperity for the population due to several factors:
- Poor management
- Ownership by foreign companies
- Corruption
- The wealthiest 5 individuals in Nigeria have more control over resources than the remaining 95% combined.
- Given the rapid population growth, the current resource allocation fails to adequately support the populace.
Causes of Population Increase
- Improvements in healthcare and sanitation leading to lower mortality rates
- High fertility rates impacting family size
- Lack of awareness and access to contraceptives
- Social and cultural norms promoting larger families
The Impact of High Birth and Fertility Rates on Population Growth
- The primary reason behind the rapid growth of the population is the high birth and fertility rates.
- In certain regions, girls can get married as early as 13 years old, leading to a higher number of children per woman. For instance, about 45% of women are married before turning 18, which contributes to a higher fertility rate of 5.32 births per woman in 2019.
- Larger families historically signify higher social standing in society.
- In the past, there were elevated infant mortality rates, such as 125 per 1000 in 1990, which decreased to 72 per 1000. This decline is linked to high fertility rates since women used to have more children to ensure survival into adulthood in the face of high infant mortality rates.
- Religious beliefs often influence larger family sizes, along with a lack of awareness about family planning and contraception.
- The decreasing death rate also plays a role in the population increase, with the death rate dropping from 19 per 1000 in 1990 to 11 per 1000 in 2020.
- As life expectancy rises, the overall population continues to grow.

Impacts of Overpopulation
- Shortage of fresh water leading to the spread of diseases:
- Approximately 29% of children in Nigeria lack access to sufficient water for their daily needs.
- Increased levels of water, air, and land pollution:
- Lagos, a major city in Nigeria, faces severe air pollution issues compared to other cities globally.
- Expansion of agricultural land causing soil erosion and desertification:
- Approximately 40 million people in northern Nigeria are at risk of losing their livelihoods due to desertification.
- 19.5 million individuals are facing acute food insecurity as a result.
- Strain on essential services like healthcare and education:
- Higher demand for already limited services due to population pressure.
- Rise in criminal activities:
- High levels of youth unemployment contributing to increased gang activities and the formation of militant groups.
- Growth of informal settlements around urban areas:
- It's estimated that about 70% of the population in Lagos resides in informal settlements.
- Approximately 66% of the population in these areas live on less than $1 a day.
Case Study: Canada
- Canada stands as the world's second-largest country with a population of 38.5 million.
- It maintains a population density of 4 individuals per square kilometer.
- Canada exhibits a natural increase rate of 2.42 per 1000 individuals.
- Notably, a significant portion of Canada's population growth is attributed to immigration.
Resources
Canada boasts abundant resources:
- Fishing: Benefitting from the world's longest coastline.
- Leading producer of zinc and uranium.
- Rich reserves of timber, gas, coal, and oil.
- Abundant in gold, nickel, lead, and aluminum.
- Significant exporter of wheat.
Causes of under-population
- The primary cause of under-population in Canada stems from low birth and fertility rates.
- Low birth rate: Canada experiences only 9 births per 1000 individuals.
- Fertility rate: The current rate stands at 1.47 children per woman, which falls below the fertility replacement rate of 2.1.
- Factors contributing to these low rates include:
- Delay in childbirth: The average age for a woman to have her first child is 31 years, resulting in reduced childbearing years.
- Family planning and access to contraceptives: Increased levels of family planning and contraceptive use impact birth rates.
- Education and career: Higher education levels lead to career pursuits, causing delays in starting a family.
- Geographical challenges:
- Canada has remote and inaccessible regions, making infrastructure development for settlements and industries costly.
Factors Affecting Fertility Rates
- Women nowadays are opting to have children later in life, with the average age for a first child being around 31 years. This trend results in a shorter span for childbearing.
- Increased availability of family planning methods and easy access to contraceptives contribute to lower birth rates.
- Higher education levels among women often lead to the prioritization of career over starting a family, causing a delay in childbirth.
Challenges of Under-Population
- Shortages of skilled workers are prevalent in sectors such as construction, engineering, food services, and healthcare.
- An aging population poses economic challenges, including low workforce participation, increased retirement-aged individuals, and reduced tax revenues.
- As the population ages, there is a strain on healthcare and social services, leading to increased costs for the government.
- Under-population results in underutilization of resources, limiting economic growth potential.
- Rural areas often face a lack of essential services due to low demand, exacerbating disparities in access to services.
Question for PopulationTry yourself: What is the primary reason behind the rapid population growth in Nigeria?View Solution
The document Population | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
Related Searches