Power Screws | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
POWER SCREWS
- The power screws are used to convert rotary motion into translatory motion. In case of screw jack, a small force applied in the horizontal plane is used to raise or lower a large load.
- In most of the power screws, the nut has axial motion against the resisting axial force while the screw rotates in its bearings. In some screws, the screw rotates and moves axially against the resisting force while the nut is stationary and in others the nut rotates while the screw moves axially with no rotation.
- Types of Screw threads used for power screws
- Square threads. A square thread is adapted for the transmission of power in either direction. This thread results in maximum efficiency and minimum radial or bursting pressure on the nut. It is difficult to cut with tapes and dies. It is usually cut on a lathe with a single point tool and it can not be easily compensated for wear.
- Acme or trapezoidal thread. An acme or trapezoidal thread is a modication of square thread. The slight slope given to its sides lowers the efficiency slightly than square thread and it also introduce some bursting pressure on the nut, but increases its area in shear. It is used where a split nut is required and may be taken up by means of adjustable split nut.
- Buttress thread. A buttress thread is used when large forces act along the screw axis in one direction only. This threads combines the higher efficiency of square thread and ease of cutting and the adaptability to a split nut of acme thread. It is stronger than other threads because of greater thickness at the base of the thread. If is employed as the thread for light jack screw.
Torque required to raise load on square threaded screws
Let, l = lead of the screw
d = mean diameter of the screw
a = helix angle
Let,
p = effort applied at the circumference of the screw to lift the load
W = weight of the body to be lifted.
µ = coefficient of friction between the screw and nut ( m = tan f).
So, P = W tan (a + f)
Torque required to overcome friction between the screw and nut,
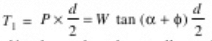
( α= a, ϕ= f)
- When the axial load is taken up by a thrust collar, so that the load does not rotate with the screw, then the torque required to overcome friction at the collar, then for uniform pressure,
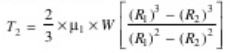
where,
R1 and R2 = outside and inside radii of collar
R = mean radius of collar
µ1 = coefficient of friction for the collar.
Total torque, T = T1 + T2
- If an effort, P1 is applied at the end of a lever of arm length l, then the total torque required to overcome friction must be equal to the torque applied at the end of a lever, T = P1 × l
- When the nomial or outer diameter (do) and the core diameter or inner diameter (dc) of the screw is given then mean diameter of screw,
- Torque required to lower load by square threaded screw
P = W tan (f – a)
and Torque required to lower the load - Efficiency of square threaded screws
Effort applied at the circumference of the screw to lift the load is
P = W tan (f + a)
It there would have been no friction between the screw and the nut the f will be equal to zero. The value of effort Po necessary to raise the load, will then given by
Po = W tan a
Maximum efficiency of a square threaded screw occurs at
- Efficiency Vs Helix Angle
- The efficiency of a square threaded screw increases rapidly upto helix angle of 20°, after which the increase space inefficiency is low. The efficiency is maximum for helix angle between 40 to 45°.
- When the helix angle further increased say 70°, the efficiency drops. This is due to the fact that the normal thread force becomes large and thus the force of friction and the work of friction becomes large as compared with the useful work. This results in low efficiency.
- Over Hauling and Self Locking Screws
Torque required to lower the load
T = P × d/2 = W tan (f – a)d/2
In above relation is f < a, then torque required to lower the load will be negative.
In other words, the load will start moving downward without the application of any torque. Such a condition is known as over hauling of screws. If however, f > a, the torque required to lower the load will be positive, indicating that and effort is applied to lower the load. Such a screw is known as self locking screw.
The efficiency of self locking screws,
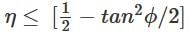
So the efficiency of self locking screws is less than 1/2 or 50%. If the efficiency is more than 50%, then the screw is said to be overhauling.
- For acme or trapezoidal threads, the frictional force
F = µ.RN = µ1.W where, µ1 = µ/cos b,
where b is the semi angle of the thread.
Stresses in Power screws
- Direct tensile or compressive stress due to an axial load
where,
W = axial load
AC = cross-sectional area of screw corresponding to core diameter (dc).
This is only applicable when the axial load is compressive and the unsupported length of the screw between the load and the nut is short. When unsupported length of the screw between the load and the nut is too great, the design is based on the column theory assuming suitable end conditions.
- Torsional shear stress-Torque transmitted by screw
when screw is subjected to both direct stresses and shear stresses than
- Shear stresses due to axial load. The threads of the screw of the core or root diameter and the threads of the nut at the major diameter may shear due to the axial load.
-Shear stress for the screw
-Shear stress for the nut
where,
w = axial load on the screw
n = Number of threads in engagement
dc = core or root diameter of the screw
do = outside or major diameter of nut or screw
t = thickness or width of thread, (= p/2)
- Bearing Pressure. In order to reduce wear of the screw and nut, the bearing pressure on the thread surface must be within limits. The bearing pressure is limited by lubrication conditions.
where,
d = mean diameter of screw
n = Number of threads in contact with nut
t
|
6 videos|104 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Power Screws - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What is a power screw in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. How does a power screw work? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using power screws in mechanical systems? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of power screws commonly used in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 5. How can power screws be selected for a specific mechanical application? |  |





















