Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - The Fundamental Unit of Life
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Cell theory was proposed by
(a) Robert Brown
(b) Robert Hook
(c) Schleiden and Schwann
(d) Anton von Leeuwenhoek
Ans: (c)
M.J. Schleiden (1838) and Theodore Schwann (1839) proposed the cell theory which states that the basic structural and functional unit of all plants and animals is cell.
Q2: Which of these is acellular?
(a) Viruses
(b) Bacteria
(c) Protozoans
(d) Fungi
Ans: (a)
Virus is sub-microscopic and acellular particle (ranging in size from 20-300 nm) that can infect the cells of a biological organism. Viruses can replicate themselves only by infecting a host cell.
Q3: Select the odd group from the following.
(a) Chlamydomonas, Paramecium, bacteria
(b) Fungi, Plants, Animals
(c) Sperm, Neuron, Amoeba
(d) Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow
Ans: (c)
Cells like Amoeba have changing shapes whereas nerve cells and sperms have definite shape.
Q4: Which structure in plant cell is responsible for providing the energy required to drive cellular processes?
(a) Chloroplast
(b) Mitochondrion
(c) Nucleus
(d) Golgi apparatus
Ans: (b)
Mitochondrion carries out aerobic respiration, which involves the oxidation of food to release stored chemical energy for various metabolic activities in the cell. Option ‘A’ is incorrect because, chloroplast converts light energy to chemical energy i.e., glucose, but this chemical energy captured in the form of glucose can only be unlocked for usage by the cell via respiration taking place in mitochondria.
Q5: Plasma membrane is composed of
(a) cellulose and lipids
(b) lipids and proteins
(c) peptidoglycan and lipids
(d) cellulose and proteins
Ans : (b)
Plasma membrane is a living, thin, delicate, elastic, selectively permeable. Chemically, it is made up of 75% phospholipid. In addition to phospholipid, the membrane contains proteins, cholesterol and polysaccharides.
Q6: What is the meaning of “Omni’s Cellulae Cellula”?
(a) All organisms are composed of cells.
(b) Cell is basic structural unit of an organism.
(c) Cells are capable of producing more of themselves.
(d) Cells arise from the division of pre-existing cell.
Ans : (d)
German physiologist Rudolf Virchow in 1958 stated (a latin phrase - Omni cellulae cellula), which means that all cells arise from the division of pre-existing cells.
Q7: Cell wall of plants is mainly composed of
(a) chitin
(b) cellulose
(c) lipids
(d) lignin
Ans : (c)
Cell wall is present in plant cells, bacteria and fungi, It is an additional protective wall present outside plasma membrane. Cell wall is a thick, non-living, rigid and permeable covering made up of cellulose. Cellulose is a kind of carbohydrate (polysaccharides). It provides structural strength to the plant.
Q8: A plant cell placed in a hypo-tonic solution will not burst because of presence of
(a) plasma membrane
(b) cell wall
(c) chloroplast
(d) cytoplasm
Ans : (b)
Cell walls permit the cells of plants, fungi and bacteria to withstand very dilute (hypo-tonic) external media without bursting. In such media the cells tend to take up water by osmosis. The cell swells, building up pressure against the cell wall. The wall exerts an equal pressure against the swollen cell. Because of their walls, such cells can withstand much greater changes in the surrounding medium than animal cells.
Q9: The transportation of materials in the cell is done by
(a) Golgi complex
(b) lysosomes
(c) mitochondria
(d) endoplamic reticulum
Ans: (d)
Endoplasmic reticulum is a tube like structure present in the cell, which extends all over the cell. The ER facilitates transport of materials from one part of the cell to another.
Q10: An organism has poorly defined nuclear membrane in its cells. This organism could be a/an
(a) bacteria
(b) animal
(c) fungi
(d) bird
Ans: (a)
In some organisms like bacteria, the nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane. Such organisms, whose cells lack a nuclear membrane, are called prokaryotes.
Q11: Which cell organelle is not bound by a unit membrane?
(a) Lysosome
(b) Ribosome
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Nucleus
Ans : (c)
Endoplasmic reticulum is not bound by a single membrane. It is a complex network of membranous system in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
Q12: Largest number of cell bodies of neuron in our body are found in:
(a) retina
(b) spinal cord
(c) brain
(d) tongue
Ans : (c)
Largest number of cell bodies of neuron are found in brain.
Q13: If the ribosome of a cell are destroyed then
(a) respiration will not take place
(b) fats will not be stored
(c) carbon assimilation will not occur
(d) proteins will not be formed
Ans: (d)
Ribosome’s are involved in the synthesis of proteins. Hence, if ribosome’s are destroyed, then proteins will not be formed.
Q14: What is ‘autolysis’?
(a) Self-replication
(b) Self-digestion
(c) Self-food producers
(d) Food decomposer
Ans: (b)
Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes (acid hydrolases). They digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria. The membrane surrounding a lysosome prevents the digestive enzymes inside from destroying the cell.
Q15. What is meant by ‘multicellular’?
(a) The single celled organism.
(b) The cytoplasmic projection which helps in locomotion & feeding of Amoeba
(c) Organisms made of more than one cell.
(d) A group of tissues which together perform specific function
Ans: (c)
Organisms made of more than one cell are called multicellular organism.
Q16: What is the function of the central vacuole in plants?
(a) Stores water and dissolved nutrients
(b) Carries out photosynthesis
(c) Releases energy from stored nutrients
(d) Protects the genetic material of the cell
Ans: (a)
The central vacuole in plants has a storage function. It consists of cell sap that has dissolved sugars, mineral salts and amino acids.
Fill in the blanks.
Q17: Ribosomes are rich in .......... and ..........
Ans: RNA, Proteins
Ribosomes are rich in RNA and Proteins: Ribosomes are tiny, spherical cellular organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis in all living cells. These organelles are rich in Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) and proteins. RNA is crucial in the process of protein synthesis as it carries the genetic information necessary for the creation of specific proteins. Proteins are the primary constituents of ribosomes, and they facilitate the function of ribosomes.
Q18: .......... are living, protoplasmic structures capable of growth and sometimes multiplication also.
Ans: Cell Organelles
Cell Organelles are living, protoplasmic structures capable of growth and sometimes multiplication also: Cell organelles are specialized structures within the cell that perform specific functions to help the cell survive. These organelles are considered to be living because they are made up of protoplasm and are capable of growth and, in some cases, multiplication. For instance, mitochondria and chloroplasts can grow and divide to increase their number.
Q19: .......... are clear spaces present in the cytoplasm enclosed by a membrane.
Ans: Vacuoles
Vacuoles are clear spaces present in the cytoplasm enclosed by a membrane: Vacuoles are storage bubbles found in cells. They are clear spaces within the cell cytoplasm that are enclosed by a membrane and are often filled with water and inorganic and organic molecules. They serve functions such as maintaining internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor within the cell, storing nutrients, and degrading waste products.
Q20: Membrane-bound non-living structures in a cell is ..........
Ans: Vacuole
Membrane-bound non-living structures in a cell is Vacuole: A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. They are non-living structures as they do not possess any metabolic activities. They are enclosed by a membrane and are involved in maintaining the shape and rigidity of the cell, besides storing waste products and nutrients.
Q21: .......... in animals are the longest cells.
Ans: Nerve cells
Nerve cells in animals are the longest cells: Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are the fundamental units of the nervous system in animals. These cells are designed to transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells. Nerve cells are typically long and have extensions known as axons, which can reach out to distant parts of the body, making them the longest cells in the animal body.
True/False
Q22: Lamarck propounded the Cell Theory.
Ans: False
The statement is false because Lamarck did not propound the Cell Theory. It was actually propounded by two scientists, Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in 1838-1839. Lamarck is known for his Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics, not the Cell Theory.
Q23: Endoplasmic reticulum may be smooth or rough.
Ans: True
The endoplasmic reticulum is a part of the cell that can indeed be smooth or rough. The difference lies in the presence of ribosomes. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached to its surface, which gives it a bumpy appearance, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks these ribosomes.
Q24: Robert Hooke discovered the wonder world of microbes.
Ans: False
Robert Hooke didn't discover the world of microbes. He is renowned for his discovery of cell in 1665 using a self-designed microscope. The discovery of the microbial world is credited to Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.
Q25: The main function of ribosomes is to synthesize proteins.
Ans: True
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis in a cell. They are composed of RNA and proteins and can be found either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or floating freely in the cytoplasm. They read the genetic information encoded in the messenger RNA and translate it into proteins.
Q26: A. Van Leeuwenhoek discovered cell.
Ans: False
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek did not discover the cell. He is known for his work on the improvement of the microscope and for his contributions towards the establishment of microbiology. The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
Matching Questions
Direction : Each question contains statements given in two columns which have to be matched. Statements (A, B, C, D) in column-I have to be matched with statements (p, q, r, s)
Q27: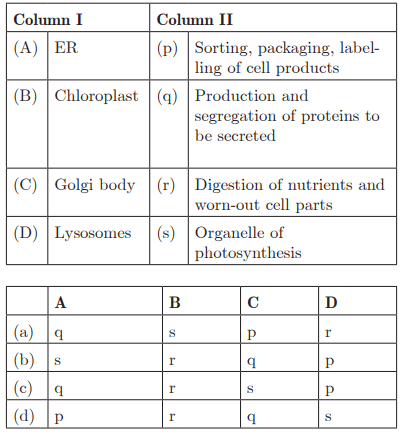 Ans : (a) A - q, B - s, C - p, D - r
Ans : (a) A - q, B - s, C - p, D - r
Q28:

Ans: (c) A - (q, s), B - r, C - s, D - p
Q29:
Ans: (c) A - q, B - r, C - s, D - p
Q30: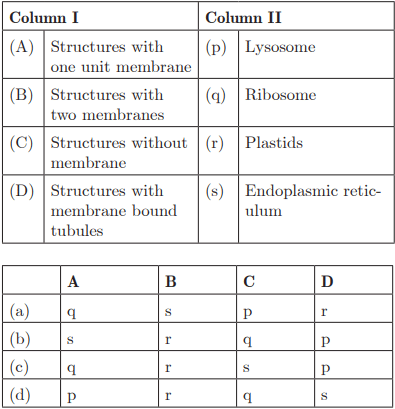
Ans: (d) A - p, B - r, C - q, D - s
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|

















