Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Practice Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: If the components of the substance can be separated by a chemical change only then it is a/an
(a) element
(b) compound
(c) mixture
(d) none of these
Ans : (b)
A compound can be separated into its components by chemical means while an element cannot be further separated. A mixture can be separated by physical means.
Q2: The zigzag movement of dispersed phase particle in a colloidal system is known as
(a) Brownian motion
(b) translational motion
(c) circular motion
(d) linear motion
Ans: (a)
The zigzag motion of colloidal particles is called Brownian motion.
Q3: The fine particles of an insoluble substance uniformly dispersed throughout a gas or liquid is called
(a) suspension
(b) precipitate
(c) colloidal solution
(d) impurity
Ans: (c)
In colloidal solution, dispersed phase is dispersed uniformly in dispersion medium.
Q4: What kind of solution is gel?
(a) Colloid
(b) Mixture
(c) Emulsion
(d) Suspension
Ans: (a)
Gel is a colloid in which liquid phase is dispersed in solid dispersion medium e.g. jelly, cheese, butter, etc.
Q5: In ‘tincture of iodine’, a solute is .......... and a solvent is .......... .
(a) alcohol, iodine
(b) iodine, tin
(c) iodine, alcohol
(d) tin, iodine
Ans: (c)
A solution of iodine in alcohol is known as ‘tincture of iodine’. It has iodine (solid) as the solute and alcohol (liquid) as the solvent.
Q6: When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, it gets
(a) reflected
(b) absorbed
(c) scattered
(d) refracted
Ans: (c)
The scattering of beam of light on passing through colloidal solution is known as Tyndall effect.
Q7: Pigments of natural colours can be separated by
(a) chromatography
(b) centrifugation
(c) filtration
(d) sublimation
Ans: (a)
By chromatography technique components of natural colours can be separated.
Q8: Which of the following upon shaking with water will not form a true solution?
(a) Alum
(b) Common salt
(c) Albumin
(d) Sucrose
Ans: (c)
Albumin will form a colloidal solution since it is not soluble in water.
Q9: What type of mixtures are separated by crystallisation?
(a) A mixture in which one component is soluble in a solvent.
(b) A mixture in which impurities are soluble in a solvent.
(c) A mixture in which both the components are soluble in a solvent.
(d) A mixture in which both the components are insoluble in water.
Ans : (a)
Crystallisation is a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution.
Q10: A student mixed a small amount of iron filings and sulphur powder in a dish. He could not affect the separation by simple hand-picking. Which liquid will you suggest to affect the separation?
(a) Carbon disulphide
(b) Cold water
(c) Boiling water
(d) Kerosene
Ans: (a)
Sulphur is soluble in carbon disulphide while iron filings remain insoluble. Hence, the sulphur will go into solution leaving behind iron filings.
Q11: Substance P has the following properties:
1. Melts at 80ºC
2. Boils at 150ºC
3. Insoluble in water
Which method of separation would you use to obtain pure P from a mixture of P and water?
(a) Paper chromatography
(b) Fractional distillation
(c) Crystallisation
(d) Filtration
Ans: (d)
As substance P is insoluble in water, it can be separated by filtration.
Q12: Pigments of natural colours can be separated by
(a) chromatography
(b) centrifugation
(c) filtration
(d) sublimation
Ans: (a)
By chromatography technique, components of natural colours can be separated.
Q13: Which of the following statements are correct about properties of colloids?
1. A colloid is a homogeneous mixture.
2. The size of particles of a colloid is too small to be individually seen by naked eye.
3. Colloids are big enough to scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 1 and 3
Ans: (b) 2 and 3
Colloidal solutions are heterogeneous in nature.
Q14: Iodized common salt is
(a) homogeneous mixture
(b) heterogeneous mixture
(c) pure substance
(d) oxidized substance
Ans: (a)
Iodized common salt is a homogeneous mixture since the composition of iodine and salt is fixed throughout the iodized salt and there are no visible boundaries.
Q15: The fine particles of an insoluble substance uniformly dispersed throughout a gas or liquid is called
(a) suspension
(b) precipitate
(c) colloidal solution
(d) impurity
Ans: (c)
In colloidal solution dispersed phase is dispersed uniformly in dispersion medium.
Fill in the blanks.
Q16: The smell of perfume gradually spreads across a room due to ..........
Ans: diffusion
The smell of perfume gradually spreads across a room due to a process called 'diffusion'. Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In the case of perfume, its particles move and mix with the air particles, spreading the scent across the room.
Q17: Rapid evaporation depends on the .......... area exposed to atmosphere.
Ans: surface
Rapid evaporation depends on the surface area exposed to atmosphere. The larger the surface area, the faster the evaporation. This is because evaporation is a surface phenomenon, i.e., it occurs from the surface of the liquid. When a larger surface area is exposed to the atmosphere, more molecules can escape into the air at the same time, leading to faster evaporation.
Q18: Matter is made up of small ...........
Ans: particles
Matter is made up of small particles. These particles can be atoms, molecules, or ions, depending on the type of matter. This is the fundamental concept of the particle theory of matter, which explains the different states and properties of matter.
Q19: As the volume of a specific amount of gas decreases, it’s pressure ..........
Ans: increases
According to Boyle's Law, the volume of a specific amount of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature. This means that as the volume of the gas decreases, its pressure increases. This is because the same number of gas particles are compressed into a smaller volume, thereby increasing the pressure.
Q20: As the temperature of a system increases, the pressure of the gases ...........
Ans: increases
As the temperature of a system increases, the pressure of the gases increases. This is due to the fact that with an increase in temperature, the kinetic energy of the gas particles increases. This causes the particles to move more rapidly and collide with each other and the walls of the container more frequently, thereby increasing the pressure.
True/False
Q21: Boiling is a bulk phenomenon.
Ans: True
True. Boiling is indeed a bulk phenomenon. This means it occurs throughout the liquid and not just at the surface. When a liquid is heated, it starts to boil and vapour bubbles form inside the liquid. These bubbles rise to the surface and escape as vapour. Thus, boiling involves the whole volume of the liquid, which is why it is considered a bulk phenomenon.
Q22: Evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
Ans: True
Evaporation is a surface phenomenon. It occurs only at the surface of a liquid. The molecules on the surface of a liquid gain energy from the surrounding environment, overcome the force of attraction of the liquid, and escape as vapour. Therefore, unlike boiling, evaporation is not a bulk phenomenon but a surface phenomenon.
Q23: The rate of evaporation depends only on the surface area exposed to the atmosphere.
Ans: False
The rate of evaporation does not depend only on the surface area exposed to the atmosphere. While it is true that a larger surface area can increase the rate of evaporation, other factors also play a role. These include temperature (higher temperatures increase evaporation rate), humidity (lower humidity increases evaporation rate), and wind speed (higher wind speeds can also increase the evaporation rate).
Q24: Plasmas are all made of the same ions. They have different colours due to different amounts of electricity.
Ans: False
Plasmas are not all made of the same ions. Plasmas are the fourth state of matter and are composed of ions and electrons. The colours of plasmas are not due to different amounts of electricity but are determined by the type of gas and the energy of the electrical discharge that ionizes the gas.
Q25: A system that changes from a solid state to a liquid state gains energy.
Ans: True
When a system changes from a solid state to a liquid state, it indeed gains energy. This is because the molecules in a solid are tightly packed and have low kinetic energy. When the solid is heated, it absorbs energy which increases the kinetic energy of its molecules. This helps to overcome the forces of attraction between the molecules, leading to a change in state from solid to liquid.
Matching Questions
Direction: In the section, each question has two matching lists. Choices for the correct combination of elements from List-I and List-II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Q26:

Ans: (b) P - 4, Q - 1, R - 2, S - 3
Q27: Ans: (b) P - 1, Q - 4, R - 2, S - 3
Ans: (b) P - 1, Q - 4, R - 2, S - 3
Q28: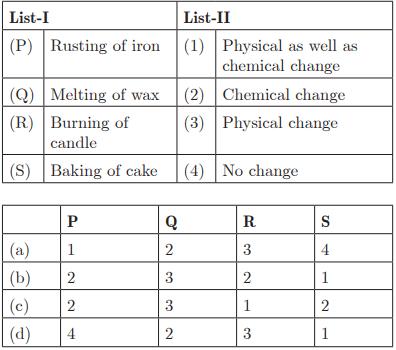 Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 3, R - 1, S - 2
Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 3, R - 1, S - 2
Q29: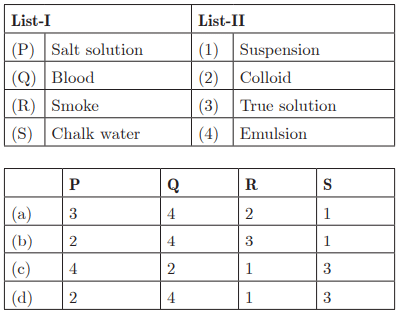 Ans: (a) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 3, S - 1
Ans: (a) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 3, S - 1
Q30:
 Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 3, R - 4, S - 1
Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 3, R - 4, S - 1
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
















