Present Perfect Continuous Tense | English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction
The Present Perfect Continuous uses two auxiliary verbs together with a main verb.
How do we make the Present Perfect Continuous tense?
The structure of the Present Perfect Continuous tense is:
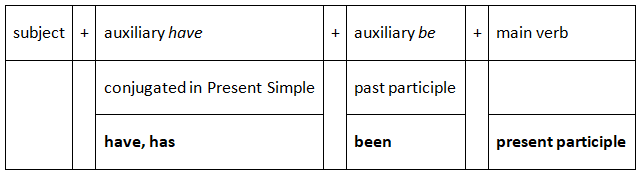
The first auxiliary (have) is conjugated in the Present Simple: have, has
The second auxiliary (be) is invariable in past participle form: been
The main verb is invariable in present participle form: -ing
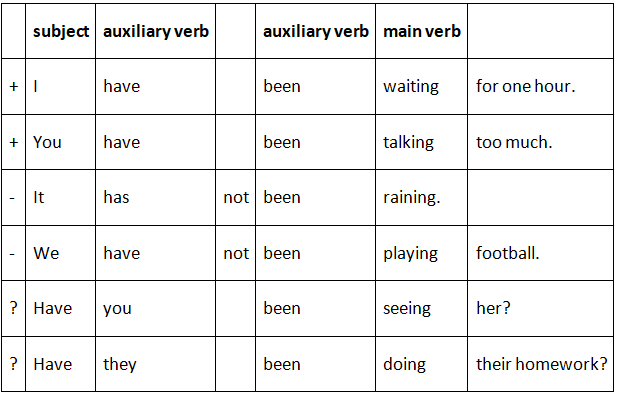
For negative sentences we insert not after the first auxiliary verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and first auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Present Perfect Continuous tense:
Contraction with Present Perfect Continuous
When utilizing the Present Perfect Continuous tense in conversation, it's common to contract the subject and the initial auxiliary verb. This contraction is also occasionally employed in informal writing.
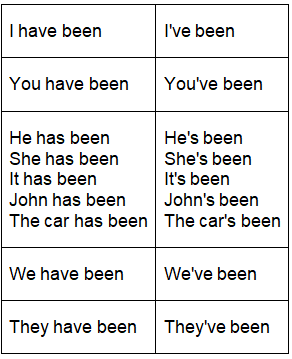
- I've been reading.
- Jenny's been helping us recently.
In negative sentences, we may contract the first auxiliary verb and "not":
- I haven't been playing tennis.
- It hasn't been snowing.
How do we use the Present Perfect Continuous tense?
This tense is called the Present Perfect Continuous tense. There is usually a connection with the present or now.
We use the Present Perfect Continuous to talk about:
- past action recently-stopped
- past action still-continuing
Present Perfect Continuous for past action just stopped
We use the Present Perfect Continuous tense to talk about action that started in the past and stopped recently. There is usually a result now.

- I'm tired [now] because I've been running.
- Why is the grass wet [now]? Has it been raining?
- You don't understand [now] because you haven't been listening.
Present Perfect Continuous for past action continuing now
We use the Present Perfect Continuous tense to talk about action that started in the past and is continuing now. This is often used with for or since.
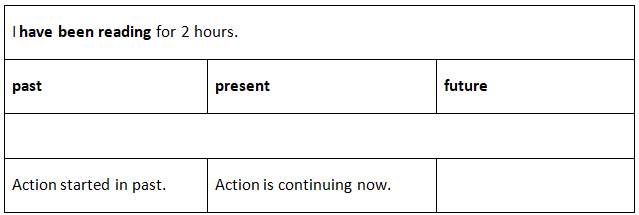
- I have been reading for 2 hours. (I am still reading now.)
- We've been studying since 9 o'clock. (We're still studying now.)
- How long have you been learning English? (You are still learning now.)
- We have not been smoking. (And we are not smoking now.)
For and Since with Present Perfect Continuous tense
We often use for and since with perfect tenses:
- We use for to talk about a period of time: three hours, two months, one decade
- We use since to talk about a point in past time: 9 o'clock, 1st January, Monday
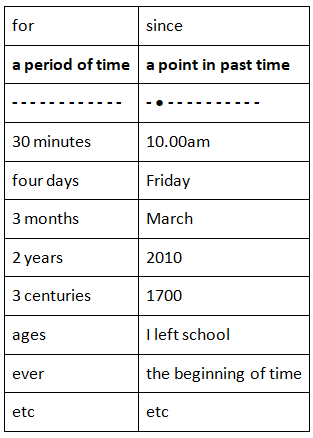
Look at these example sentences using for and since with the Present Perfect Continuous tense:
- I have been studying for three hours.
- I have been watching TV since 7pm.
- Tara hasn't been feeling well for two weeks.
- Tara hasn't been visiting us since March.
- He has been playing football for a long time.
- He has been living in Bangkok since he left school.
|
133 videos|227 docs|152 tests
|
















