Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Previous Year Questions - Force and Laws of Motion
Short Answer Questions
Q1: The velocity-time graph of a car of 1000 kg mass is given alongside. From the graph answer the following: [2023]
(а) When is the maximum force acting on the car? Why?
(b) What is the retarding force?
(c) For how long is there no force acting?
Ans. (a) In the v-t graph, the OA part represents uniformly accelerated motion with an acceleration 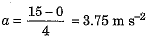
∴ Force in this region is maximum having a value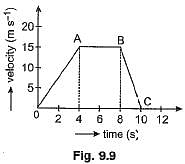
F = ma = 1000 x 3.75 = 3750 N
(b) In the v-t graph the part BC represents uniformly retarded motion with an acceleration.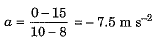
∴ Retarding force F = ma = 1000 x (-7.5) = - 7500 N
(c) The region AB of the graph represents uniform motion with a constant velocity of 15 m s-1. Hence there is no force acting on the car during the part AB from 4 s to 8 s.
Q2: Define inertia. What determines the inertia of a body? Between a football and a rock of same size which will have more inertia? [2023]
Ans. The inertia of an object is its natural tendency to maintain its state of rest or of uniform linear motion.
The mass of an object is a measure of its inertia.
A rock of the same size has more inertia than a football because mass of rock is much more.
Q.3 A boy of mass 50 kg running at 5 m s-1 jumps onto a 20 kg trolley travelling in the same direction at 1.5 m s-1. Find their common velocity. [2023]
Ans: Here the mass of boy m1 = 50 kg, the initial velocity of boy u1 = 5 m s-1, the mass of trolley m2 = 20 kg and initial velocity of trolley u2 = 1.5 m s-1.
If their common velocity be v, then from law of conservation of momentum, we have (m1 + m2)v = m1u1 + m2u2
⇒ 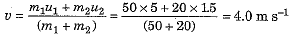
Q4: A bullet of mass 10 g is fired with a rifle. The bullet takes 0.004 s to move through the barrel and leaves it with a velocity of 400 m s-1. Calculate the force exerted on the bullet by the rifle. [2022]
Ans: Here the mass of bullet m = 10 g = 0.01 kg, the initial velocity of bullet u = 0. final velocity v = 400 m s-1 and time t = 0.004 s.
∴ 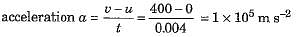
∴ Force exerted on the bullet by the rifle.
F = ma = 0.01 x (1 x 105) = 1 x 103 N = 1000 N
Q5: If the time taken to bring a ball to rest from a certain velocity v is reduced to half, what will be the changes in values of: [2022]
(a) initial and final momentum
(b) change of momentum
(c) rate of change of momentum.
Ans: (a) Initial momentum remains unchanged at pi = mv.
Final momentum remains unchanged at Pf = 0.
(b) Change of momentum of ball remains unchanged at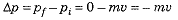
(c) Initially rate of change of momentum 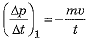 but on reducing time to half, the new rate of change of momentum will be
but on reducing time to half, the new rate of change of momentum will be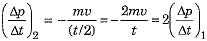
Q6: Name the physical quantities whose units are given below:
(i) kg m s-2 (ii) kg m s-1 (iii) N m2 kg-2 (iv) N (v) m s-2 (vi) m s-1 [2021]
Ans. The physical quantities having the given units are: (i) Force, (ii) momentum, (iii) gravitational constant G, (iv) force, (v) acceleration and (vi) speed or velocity.
Q7: Do action and reaction act on the same body or on different bodies? Explain your answer with the help of an example. How are they related in magnitude and direction? Write the total momentum of the gun and the bullet before firing. [2020]
Ans: Action and reaction forces act on two different bodies. For example, when a person swims in water, he applies a backward push of action on the water. In turn, the water exerts a forward reaction force on the swimmer due to which he swims forward.
The magnitude of action and reaction forces are exactly equal but their directions are mutually opposite.
The total momentum of the gun and the bullet system before firing is zero.
 Recoil: Total Momentum = 0
Recoil: Total Momentum = 0
Q8: What's Newton's third law? [2020]
Ans: Formally stated, Newton's third law is: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the force on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object.
Q9: State the relation between the momentum of a body and the force acting on it. [2020]
Ans: The rate of change of momentum of a body is equal to the external unbalanced force acting on it.
Q10: What is the momentum of a body of mass 5 kg moving with a velocity of 0.20 m s-1. [2020]
Ans. Momentum p = mass (m) x velocity (v) = 5 x 0.20 = 1.0 kg m s-1.
Q11: A boy of mass 50 kg running 5 m/s jumps on to a 20 kg trolley travelling in the same direction at 1.5 m/s. Find their common velocity. [2019]
Ans: Mass of boy = m1 = 50 kg
Mass of trolley = m2 = 20 kg
Initial velocity of boy = u1 = 5 ms-1
Initial velocity of trolley = u2 = 1.5 ms-1
Final velocity = v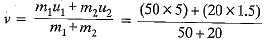
= 4 ms-1
Q12: Define the SI unit of force. A force of 2N acting on a body changes its velocity uniformly from 2 m/s to 5 m/s in 10 s. Calculate the mass of the body. [2019]
Ans: SI unit of force is Newton (N). The force applied by a body is equal to 1 N if it accelerates a unit mass by 1 m/s2 in its direction.
Given: F = 2N, t = - 10 s, u = 2 ms-1,
v = 5 ms-1.
Since, 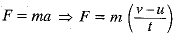
or 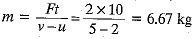
Q13: A runner presses the ground with his feet before he starts his run. Identify action and reaction in this situation. [2018]
Ans: The force applied by the runner on the ground is action force. The reaction force of ground acts on runner and pushes him forward.
Q14: Out of the four physical quantities associated with the motion of an object viz force, velocity, acceleration and momentum which one remains constant for all bodies large or small, undergoing a free fall? [2018]
Ans: During free fall, the body accelerates. Thus velocity and momentum increase at every point of motion.
Acceleration remains constant. Thus force also remains constant (as F = ma).
Q15: How are action-reaction forces related in magnitude and direction? [2018]
Ans: They have the same magnitude but different directions.
Q16: A stone released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground. [2018]
Ans: Given u = 0, s = 19.6 m, g = 9.8 m s-2.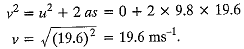
Q17: A stone released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 in. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground. [2017]
(Take g = 9.8 m/s2)
Ans: Initial velocity, u = 0
Height of fall, h = 19.6 m
g = 9.8 ms-2
Final velocity,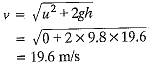
Q18: Car A of mass 1500 kg travelling at 25 m/s collides with another car B of mass 1000 kg travelling at 15 m/s in the same direction. After collision, the velocity of car A becomes 20 m/s. Calculate the velocity of car B after collision. [2017]
Ans: Masses: ma = 1500 kg; mb = 1000 kg
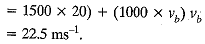
Q19: State the meaning of balanced force. [2017]
Ans: Forces are said to be balanced force if their resultant force is zero.
Q20: When an athlete comes running from a distance, he is able to jump longer. Why? [2016]
Ans: Athlete gains momentum which helps him in taking a longer jump.
Q21: A heavy person experiences more sideways push when a moving" vehicle turns suddenly. Why? [2016]
Ans: A heavy person experiences more sideways push when a moving vehicle turns suddenly because his inertia is greater.
Q22: Give a reason of the following:
(a) A footballer kicks a ball, which rolls on the ground and after covering some distance comes to rest.
(b) Only the carrom coin at the bottom of a pile is removed when a fast moving striker hits it. [2015]
Ans:(a) When a football is rolling on the ground, a force of friction acts on it due to ground in a direction opposite to its motion. As a result, the motion of football gets slowed down and after covering some distance it comes to rest.
(b) The carrom coin at the bottom of a pile comes in a state of motion due to force exerted by the striker on it. However, other coins of pile remain intact due to their inertia of rest.
Q23: A person is prone to more serious injuries when falling from a certain height on a hard concrete floor than on a sandy surface. Explain why. [2015]
Ans: When a person falls from a height on a hard concrete floor, he immediately comes in rest position. It means change in momentum is taking place in an extremely short time and consequently, force exerted by the floor on the person to destroy its momentum is extremely large. Hence, chances of more injuries. When a person falls on a sandy surface, the surface gets compressed downward and it increases the time of fall. As a result for same change in momentum force exerted by sandy surface on the person is less and chances of his being hurt are less.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: (a) State the reason why a bullet of small mass fired from a gun kills a person.(b) A bullet of mass 4 g fired with a velocity of 50 m s-1 enters a wall up to a depth of 10 cm. Calculate the average resistance offered by the wall.
(c) How will the depth of penetration into the wall change if a bullet of mass 5 g strikes against it with a velocity of 40 m s-1? Give reason to justify your answer. [2023]
Ans: (a) Although mass of a bullet is small but its momentum is very large on account of its extremely large velocity. When a bullet hits a person this large momentum is transferred to the person within a very short time and thus produces a large force and may kill the person.
(b) Here mass of bullet m = 4 g = 0.004 kg, initial velocity u = 50 m s-1, final velocity v = 0 and distance covered in wall s = 10 cm = 0.1 m.
As per relation v2 - u2 = 2 as, the acceleration
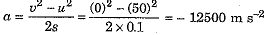
Average resistance force offered by wall F = ma = 0.004 x (- 12500) = - 50 N
(c) Depth of penetration will decrease because initial velocity of bullet is less but magnitude of retardation due to the wall remains unchanged.
Q2: If you are trying to push a heavy box on a horizontal surface, list various forces on the box. State the condition under which this box will start sliding on the surface. How will the magnitude of applied force required to move the box change if:
(i) weight of the box is increased,
(ii) the surface on which the box is placed is made more rough? [2022]
Ans: Various forces acting on the box are:
(i) Its weight ‘W acting vertically downward, (ii) reaction force 'R’ due to horizontal, surface, (iii) force of push 'F’ and (iv) frictional force 'f’. Forces have been shown in Fig. 9.13.
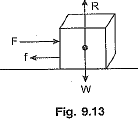
The box will start sliding on the surface only if the pushing force F is greater than the frictional force f i.e.,F>f.
(i) If weight of the box is increased, the magnitude of applied force must increase.
(ii) If the surface is made more rough, the magnitude of applied force must increase.
Q3: (i) Define m om entum. State its SI unit.
(ii) An object of mass 50 kg is accelerated uniformly from a velocity of 4 m/s to 8 m/s in 8 s. Calculate the initial and final momentum of the object. Also find the magnitude of the force exerted on the object. [2018]
Ans: The product of the mass and velocity of a body is called momentum.
SI unit: kg ms-1
mass, m = 50 kg, velocities,
u = 4 ms-1 and v = 8 ms-1, time, t = 8 s.
Initial momentum, p1 = mu = 50 x 4
= 200 kg m/s
Final momentum, p2 = mv = 50 x 8
= 400 kg ms-1
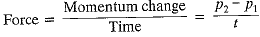
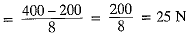
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Previous Year Questions - Force and Laws of Motion
| 1. What is Newton's First Law of Motion? |  |
| 2. How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect motion? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for calculating force? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of inertia with an example? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of Newton's laws of motion? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















