Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Drainage
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1. What is the major reason for the non-perennial nature of the peninsular rivers? [2025]
These rivers are non-perennial because they are dependent on rainfall.
Q2. Explain three common features of the Narmada and Tapi rivers. [2024]
The common features of the Narmada and Tapi rivers are as mentioned below:
- Both the rivers flow in rift valleys.
- Both are the only long rivers which flow west.
- Both the rivers make estuaries.
Narmada River
Tapi River
Q3. Describe any three important features of the Mahanadi basin. [2022]
The three important features of the Mahanadi basin are:
- Mahanadi basin covers parts of the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha and Maharashtra.
- It rises in the highlands of Chhattisgarh and flows through Odisha to form a delta in the Bay of Bengal. Its length is 860 km,
- Due to the devastating floods that the river causes every year, the Hirakund dam has been built on it.
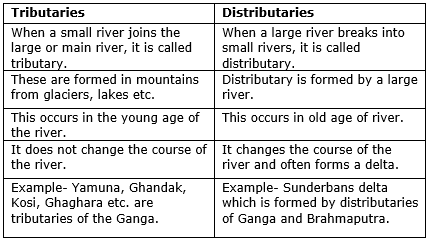
Q4. What is the difference between a Tributary and a Distributary? [2020]
Long Answers Type Questions
Q1. What are the factors for the formation of patterns within a drainage basin? Which are different types of patterns? Explain how do these patterns develop? [2025]
The main factors for the formation of drainage patterns are as given below :
- The slope of the land.
- Underlying rock structure.
- Climatic conditions of the area.
Different types of patterns are dendritic, trellis, rectangular, and radial patterns.
These patterns develop as mentioned below :
- Dendritic: The dendritic pattern develops where the river channel follows the slope of the terrain. The stream with its tributaries resembles the branches of a tree, thus the name dendritic.
- Trellis: A river joined by its tributaries, at approximately right angles, develops a trellis pattern. This pattern develops where hard and soft rocks exist parallel to each other.
- Rectangular: A rectangular drainage pattern develops on a strongly jointed rocky terrain.
- Radial: A radial pattern develops when streams flow in different directions from a central peak or dome-like structure.
A combination of several patterns may be found in the same drainage basin.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Drainage
| 1. What are the main types of drainage patterns? |  |
| 2. How does drainage influence the landscape? |  |
| 3. What factors affect drainage in a given region? |  |
| 4. Why is studying drainage important for agriculture? |  |
| 5. What are the impacts of poor drainage on the environment? |  |