Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers: Principles of Management | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: State the role of 'Gang Boss' in functional foremanship.
Ans: The Gang Boss plays a crucial role in functional foremanship by ensuring:
- The readiness of both workers and machines for production.
- Machines and tools are maintained in a state of operational readiness.
- Efficient workflow by coordinating tasks and resources.
Q2: What is meant by Management principles?
Ans: Management Principles are essential guidelines that help managers make decisions and take action. They are based on broad truths about how things work in an organisation.
 Q3: State the technique of scientific management which is the strong motivator for a worker to reach standard performance.
Q3: State the technique of scientific management which is the strong motivator for a worker to reach standard performance.
Ans: The differential piece wage system rewards workers based on their performance.
Q4: State the role of 'route clerk' in functional foremanship.
Ans: The route clerk plays a crucial role in functional foremanship by:
- Providing clear instructions on the order in which tasks should be completed.
- Specifying the production route to ensure efficiency.
- Coordinating with other personnel to streamline operations.
Q5: Factory owners or managers relied on personal judgment in attending to the problems they confronted in the course of managing their work. Which principle of Taylor is it referring to?
Ans: Science, not Rule of Thumb: The principle referred to is the concept of scientific management, which advocates for systematic methods over personal judgment.
Q6: What do you mean by Mental Revolution?
Ans: Mental revolution involves transformation in the thinking of both the management and the workers from competition to cooperation.
Q7: Name the organizational structure which helps in increasing managerial and operational efficiency.
Ans: Functional Structure is an organisational framework that enhances both managerial and operational efficiency.
Q8: A company manufacturing motorcycles and cars should have separate divisions for both, headed by separate divisional managers, separate plans and resources. Identify the principle with the help of this example.
Ans: Unity of Direction is a principle that emphasises the importance of having a clear focus within an organisation.
Q9: The directors of XYZ limited, an organization manufacturing computer, wants to double the sales and have given the responsibility to the sales manager. The sales manager has no authority either to increase sales expense or appoint new salesmen. Hence, he could not achieve this target. Identify the principle violated in this situation.
Ans: The principle violated in this situation is the Principle of Authority and Responsibility.
- The sales manager was tasked with doubling sales.
- However, he lacked the authority to increase sales expenses or hire new salesmen.
- This imbalance prevented him from achieving the target.
Q10: Who suggested the concept of functional foremanship?
Ans: Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Q11: A subordinate receives order from more than one boss’. Which principle in violated?
Ans: Unity of Command is the principle that states each employee should receive orders from only one superior. When a subordinate receives instructions from multiple bosses, this principle is violated.
- It can lead to confusion about responsibilities.
- Authority becomes unclear, which may disrupt discipline.
- Coordination between departments is essential to avoid such conflicts.
Q12: Hina & Hitesh are typists in a company having the same educational qualification. Hina is getting Rs. 3000 per month and Hitesh is getting Rs 4000 per month as salary for the same work hours. Which principle of management is violated in this case? Name the principle and explain it.
Ans: The Principle of Equity is violated in this case. This principle emphasises that:
- Employees in similar roles should be treated equally.
- Management must act fairly, kindly, and justly towards all employees.
- Disparities in pay for the same work can lead to discontent and affect morale.
Q13: What is meant by flexibility of principles of management?
Ans: Flexibility of principles of management refers to the ability of managers to adjust management principles based on their specific needs. This flexibility allows for creative solutions to business challenges.
- Managers can modify principles to suit different situations.
- They can use these principles creatively to solve problems.
- This adaptability helps in responding to changing business environments.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Explain why it is said that principles of management are 'mainly behavioural' and 'contingent' in nature. Also explain how principles of management ‘provides managers with useful insights into reality' and 'helps in thoughtful decision-making'.
Ans: The principles of management are 'mainly behavioural' and 'contingent' in nature and ‘provide managers with useful insights into reality' and 'helps in thoughtful decision-making'. This can be explained as follows:
- Mainly Behavioural: Principles of management explains the relationship between human and physical resources but they influence human behaviour the most while achieving organizational goals.
- Contingent: The applicability of principles of management depends on the given situation and that point of time according to the needs in which that situation happens.
- Provides managers with useful insights into reality: The principles of management are formed after experimentation and practice. So they provide ideas, hints or guidelines to cope up with similar business problems.
- Helps in thoughtful decision-making: Principles of management based on experiments, observations and logic provide realistic, timely objective assessments of the given situation.
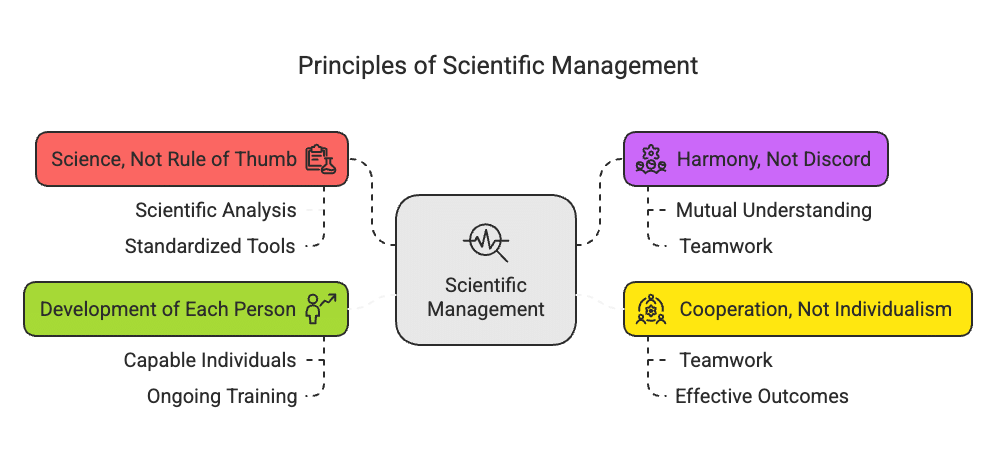
Q2: Explain the principles of scientific management.
Ans: The principles of scientific management are as follows:
- Science, Not Rule of Thumb: Tasks should be based on scientific analysis rather than guesswork. This involves creating a scientific plan and using standardised tools to enhance efficiency.
- Harmony, Not Discord: A positive relationship between management and workers is essential. Mutual understanding fosters teamwork and helps achieve organisational goals.
- Cooperation, Not Individualism: This principle emphasises that all employees should work together towards common objectives. Teamwork is crucial for effective outcomes.
- Development of Each Person: Organisations should hire capable individuals and provide ongoing training. This helps improve productivity and supports personal growth.
Q3: Explain briefly 'discipline' and 'scalar chain' as principles of general management.
Ans: The explanations are:
- Discipline: Discipline means following organizational rules and terms of employment agreement while working in the organization. To maintain discipline, an organization must have a good supervisor, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties.
- Scalar Chain: This principle states that an organization must follow a line of authority and communication from the highest to the lowest ranks. Only in emergencies, the two people at the same authority levels but working in different departments may follow the concept of gang plank and communicate directly.
Q4: Sanchit, after completing his entrepreneurship course in Sweden, returned to India and started a coffee shop, 'Aroma Coffee Can', in a famous mall in New Delhi. The specialty of the coffee shop was the special aroma of coffee and wide variety of flavours to choose from. Somehow, the business was neither profitable nor popular; Sanchit was keen to find out the reason. He appointed Sandhya, an MBA from a reputed college, as a Manager to find out the causes for the same. Sandhya took feedback from the clients and found out that though they loved the special unique aroma of coffee, but were not happy with the long wait time being taken to process the order. She analyzed and found out that there were many unnecessary obstructions in between which could be eliminated. She fixed a standard time for processing the order. She also realised that there were some flavors whose demand was not enough. So, she also decided to stop the sale of such flavors. As a result, within a short period, Sandhya was able to attract customers. Identify and explain any two techniques of scientific management used by Sandhya to solve the problem.
Ans: The techniques of scientific management used by Sandhya to solve the problems were:
- Motion Study: It is a study of movements undertaken while doing a job. It eliminates unnecessary movement to complete the task in minimum time with greater efficiency.
In this case, Sandhya identified many unnecessary obstructions in between the processes which could be eliminated.
Simplification of Work: It means simplifying work by eliminating needless varieties, sizes, dimensions etc. of products produced to utilise resources optimally and reduce labour and overhead costs.
In this case, Sandhya stopped the sale of those flavors whose demand was not enough.
Q5: Explain briefly 'Unity of Direction' and 'Order' as principles of general management.
Ans: The explanations are:
- Unity of Direction: This principle states that each department or group of activities with the same objective should have their own plans and must be headed by independent incharge. One head and one plan concept must be followed.
- Order: This principle states that there should be orderliness in the organization. It means there should be a defined place for all resources and all resources should be in the assigned place.
For Example: In a plant layout, production is supposed to be taken on Machine 1 and Machine 2 in a sequence, then both the machines should be arranged near to each other. If both the machines are far away from each other, then there can be delay in the production process, thus causing reduced productivity, and high costs.
Q6: How are management principles derived?
OR
"Management principles are evolutionary." Explain.
OR
"Derivation of management principles may be said to be a matter of science." Explain.
Ans: Management principles are derived through a combination of observation, experimentation, and practical experience by various managers. Over time, these principles have evolved based on:
- Observation: Managers observe real-life situations and behaviours, leading to the formulation of principles.
- Experimentation: Practical tests help refine these principles, ensuring they are effective in different contexts.
- Experience: The collective wisdom of managers contributes to the development of these principles, making them relevant and applicable.
Q7: ‘Discipline is double-edged tool’ Comment.
Ans: Discipline is a double-edged tool in an organisation. It serves two main purposes:
- Establishing Rules: Discipline involves creating clear rules and regulations that employees must follow.
- Encouraging Compliance: It also motivates employees to adhere to these rules.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Explain the features of the principles of Management.
Ans: The features of management are as follows:
- Universal Applicability: Principles of management have universal validity. These are applicable to all types of organizations, business as well as non-business, small as well as large enterprises and at different levels of authority. As these principles are universal, it can be applied in different managerial situations
- General guidelines: Principles of management provide broad and general guidelines for the organization to solve the problems arising in the business.
- Formed by practice and experimentation: Principles are formed after observation, experimentation and practice by different managers over a long period of time. These are evolved after continuous practicing and personal experiences of the managers in the past in real life situations.
- Flexibility: Flexibility means that the managers can modify the principles according to their need and use them creatively for solving the business problems.
- Mainly behavioural: Principles of management explains relationship between human and physical resources but they influence human behaviour the most while achieving organizational goals.
- Cause and Effect relationship: They establish a relationship between cause and effect so that they can be used in different situations.
- Contingent: The principles are relative and not absolute. Depending upon the current situation at a certain point of time, the principles are applied.
Q2: Explain the importance of management principles.
Ans: The following are the importance of principles of management:
- Provides managers with useful insights into reality: The principles of management are formed after experimentation and practice. So they provide ideas, hints or guidelines to cope up with similar business problems.
- Optimum utilisation of resources and effective administration: The cause and effect relationship helps managers to foresee the effect of their decisions and actions thus, enabling them to use resources most effectively i.e., maximum benefit with minimum cost.
- Scientific decisions: Principles of management are based on experiments, observations and logic. Hence, they provide realistic, timely and objective assessment of the given situation.
- Meeting changing requirements: The flexible nature of principles of management provides opportunities to managers to modify principles to meet the needs of the dynamic business environment.
- Fulfilling Social Responsibility: Incorporating values as a part of principles has enabled businesses to fulfil social responsibilities. Providing equal opportunities, following environment-friendly production techniques, and producing good quality products are examples of social responsibilities of business.
- Management training, education and research: The principles of management and the managerial experiences are used as case studies to train employees or for further modification or development of principles already applied.
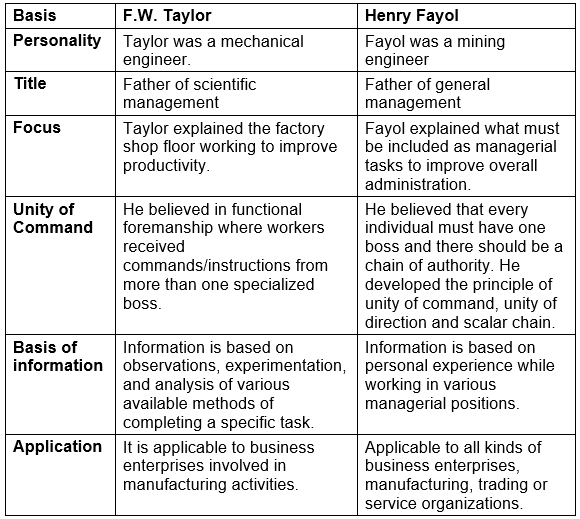
Q3: Discuss the differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol.
Ans: The differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol are:
Q4: Explain why it is said that principles of management are 'mainly behavioural' and 'contingent' in nature. Also, explain how principles of management ‘provides managers with useful insights into reality' and 'helps in thoughtful decision-making'.
Ans: The principles of management are 'mainly behavioural' and 'contingent' in nature and ‘provide managers with useful insights into reality' and 'helps in thoughtful decision-making'. This can be explained as follows:
- Mainly Behavioural: Principles of management explains the relationship between human and physical resources but they influence human behaviour the most while achieving organizational goals.
- Contingent: The applicability of principles of management depends on the given situation and that point of time according to the needs in which that situation happens.
- Provides managers with useful insights into reality: The principles of management are formed after experimentation and practice. So they provide ideas, hints or guidelines to cope up with similar business problems.
- Helps in thoughtful decision-making: Principles of management based on experiments, observations and logic provide realistic, timely objective assessments of the given situation.
Q5: Discuss the following techniques of Scientific Work Study:
(a) Time Study:
Ans: Time study is concerned with determining the standard time for performing a well defined work. In this, standard time is fixed by using the average time taken to perform the same activity several times. Time study also assists in the determination of wages, drafting incentive schemes, manpower requirements etc.
(b) Motion Study:
Ans: It is a study of movements undertaken while doing a job. It eliminates unnecessary movement to complete the task in minimum time with greater efficiency. Also, it aids in designing the best possible method to perform the repetitive work. The major objective of motion study is to eliminate the unnecessary movements in order to complete a task in a shorter time.
(c) Fatigue Study:
Ans: Fatigue study helps in determining the amount and frequency of rest intervals required to complete a task without getting physically or mentally tired. The break interval in between work helps workers to regain the stamina to work with the same energy, and hence, rest is essential to perform the work with full capacity. This study helps to find out the standard intervals of break that help a worker to regain its energy.
(d) Method Study:
Ans: The objective of method study is to find out the best way of doing the job. By determining the best method one can minimise the cost of production and maximise the quality and satisfaction of the customer.
(e) Simplification and Standardisation of work:
Ans: Simplification of work aims at eliminating the unnecessary diversity in the products. It helps in savings of cost of labor, machine and tools and increased turnover. There are shoe sizes, cloth sizes such as M, L, XL etc., this is done to reduce unnecessary variations, and expenses.
Standardization refers to setting of standards or benchmarks for every business activity, such as standardization of work, process, etc. Standardization thrives to achieve quality work, and quality products by establishing standards of performance for men and machines. For example there are standards for gold (hallmark), agricultural products (Agmark), industrial products(ISI) that assure that the product is a quality product.
|
51 videos|230 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers: Principles of Management - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key functions of management in an organization? |  |
| 2. How does effective communication impact management practices? |  |
| 3. What is the role of leadership in management? |  |
| 4. How do management theories evolve over time? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by managers in today's business environment? |  |






















