Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE > Price: The Significance of Price Elasticity of Demand
Price: The Significance of Price Elasticity of Demand | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
An Introduction to Price Elasticity of Demand
- Price elasticity of demand (PED) gauges how responsive consumer demand is to changes in price.
- Typically, an increase in price results in a decrease in demand for a product, while a decrease in price leads to an increase in demand.
- PED quantifies the extent of demand changes in response to price adjustments.
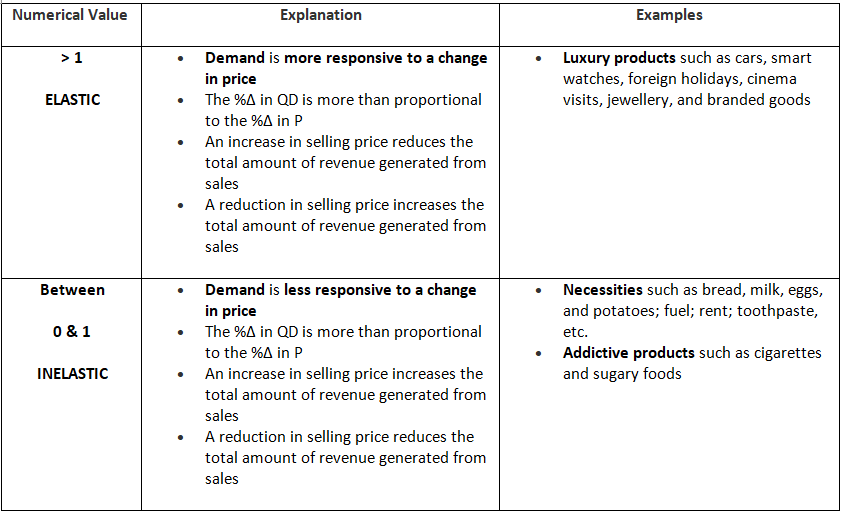
- Price elastic demand occurs when the volume of sales changes by a higher percentage than the price change (e.g., a 10% price increase causes a 20% decrease in sales).
- Price inelastic demand occurs when the volume of sales changes by a lower percentage than the price change (e.g., a 10% price increase causes a 5% decrease in sales).
Calculation of Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
- It is calculated using the following formula:
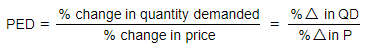
- PED is inherently negative because of the inverse correlation between price and quantity.
- When price rises, quantity demanded typically decreases, and when price falls, quantity demanded usually increases.
- The numerical value of PED signifies the degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
Interpretation of PED Values
The Significance of Price Elasticity of Demand
- By understanding the price elasticity of demand for their products, businesses can adjust their pricing strategies to optimize revenue.
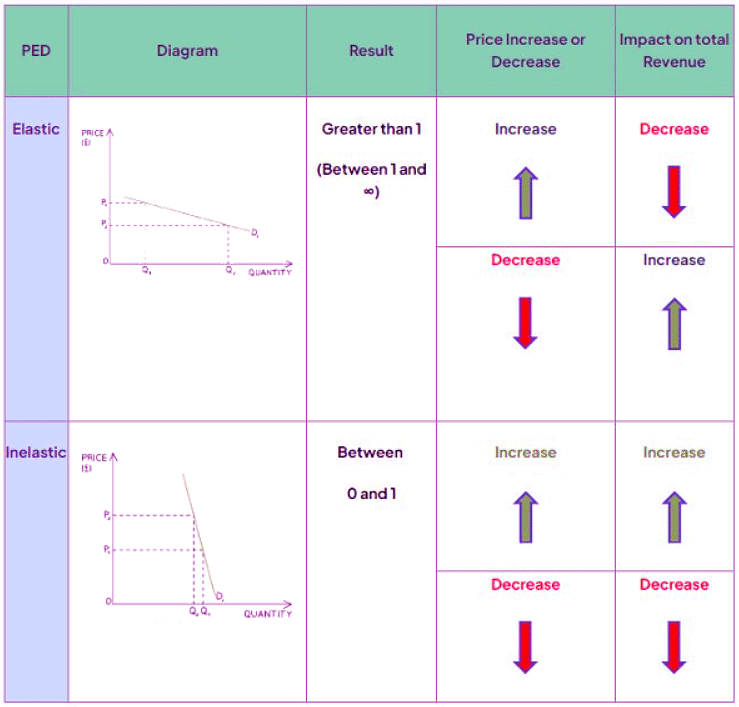
- If products have relatively inelastic demand (PED < -1), increasing the price will result in higher total revenue, while reducing the price will decrease total revenue. Price skimming strategies are most suitable for such products.
- Conversely, if products have relatively elastic demand (PED > -1), raising the price will decrease total revenue, while lowering the price will increase it. Competitive pricing strategies are more appropriate for these products.
The Relationship Between Price Elasticity of Demand and Total Revenue
Question for Price: The Significance of Price Elasticity of DemandTry yourself: Which of the following statements is true about price elasticity of demand (PED)?View Solution
Factors Influencing the Price Elasticity of Demand
PED Influencers
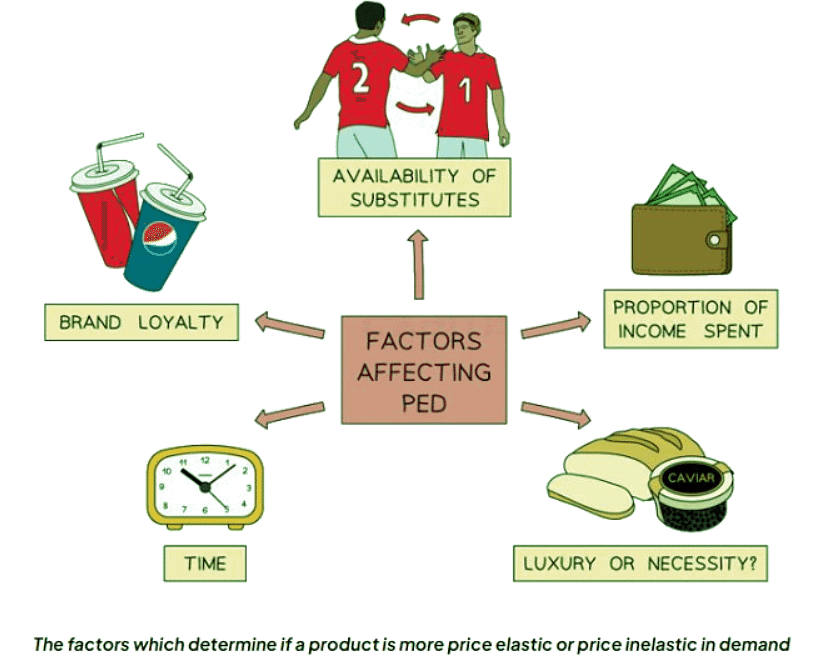
- Brand Loyalty:
- Businesses invest in advertising and marketing to shift the demand curve rightward and render demand less responsive to price changes.
- For instance, Coke consumers often exhibit brand loyalty and are unlikely to switch to Pepsi, even with similar taste and pricing.
- Availability of Substitutes:
- Goods with fewer substitutes typically have price inelastic demand.
- For example, petrol, with fewer substitutes, tends to have price inelastic demand, while chocolate bars, with more substitutes, exhibit price elasticity.
- Proportion of Income:
- Demand elasticity is influenced by the proportion of income allocated to a product.
- Products like salt, which represent a small portion of income, tend to have price inelastic demand, whereas goods like cars, which consume a larger share of income, exhibit price elasticity.
- Luxury or Necessity:
- Necessities, essential for daily life, tend to have price inelastic demand.
- Examples include bread, milk, petrol, gas, and electricity.
- Luxuries, non-essential items, typically exhibit price elasticity.
- Examples include smoked salmon, Nike Air Jordans, and foreign holidays.
- Time:
- Demand elasticity often varies with the time horizon.
- Longer time periods usually result in more price elastic demand as consumers have more opportunity to seek substitutes.
- Conversely, shorter time frames tend to lead to more price inelastic demand.
- For instance, when petrol prices rise, consumers might have little immediate choice but to pay the higher prices to maintain transportation.
- However, over time, they may explore alternatives like public transport or bicycles, making demand for petrol more price elastic in the long run.
The document Price: The Significance of Price Elasticity of Demand | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
70 videos|93 docs|26 tests
|
FAQs on Price: The Significance of Price Elasticity of Demand - Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is price elasticity of demand and why is it significant? |  |
Ans. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. It is significant because it helps businesses understand how consumers will react to price changes, allowing them to make informed decisions on pricing strategies.
| 2. What are some factors that influence the price elasticity of demand? |  |
Ans. Some factors that influence the price elasticity of demand include the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the product, the proportion of income spent on the product, and the time period in which the price change occurs.
| 3. How does price elasticity of demand affect the revenue of a business? |  |
Ans. Price elasticity of demand can impact a business's revenue. If demand is elastic (greater than 1), a decrease in price can lead to an increase in revenue. If demand is inelastic (less than 1), a decrease in price may lead to a decrease in revenue.
| 4. Why is it important for businesses to understand the price elasticity of demand? |  |
Ans. Understanding price elasticity of demand allows businesses to make informed decisions on pricing strategies. It helps them predict how consumers will react to price changes and adjust their pricing to maximize revenue.
| 5. How can businesses use price elasticity of demand to their advantage? |  |
Ans. Businesses can use price elasticity of demand to set optimal prices, determine the impact of price changes on revenue, identify opportunities for price discrimination, and understand consumer preferences for their products.
Related Searches















