Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Pythagoras Theorem
Pythagoras Theorem | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
What is Pythagoras?
- Pythagoras, an ancient Greek mathematician, lived more than 2500 years ago.
- He is renowned for Pythagoras' Theorem, a fundamental formula for right-angled triangles.
What is Pythagoras' theorem?
- The longest side in a right-angled triangle is known as the hypotenuse.
- It always stands opposite the right angle.
- If we denote the hypotenuse as 'c' and the other two sides as 'a' and 'b', Pythagoras' Theorem states: a2 + b2 = c2, where a, b, and c represent the lengths of the three sides.
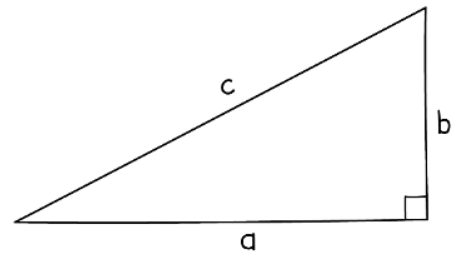
How do I use Pythagoras’ theorem?
- To find the length of the hypotenuse use
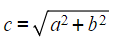
- This is just a rearrangement of the formula a2 + b2 = c2, to make c the subject
- Note that when finding the hypotenuse you add inside the square root
- To find the length of one of the other sides use

- This is a rearrangement of the formula a2 + b2 = c2, to make either a or b the subject
- Note that when finding one of the shorter sides you subtract inside the square root
Question for Pythagoras TheoremTry yourself: What is the formula for Pythagoras' Theorem?View Solution
The document Pythagoras Theorem | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
38 videos|395 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Pythagoras Theorem - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How can Pythagoras' Theorem be applied in real-life situations? |  |
Ans. Pythagoras' Theorem can be used to calculate distances, such as the length of a ladder leaning against a wall or the diagonal of a square. It is also used in fields such as architecture, engineering, and physics.
| 2. Can Pythagoras' Theorem be used for non-right-angled triangles? |  |
Ans. No, Pythagoras' Theorem can only be applied to right-angled triangles where one angle is 90 degrees. For non-right-angled triangles, trigonometry formulas such as the sine rule or cosine rule are used.
| 3. How can Pythagoras' Theorem be proven geometrically? |  |
Ans. Pythagoras' Theorem can be proven geometrically using squares constructed on each side of a right-angled triangle. The areas of these squares can be compared to show that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
| 4. What are the key components of a right-angled triangle that Pythagoras' Theorem applies to? |  |
Ans. Pythagoras' Theorem applies to right-angled triangles, which have one angle measuring 90 degrees. The sides of the triangle are known as the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) and the two legs (the other two sides).
| 5. How can Pythagoras' Theorem be used to find the length of a side in a triangle? |  |
Ans. To find the length of a side in a triangle using Pythagoras' Theorem, identify the two sides that form the right angle (the legs) and the side opposite the right angle (the hypotenuse). Square the lengths of the legs, add them together, and then take the square root to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Related Searches





















