Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:A scientist needs a 10% saline solution for an experiment. In his closet he finds a 20 ounce bottle of 25% saline solution. How many ounces of pure water should he add to the mixture to produce the correct saline solution?
Explanation
The solution he needs has only a 10% salt level. Currently we know that his solution has 20 ounces at 25% salt. We can calculate the amount of salt in the 20 ounce container by utilizing the given information. (20) * (.25) = 5 ounces of salt. Let x be the volume of pure water (in ounces) added.
Therefore, we know the total volume of our new solution will be 20 + x. We know we want our solution to have 10% salt, so our salt amount in the new solution will have to be (20+x) * (.10). Since we are not adding any salt when we add our "pure water", we know the total salt in the solution will not change. Therefore, we can write the equation. (20+x) * (.10) = 5
Solve for x and you get x = 30 ounces of pure water.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Grandpa Jack wants to help pay for college for his grandson, Little Jack. Little Jack is currently 8 years old. Grandpa Jack makes a one-time deposit into an account that earns simple interest every year. Grandpa Jack invests $10,000 now and in ten years, that will grow to $15,000. What rate of simple interest did Grandpa Jack receive?
Explanation
To calculate simple interest, the formula is
FV = PV(1 + it)
where FV stands for Future Value, PV stands for Present Value, i stands for the interest rate, and t stands for the number of periods (in this case years). So plugging in,
15,000 = 10,000(1+10i) = 10,000 + 100,000i
Solving this we get i =. 05
or 5%
ALTERNATE SOLUTION:
Another way of finding this is to calculate the amount of interest per year. Since this is simple interest, Grandpa Jack earns the same amount of interest per year. The total interest earned is 15,000 - 10,000 = 5,000. $5,000 over 10 years, equates to $500 per year. $500 divided by the original $10,000 is .05, or 5%.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:A refrigorator is on sale for 20% off the original price. A store-wide sale results in an additional reduction of 25%. What is the total discount based on the original price?
Explanation
Let x equal the original price.
First discount: x(1 − 0.20) = 0.80x (sale price).
Second discount: 0.80x(1 − 0.25) = 0.60x (final sale price)
Therefore, the final price is 60% of the original price. To calculate the discount:
1 − 0.60 = 0.40 or 40%
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Two dice are rolled. What is the probability that the sum of both dice is greater than 8?
Explanation
There are 36 possible outcomes ( 6 × 6= 36 ). 10 out of the 36 outcomes are greater than 8: (6 and 3)(6 and 4)(6 and 5)(6 and 6)(5 and 4)(5 and 5)(5 and 6)(4 and 5)(4 and 6)(3 and 6).
10/36 = 5/18
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:In a room filled with 100 people, 52 are men and 40 are blonde. There were 16 blonde men in the room. How many non-blonde women were there? Use the following diagram.

Explanation
Of the 100 people, 76 (36 + 16 + 24) were either men or blonde or both. Therefore, 24 are non-blonde and non-men (women).
100 − 76 = 24
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:A die is rolled and then a coin is tossed. What is the probability that the die shows an even number AND the coin shows a tail?
Explanation
We can calculate the two individual probabilities first.
Prob(die shows even) = 3 / 6 = 1/ 2 (2, 4, and 6 out of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6)
Prob(tail) = 1/2 (tail out of head and tail)
Then, Prob(even AND tail) is

= 1/4
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Abe is a big gambler. He is equally likely to win, lose, or break even. When he loses, his loss is $1000. When he wins, he either makes $500 or $1000 with equal probability. How much money does Abe win or lose on average?
Explanation
To find the average, multiply each expected profit or loss by its probability:

Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Vanessa purchased an mp3 player, originally priced at $290, but discounted by $27. Approximately what percent discount did Vanessa receive on the mp3 player?
Explanation
27 is a little less than 29, which is 10% of $290. Therefore, 9% is the closest approximation.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:It takes Jim 30 minutes to drive to work and 45 minutes to drive home from work. What is Jim's average driving speed in miles per hour if Jim lives 25 miles from work?
Explanation
The formula to find the average speed is avg. speed = total distance / total time .
Since the question deals with miles per hour, the time must be converted to hours from minutes:
75 min / 60 min = 1.25 hours
Plugging the numbers into the equation gives 50 miles / 1.25 hours = 40 mph .
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:The inlet pipe leading into a water tank can fill the tank in 45 minutes; the drain can empty the tank in 25 minutes.
One day while draining the tank, someone left the inlet pipe on.
To the nearest minute, how long did it take for the tank to drain completely?
Explanation
Let x be the number of minutes that it takes to drain the tank.
Think of emptying the tank as one job. Then the drain can do one job in 25 minutes, or 1 / 25 jobs per minute.
Now, think of the inlet pipe as doing a "negative" job - it is doing the opposite of emptying the tank, working against the drain. It is doing "negative one" job in 45 minutes, or −1 / 45 jobs per minute.
Now, think of this as a rate problem. In x minutes, the drain does
1 / 25x jobs
and the pipe does
−1 / 45x jobs.
Together they do 1 job, the draining of the whole tank.
Set up an equation to solve for x:

x = 56.25 , which rounds to 56 minutes.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Refer to the Venn diagram. Let universal set U be the set of all natural numbers, N.
Let A be the set of all multiples of 3; let B be the set of all perfect squares; let C be the set of all perfect cubes.
Which region of the Venn diagram contains the number 1,728?

Explanation
1,728 ÷ 3 = 576 , making 1,728 a multiple of 3, and thus, an element of A.
1,728 is not a perfect square; 412 = 1,681 < 1,728 < 1,764 = 422. Thus, 1,728 is not an element of B.
1,728 is a perfect cube: 1,728 = 123. Thus, 1,728 is an element of C.
 , which is represented by the region inside circles A and C and outside B. This is region IV.
, which is represented by the region inside circles A and C and outside B. This is region IV.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Jessica deposits $5,000 in a savings account that collects 6% simple interest. How much money will she have accumulated after 5 years?
Explanation
A = p + prt
A = accumulated sum; p = principle; r = rate; t = time in years
A = 5000 + 5000(0.06)5 = 6500
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:A cat runs at a rate of 12 miles per hour. How far does he run in 10 minutes?
Explanation
We need to convert hours into minutes and multiply this by the 10 minute time interval:

= 2 miles
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:On average, Stephanie walks 2π feet every 4 seconds. If Stephanie walks at her usual pace, how long will it take her to walk around a circular track with a radius of 200 feet, in seconds?
Explanation
The length of the track equals the circumference of the circle.
C = 2πr
C = 2π(200) = 400π
Speed = Distance / Time
Therefore, Time = Distance / Speed


= 800 seconds
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Daria has 5 plates: 2 are green, 1 is blue, 1 is red, and 1 is both green and blue. What is the probability that Daria randomly selects a plate that has blue OR green on it?
Explanation
Explanation:
The easiest way to solve this is by using the complement. Only one of the five plates is NOT blue or green. So 1/5 of the plates are NOT blue or green. Therefore1 - 1/5 = 4 / 5 of the plates are blue or green.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Two trucks travel from Alphaburg to Betaville along the same route. The speed limit for the first 30 miles is 60 miles per hour. The speed limit for the next 10 miles is 40 miles per hour, and the limit for the final 60 miles is 55 miles per hour. Truck F has a maximum speed of 70 miles per hour, but Truck S has a speed-limiting governor installed to cap its maximum speed at 50 miles per hour. Truck S departs Alphaburg 12 minutes before Truck F. If each truck travels at the lesser of the speed limit or the maximum speed of the truck, how far from Betaville is the point where Truck F catches up with Truck S?
Explanation
One of the easiest way would be to equate time..
In 12 minutes, S covers = 12/60*50=10 miles..
Let the two catch up at x miles in third stretch
1) S covers 20 miles at 50mph, then 10 and 40mph and say x at 50mph ----- Time taken 
2) F covers 30 miles at 60mph, then 10 and 40mph and x at 55mph ----- Time taken
Both should be equal.. 
So, ----- Time taken 

So they meet when they have covered 55 miles in last 60 miles. Hence 5 miles short of final destination.
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:Let a “2-placer” be a terminating decimal, between 0 and 1, for which the shortest possible representation has exactly 2 decimal places. For example, 0.09 and 0.87 are 2-placers, but 0.70 is not a 2-placer (because it can be written as 0.7, with only one decimal place). If m, n, and the product of m and n are each 2-placers, how many different values are possible for the sum m + n?
Explanation
Since 'm' and 'n' are 2-Placer , product m∗n can be rewritten as  and n/100 = N
and n/100 = N
In Order for product M*N/10000 to be 2-Placer there should be 2 '0' in product of M*N so , there should be 2*2*5*5 i.e. 100 in M*N .
Also , note that neither M nor N will be a multiple of 10 so M will be a multiple of 4 (without 5) and N will be a multiple of 25.
Possible values of 
Possible values of N = 25, 75 = 2 Values
Answer 2*20 = 40 = A
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:A set of five positive integers has an arithmetic mean of 150. A particular number among the five exceeds another by 100. The rest of the three numbers lie between these two numbers and are equal. How many different values can the largest number among the five take?
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:A box contains three pairs of blue gloves and two pairs of green gloves. Each pair consists of a left-hand glove and a right-hand glove. Each of the gloves is separate from its mate and thoroughly mixed together with the others in the box. If three gloves are randomly selected from the box, what is the probability that a matched set (i.e., a left- and right-hand glove of the same color) will be among the three gloves selected?
Explanation
To find the probability of selecting a matched set of gloves, the following calculations are performed:
-
Total Number of Ways to Select Three Gloves:
There are 10 gloves in total: 6 blue (3 left, 3 right) and 4 green (2 left, 2 right). The total number of ways to select three gloves is calculated using the combination formula:
C(10, 3) = 10! / [3! × (10 - 3)!]
= (10 × 9 × 8) / (3 × 2 × 1)
= 120
Total ways to select three gloves: 120
-
Favorable Outcomes:
We calculate the number of outcomes where at least one pair of gloves is complete. Two main cases are considered:
Case 1: Selecting one complete pair (either blue or green) and one glove of a different color:
- Ways to select a blue pair = C(3, 2) = 3
- Ways to select a green pair = C(2, 2) = 1
- Ways to select one glove from the remaining gloves = C(8, 1) = 8
- Total outcomes for this case: (3 + 1) × 8 = 32
Case 2: Selecting two gloves of one color and one glove of another color, ensuring at least one pair is complete:
- Ways to select two blue gloves and one green glove = C(3, 2) × C(2, 1) = 3 × 2 = 6
- Ways to select two green gloves and one blue glove = C(2, 2) × C(3, 1) = 1 × 3 = 3
- Total outcomes for this case: 6 + 3 = 9
Total Favorable Outcomes:
Total for both cases = 32 + 9 = 104
-
Probability Calculation:
The probability of selecting a matched set of gloves is:
P = Favorable Outcomes / Total Outcomes
P = 104 / 120
Simplify the fraction:
P = 52 / 60
-
Final Answer:
The probability of selecting a matched set is 52/60.
4o
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:There are 500 cars on a sales lot, all of which have either two doors or four doors. There are 165 two-door cars on the lot. There are 120 four-door cars that have a back-up camera. Eighteen percent of all the cars with back-up cameras have standard transmission. If 40% of all the cars with both back-up cameras and standard transmission are two-door cars, how many four-door cars have both back-up cameras and standard transmission?
Explanation
First let's find the max these can be
Say cars with camera is C..
So 18% of C have both C & S...
Now 120 of 4-door cars have C..
Say all 2-door cars have C, that is 165..
So C has to be lesser than or equal to 120+165 or 285
What is the number of 4-door cars with C&S
60% of 18% of C or 
But 0.108*C has to be an integer
There are three DECIMALS, so it has to multiplied with 3 TENS or 3*2s and 3*5s..
108 is a multiple of 4 so 2*2s are already there so C has to be multiple of (3-2)*2s and 3*5s..
That is 2*5*5*5=250.. so 250 or 250*2=500
Also C cannot be MORE than 285, so ONLY possible value is 250..
Now 0.108*C= 0.108*250 = 27
Report a problem
Question for Quantitative Practice Questions - 2
Try yourself:On a purchase of $120, a store offered a payment plan consisting of a $20 down payment and 12 monthly payments of $10 each. what percent of the purchase price, to the nearest tenth of a percent, did the customer pay in interest by using this plan?
Explanation
Actual price = 120
Payment with interest = 20+12*10 = 140
Interest = 140-120 = 20
% of interest of the purchase price = 20/120 = 1/6 = 16.67%
Report a problem











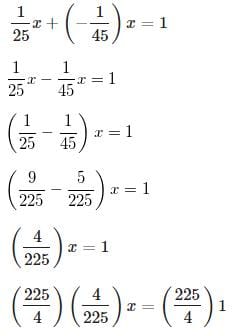
 , which is represented by the region inside circles A and C and outside B. This is region IV.
, which is represented by the region inside circles A and C and outside B. This is region IV.






 and n/100 = N
and n/100 = N
 , note that 'b' has to be an even integer in order to get a an integer value
, note that 'b' has to be an even integer in order to get a an integer value



















