Queues Representation & Operations | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
Queue is an abstract data structure, somewhat similar to Stacks. Unlike stacks, a queue is open at both its ends. One end is always used to insert data (enqueue) and the other is used to remove data (dequeue). Queue follows First-In-First-Out methodology, i.e., the data item stored first will be accessed first.
A real-world example of queue can be a single-lane one-way road, where the vehicle enters first, exits first. More real-world examples can be seen as queues at the ticket windows and bus-stops.
Queue Representation
As we now understand that in queue, we access both ends for different reasons. The following diagram given below tries to explain queue representation as data structure −
As in stacks, a queue can also be implemented using Arrays, Linked-lists, Pointers and Structures. For the sake of simplicity, we shall implement queues using one-dimensional array.
Basic Operations
Queue operations may involve initializing or defining the queue, utilizing it, and then completely erasing it from the memory. Here we shall try to understand the basic operations associated with queues:
- enqueue(): add (store) an item to the queue.
- dequeue(): remove (access) an item from the queue.
1. Enqueue Operation
Queues maintain two data pointers, front and rear. Therefore, its operations are comparatively difficult to implement than that of stacks.
The following steps should be taken to enqueue (insert) data into a queue:
- Step 1: Check if the queue is full.
- Step 2: If the queue is full, produce overflow error and exit.
- Step 3: If the queue is not full, increment rear pointer to point the next empty space.
- Step 4: Add data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing.
- Step 5: return success.
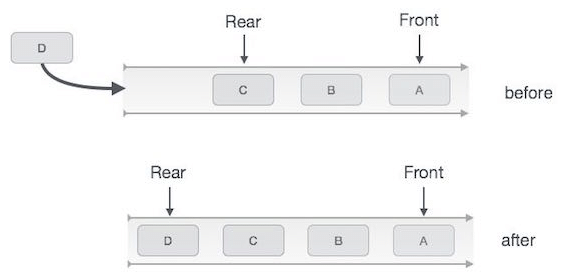 Queue Enqueue
Queue Enqueue
Sometimes, we also check to see if a queue is initialized or not, to handle any unforeseen situations.
Algorithm for enqueue operation
procedure enqueue(data)
if queue is full
return overflow
endif
rear ← rear + 1
queue[rear] ← data
return true
end procedure
Implementation of enqueue() in C programming language:
Example
int enqueue(int data)
if(isfull())
return θ;
rear = rear + 1;
queue[rear] = data;
return 1;
end procedure
2. Dequeue Operation
Accessing data from the queue is a process of two tasks − access the data where front is pointing and remove the data after access.
The following steps are taken to perform dequeue operation:
- Step 1: Check if the queue is empty.
- Step 2: If the queue is empty, produce underflow error and exit.
- Step 3: If the queue is not empty, access the data where front is pointing.
- Step 4: Increment front pointer to point to the next available data element.
- Step 5: Return success.
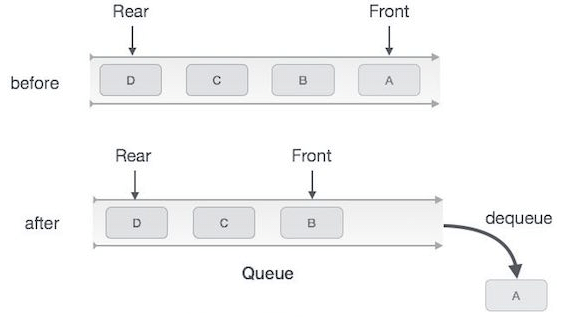 Queue DequeueAlgorithm for dequeue operation
Queue DequeueAlgorithm for dequeue operation
procedure dequeue
if queue is empty
return underflow
end if
data = queue[front]
front ← front + 1
return true
end procedure
Implementation of dequeue() in C programming language:
Example
int dequeue() {
if(isempty())
return θ;
int data = queue[front];
front = front + 1;
return data;
}
Few more functions are required to make the above-mentioned queue operation efficient. These are:
- peek(): Gets the element at the front of the queue without removing it.
- isfull(): Checks if the queue is full.
- isempty(): Checks if the queue is empty.
In queue, we always dequeue (or access) data, pointed by front pointer and while enqueing (or storing) data in the queue we take help of rear pointer.
Let's first learn about supportive functions of a queue:
1. peek()
This function helps to see the data at the front of the queue. The algorithm of peek() function is as follows:
Algorithm
begin procedure peek
return queue[front]
end procedure
Implementation of peek() function in C programming language:
Example
int peek() {
return queue[front];
}
2. isfull()
As we are using single dimension array to implement queue, we just check for the rear pointer to reach at MAXSIZE to determine that the queue is full. In case we maintain the queue in a circular linked-list, the algorithm will differ. Algorithm of isfull() function:
Algorithm
begin procedure isfull
if rear equals to MAXSIZE
return true
else
return false
endif
end procedure
Implementation of isfull() function in C programming language:
Example
bool isfull() {
if(rear == MAXSIZE - 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
3. isempty()
Algorithm of isempty() function −
begin procedure isempty
if front is less than MIN OR front is greater than rear
return true
else
return false
endif
end procedure
If the value of front is less than MIN or θ, it tells that the queue is not yet initialized, hence empty.
Here's the C programming code:
Example
bool isempty() {
if(front < θ || front > rear)
return true;
else
return false;
}
|
159 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Queues Representation & Operations - Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is the representation of a queue? |  |
| 2. What are the basic operations performed on a queue? |  |
| 3. How is a queue represented in the GATE exam? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue? |  |
| 5. Can a queue be implemented using a stack? |  |





















