Chapter 18 - Practical Geometry (Constructions) (Part - 1), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 18.10:
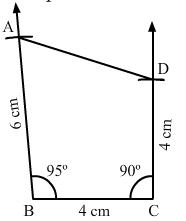
Question 1:
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, in which AB = 6 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, ∠B = 95° and ∠C = 90°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw BC = 4 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠ABC = 95° at B.
Step III : With B as the centre and radius 6 cm, cut off BA = 6 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠BCD = 90° at C.
Step V :With C as the centre and radius 4 cm, cut off BA = 4 cm.
Step VI: Join CD.The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
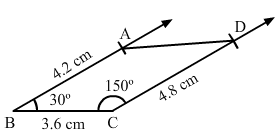
Question 2:
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, where AB = 4.2 cm, BC = 3.6 cm, CD = 4.8 cm, ∠B = 30° and ∠C = 150°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw BC = 3.6 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠ABC = 30° at B.
Step III : With B as the centre and radius 4.2 cm, cut off BA = 4.2 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠BCD = 150° at C.
Step V :With C as the centre and radius 4.8 cm, cut off CD = 4.8 cm.
Step VI: Join AD.The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
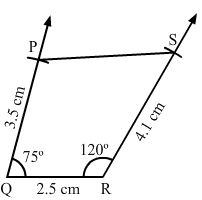
Question 3:
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, in which PQ = 3.5 cm, QR = 2.5 cm, RS = 4.1 cm, ∠Q = 75° and ∠R = 120°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw QR = 2.5 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠PQR = 75° at Q.
Step III : With Q as the centre and radius 3.5 cm, cut off QP = 3.5 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠QRS = 120° at R.
Step V :With R as the centre and radius 4.1 cm, cut off RS = 4.1 cm.
Step VI: Join PSThe quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
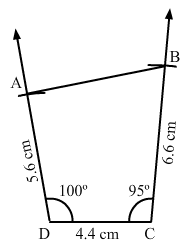
PAGE NO 18.11:
Question 4:
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD given BC = 6.6 cm, CD = 4.4 cm, AD = 5.6 cm and ∠D = 100° and ∠C = 95°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw DC = 4.4 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠ADC = 100° at D.
Step III : With D as the centre and radius 5.6 cm, cut off DA = 5.6 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠BCD = 95° at C.
Step V :With C as the centre and radius 6.6 cm, cut off CB = 6.6 cm.
Step VI: Join AB.The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
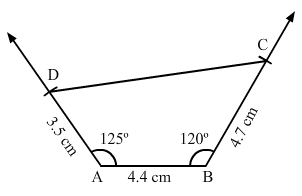
Question 5:
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, in which AD = 3.5 cm, AB = 4.4 cm, BC = 4.7 cm, ∠A = 125° and ∠B = 120°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw AB = 4.4 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠BAD = 125° at A.
Step III : With A as the centre and radius 3.5 cm, cut off AD = 3.5 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠ABC = 120° at B.
Step V :With B as the centre and radius 4.7 cm, cut off BC = 4.7 cm.
Step VI: Join CD.The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
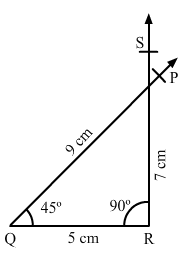
Question 6:
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, in which ∠Q = 45°, ∠R = 90°, QR = 5 cm, PQ = 9 cm and Rs = 7 cm.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw QR = 5 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠PQR = 45° at Q.
Step III : With Q as the centre and radius 9 cm, cut off QP = 9 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠QRS = 90° at R.
Step V :With R as the centre and radius 7 cm, cut off RS = 7 cm.
Since, the line segment PQ and RS intersect each other, the quadrilateral cannot be constructed.
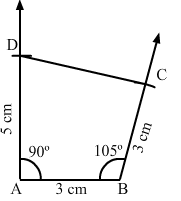
Question 7:
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, in which AB = BC = 3 cm, AD = 5 cm, ∠A = 90° and ∠B = 105°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:Step I: Draw AB = 3 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠DAB = 90° at A.
Step III : With A as the centre and radius 5 cm, cut off AD = 5 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠ABC = 105° at B.
Step V: With B as the centre and radius 3 cm, cut off BC = 3 cm.
Step VI: Join CD.The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
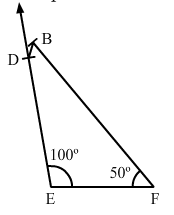
Question 8:
Construct a quadrilateral BDEF, where DE = 4.5 cm, EF = 3.5 cm, FB = 6.5 cm, ∠F = 50° and ∠E = 100°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw EF = 3.5 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠DEF = 100° at E.
Step III : With E as the centre and radius 4.5 cm, cut off DE = 4.5 cm.
Step IV: Construct ∠EFB = 50° at F.
Step V :With F as the centre and radius 6.5 cm, cut off FB = 6.5 cm.
Step VI: Join BD. The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
FAQs on Chapter 18 - Practical Geometry (Constructions) (Part - 1), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What are practical geometrical constructions? |  |
| 2. What are the basic tools required for practical geometrical constructions? |  |
| 3. How are angles constructed using practical geometry? |  |
| 4. How can we construct a perpendicular bisector using practical geometry? |  |
| 5. Can practical geometry be used to construct similar triangles? |  |





















