Chapter 27 - Introduction to Graphs (Part - 2), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 27.5:
Question 1:
Plot the points (5, 0), (5, 1), (5, 8). Do they lie on a line? What is your observation?
Ans:
Take a point O on the graph paper and draw horizontal and vertical lines OX and OY respectively.
Then, let on the x-axis and y axis 1 cm represents 1 unit.
In order to plot point (5, 0), we start from the origin O and move 5 cm along OX. The point we arrive at is point (5,0).
To plot point (5, 1), we move 5 cm along OX and 1 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is point (5,1).
To plot point (5,8), we move 5 cm along OX and 8 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is point (5,8).
From the graph below, it can be seen that the points lie on a line parallel to y-axis. This is because they have the same x-coordinate.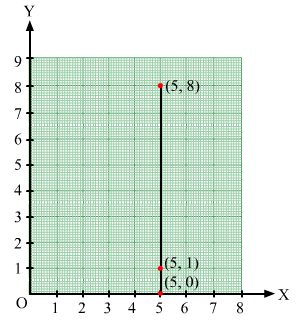
Question 2:
Plot the points (2, 8), (7, 8) and (12, 8). Join these points in pairs. Do they lie on a line? What do you observe?
Ans:
Take a point O on the graph paper and draw the horizontal and vertical lines OX and OY respectively.
Then, let on the x-axis and y axis 1 cm represents 1 unit.
In order to plot point (2, 8), we start from the origin O and move 8 cm along OX. The point we arrive at is (2, 8).
To plot point (7, 8), we move 7 cm along OX and 8 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is (7, 8).
To plot point (12, 8), we move 12 cm along OX and 8 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is (12,8).
From the graph below, it can be seen that the points lie on a line parallel to x-axis because they have the same y-coordinate.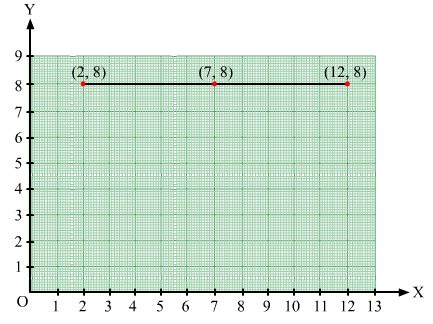
Question 3:
Locate the points:
(i) (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4)
(ii) (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4)
(iii) (1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 3), (4, 3)
(iv) (1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 4).
Ans:
(i) In order to plot these points, the given steps are to be followed:
Take a point O on a graph paper and draw horizontal and vertical lines OX and OY respectively.
Then, let on x-axis and y axis 1 cm represents 1 unit.
In order to plot point (1, 1), we start from the origin O and move 2 cm along OX and 1 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is (1, 1).
To plot point (1, 2), we move 1 cm along OX and 2 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is (1, 2).
To plot point (1, 3), we move 1 cm along OX and 3 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is (1, 3).
To plot point (1, 4), we move 1 cm along OX and 4 cm along OY. The point we arrive at is (1, 4).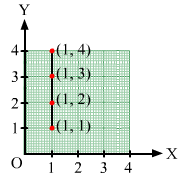
(ii) Follow the steps mentioned in point (i).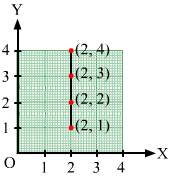
(iii) Follow the steps mentioned in point (i).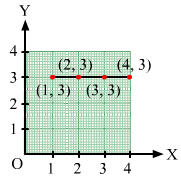
(iv) Follow the steps mentioned in point (i).
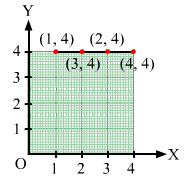
PAGE NO 27.6:
Question 4:
Find the coordinates of points A, B, C, D in Fig. 27.7.
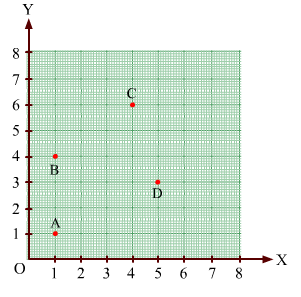
Ans:
Draw perpendiculars AP, BP, CQ and DR from A, B, C and D on the x-axis. Also, draw perpendiculars AW, BX, CY and DZ on the y-axis.
From the figure, we have:
AW = 1 unit and AP= 1 unit
So, the coordinates of vertex A are (1, 1).
Similarly, BX=1 unit and BP= 4 units
So, the coordinates of vertex B are (1, 4).
CY = 4 units and CQ= 6 units
So, the coordinates of vertex B are (4, 6).
DZ = 5 units and DR= 3 units
So, the coordinates of vertex B are (5, 3).
Question 5:
Find the coordinates of points P, Q, R and S in Fig. 27.8.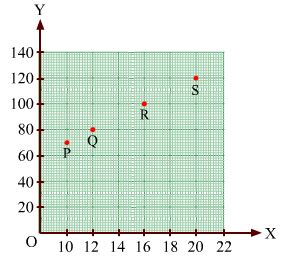
Ans:
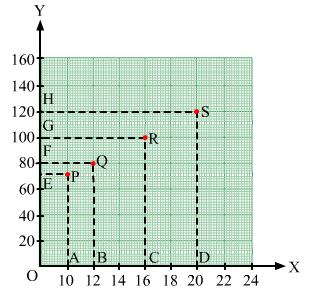
Draw perpendiculars PA, QB, RC and SD from vertices P, Q, R and S on the x-axis. Also ,draw perpendiculars
PE, QF, RG and SH on the y-axis from these points.
PE = 10 units and PA = 70 units
Therefore, the coordinates of vertex P are (10, 70).
QF = 12 units and QB = 80 units
Therefore, the coordinates of vertex Q are (12, 80).
RG = 16 units and RC = 100 units
Therefore, the coordinates of vertex R are (16, 100).
SH = 20 units and SD = 120 units
Therefore, the coordinates of vertex S are (20, 120).
Question 6:
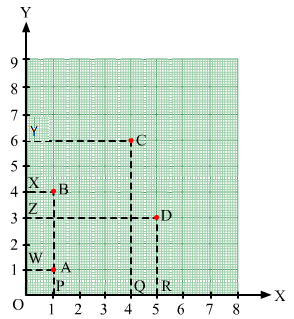
Write the coordinates of each of the vertices of each polygon in Fig. 27.9.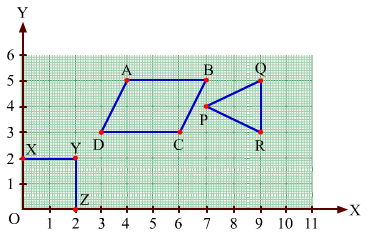
Ans:
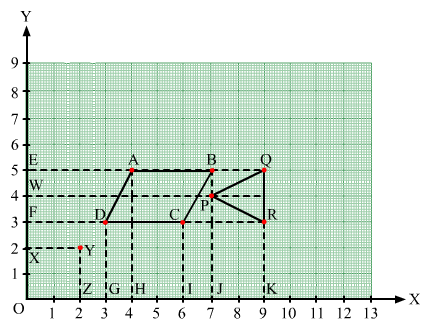
From the figure, we have:
In polygon OXYZ:
O lies on the origin and the coordinates of the origin are (0, 0). So, the coordinates of O are (0, 0).
X lies on the y-axis. So, the x-coordinate is 0. Hence, the coordinate of X is (0, 2).
Also, YX is equal to 2 units and YZ is equal to 2 units. So, the coordinates of vertex Y are (2, 2).
Z lies on the x-axis. So, the y-coordinate is 0. Hence, the coordinates of Z are (2, 0).
In polygon ABCD:
Draw perpendiculars DG, AH, CI and BJ from A, B, C and D on the x-axis.
Also, draw perpendiculars DF, AE, CF and BE from A, B, C and D on the y-axis.
Now, from the figure:
DF = 3 units and DG = 3 units
Therefore, the coordinates of D are (3, 3).
AE = 4 units and AH = 5 units
Therefore, the coordinates of A are (4, 5).
CF = 6 units and CI = 3 units
Therefore, the coordinates of C are (6, 3).
BE = 7 units and BJ = 5 units
Therefore, the coordinates of B are (7, 5).
In polygon PQR:
Draw perpendiculars PJ, QK and RK from P, Q and R on the x-axis.
Also, draw perpendiculars PW, QE and RF from P, Q and R on the y-axis.
Now, from the figure:
PW = 7 units and PJ = 4 units
Therefore, the coordinates of P are (7, 4).
QE = 9 units and QK = 5 units
Therefore, the coordinates of Q are (9, 5).
RF = 9 units and RK = 3 units
Therefore, the coordinates of R are (9, 3).
PAGE NO 27.7:
Question 7:
Decide which of the following statements is true and which is false. Give reasons for your answer.
(i) A point whose x-coordinate is zero, will lie on the y-axis.
(ii) A point whose y-coordinate is zero, will lie on x-axis.
(iii) The coordinates of the origin are (0, 0).
(iv) Points whose x and y coordinates are equal, lie on a line passing through the origin.
Ans:
(i) The examples of points having x-coordinate as zero are (0,3), (0,6), (0,9). This can be represented in the following manner: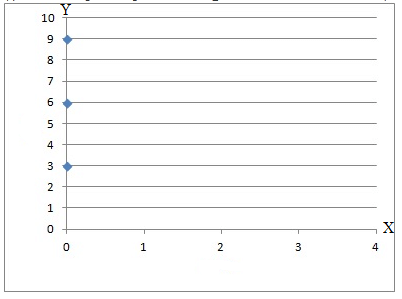
From the figure, it can be seen that these points lie on the y-axis. Hence, the statement is true.
(ii) The examples of points having y-coordinate as zero are (3,0), (6,0), (9,0). This can be represented in the following manner: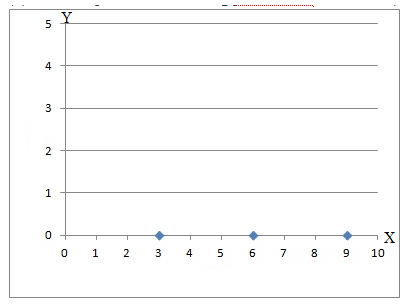
From figure above, it can be seen that these points lie on the x-axis. Hence, the statement is true.
(iii) The origin divides each of these axes into a positive and a negative semi-axis. The coordinates of the origin are always are zero, i.e. (0,0). Thus, the statement is true.
(iv) The examples of points having equal x and y coordinates are (0,0), (1,1), (2,2), etc. If these points are joined, they will lie on a line passing through the coordinates (0,0). Thus, the statement is true.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|

















