Ex-19.6, Geometrical Constructions, Class 6, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics PDF Download
Q.1 Construct an angle of 600 with the help of compasses and bisect it by paper folding.
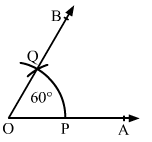
Sol.1 : Draw a ray OA.
With convenient radius and centre O, draw an arc cutting the ray OA at P.
With the same radius and centre at P, draw another arc cutting the previous arc at Q.
Draw OQ and extend it to B.
∠AOB is the required angle of 600.
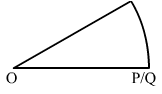
We cut the part of paper as sector OPQ.
Now, fold the part of paper such that line segments OP and OQ get coincided.
Angle made at point O is the required angle, which is half of angle ∠AOB.
Q.2 Construct the following angles with the help of ruler and compasses only.
(i) 300
(ii) 900
(iii) 450
(iv) 1350
(v) 1500
(vi) 1050
Sol.2 :
(i) 300
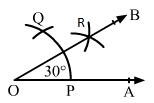
Draw a ray OA.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc, which cuts OA at P.
With the same radius and centre at P, draw an arc cutting the previous arc at P.
Taking P and Q as centres and radius more than half of PQ, draw two arcs, which cuts each other at R.
Draw OR and extend it to B.
∠AOB is the required angle of 300.
(ii) 900
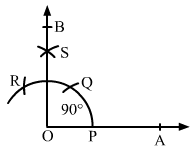
Draw a ray OA.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc cutting the ray OA at P.
With the same radius and centre at P, draw another arc, which cuts the first arc at Q.
With the same radius and centre at Q, draw another arc, which cuts the first arc at R.
With Q and R as centres and radius more than half of QR, which cuts each other at S.
Draw OS and extend it to B from the ray OB.
∠AOB is required angle of 900.
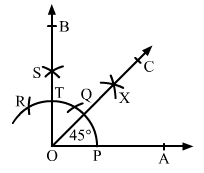
(iii) 450
To construct an angle of 450, construct an angle of 900 and bisect it.
Construct the angle ∠AOB = 900, where rays OA and OB intersect the arc at points P and T as shown in figure.
With P and T as centres and radius more than half of PT, draw two arcs, which cut each other at X
Draw OX and extend it to C to form the ray OC.
∠AOC is the required angle of 450.
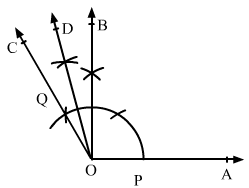
(iv) 1350
Draw the line AB and take the point O at the middle of AB.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc, which cuts AB at P and Q, respectively.
Draw an angle of 900 on the ray OB as ∠BOC = 900, where ray OC cuts the arc at R.
With Q and R as centres and radius more than half of QR, draw two arcs, which cuts each other at S.
Draw OS and extend it to form the ray OD.
∠BOD is required angle of 1350.
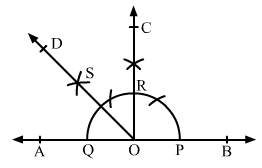
(v) 1500
Draw a line AB and take point O at the middle of AB.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc, which cuts the line AB at P and Q.
With the same radius and centre at Q, draw an arc, which cuts the first arc at R.
With the same radius and centre at R, draw an arc, which cuts the first arc at S.
With the centres P and S and radius more than half of PS, draw two arcs, which cut each other at T.
Draw OT and extend it to C to form the ray OC.
∠BOC is required angle of 1500.
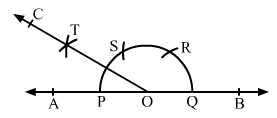
(vi) 1050
Draw a ray OA and make an angle ∠AOB = 900 and ∠AOC = 1200
Now bisect ∠BOC and get the ray OD.
∠AOD is the required angle of 1050
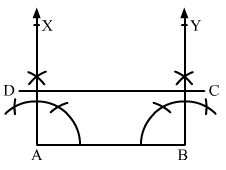
Q.3 Construct a rectangle whose adjacent sides are 8 cm and 3 cm.
Sol.3 : Draw a line segment AB of length 8 cm.
Construct ∠BAX = 900 at point A and ∠ABY = 900 at point B.
Using a compass and ruler, mark a point D on the ray AX such that AD = 3 cm.
Similarly mark the point C on the ray Y such that BC = 3 cm.
Draw the line segment CD.
ABCD is the required rectangle.
FAQs on Ex-19.6, Geometrical Constructions, Class 6, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics
| 1. What are geometrical constructions in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of geometrical constructions in mathematics? |  |
| 3. How do you construct an equilateral triangle using geometrical constructions? |  |
| 4. Can you construct a square using geometrical constructions? |  |
| 5. How do you construct a perpendicular bisector using geometrical constructions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|

















