Exercise 3.2 - Squares And Square Roots RD Sharma Solutions | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Q.1. The following numbers are not perfect squares. Give reason.
(i) 1547
(ii) 45743
(iii) 8948
(iv) 333333
Ans: A number ending with 2, 3, 7 or 8 cannot be a perfect square.
(i) Its last digit is 7. Hence, 1547 cannot be a perfect square.
(ii) Its last digit is 3. Hence, 45743 cannot be a perfect square.
(iii) Its last digit is 8. Hence, 8948 cannot be a perfect square.
(iv) Its last digit is 3. Hence, 333333 cannot be a perfect square.
Q.2. Show that the following numbers are not perfect squares:
(i) 9327
(ii) 4058
(iii) 22453
(iv) 743522
Ans: A number ending with 2, 3, 7 or 8 cannot be a perfect square.
(i) Its last digit is 7. Hence, 9327 is not a perfect square.
(ii) Its last digit is 8. Hence, 4058 is not a perfect square.
(iii) Its last digit is 3. Hence, 22453 is not a perfect square.
(iv) Its last digit is 2. Hence, 743522 is not a perfect square.
Q.3. The square of which of the following numbers would be an odd number?
(i) 731
(ii) 3456
(iii) 5559
(iv) 42008
Ans: The square of an odd number is always odd.
(i) 731 is an odd number. Hence, its square will be an odd number.
(ii) 3456 is an even number. Hence, its square will not be an odd number.
(iii) 5559 is an odd number. Hence, its square will not be an odd number.
(iv) 42008 is an even number. Hence, its square will not be an odd number.
Hence, only the squares of 731 and 5559 will be odd numbers.
Q.4. What will be the units digit of the squares of the following numbers?
(i) 52
(ii) 977
(iii) 4583
(iv) 78367
(v) 52698
(vi) 99880
(vii) 12796
(viii) 55555
(ix) 53924
Ans: The units digit is affected only by the last digit of the number. Hence, for each question, we only need to examine the square of its last digit.
(i) Its last digit is 2. Hence, the units digit is 22, which is equal to 4.
(ii) Its last digit is 7. Hence, the units digit is the last digit of 49 (49 = 72), which is 9.
(iii) Its last digit is 3. Hence, the units digit is 32, which is equal to 9.
(iv) Its last digit is 7. Hence, the units digit is the last digit of 49 (49 = 72), which is 9.
(v) Its last digit is 8. Hence, the units digit is the last digit of 64 (64 = 82), which is 4.
(vi) Its last digit is 0. Hence, the units digit is 02, which is equal to 0.
(vii) Its last digit is 6. Hence, the units digit is the last digit of 36 (36 = 62), which is 6.
(viii) Its last digit is 5. Hence, the units digit is the last digit of 25 (25 = 52), which is 5.
(ix) Its last digit is 4. Hence, the units digit is the last digit of 16 (16 = 42), which is 6.
Q.5. Observe the following pattern
1 + 3 = 22
1 + 3 + 5 = 32
1 + 3 × 5 + 7 = 42
and write the value of 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + ... upto n terms.
Ans: From the pattern, we can say that the sum of the first n positive odd numbers is equal to the square of the n-th positive number. Putting that into formula:
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + ... n = n2, where the left hand side consists of n terms.
Q.6. Observe the following pattern
22 − 12 = 2 + 1
32 − 22 = 3 + 2
42 − 32 = 4 + 3
52 − 42 = 5 + 4
and find the value of
(i) 1002 − 992
(ii) 1112 − 1092
(iii) 992 − 962
Ans: From the pattern, we can say that the difference between the squares of two consecutive numbers is the sum of the numbers itself.
In a formula:
(n+1)2 − (n)2 = (n+1) + n
Using this formula, we get:
(i) 1002 − 992 = (99 + 1) + 99
= 199
(ii) 1112 − 1092 = 1112 − 1102 + 1102 − 1092
= (111 + 110) + (110 + 109)
= 440
(iii) 992 − 962 = 992 − 982 + 982 − 972 + 972 − 962
= 99 + 98 + 98 + 97 + 97 + 96
= 585
Q.7. Which of the following triplets are pythagorean?
(i) (8, 15, 17)
(ii) (18, 80, 82)
(iii) (14, 48, 51)
(iv) (10, 24, 26)
(v) (16, 63, 65)
(vi) (12, 35, 38)
Ans: Only (i), (ii), (iv) and (v) are Pythagorean triplets.
A triplet (a, b, c) is called Pythagorean if the sum of the squares of the two smallest numbers is equal to the square of the biggest number.
(i) The two smallest numbers are 8 and 15. The sum of their squares is:
82 + 152 = 289 = 172
Hence, (8, 15, 17) is a Pythagorean triplet.
(ii) The two smallest numbers are 18 and 80. The sum of their squares is:
182 + 802 = 6724 = 822
Hence, (18, 80, 82) is a Pythagorean triplet.
(iii) The two smallest numbers are 14 and 48. The sum of their squares is:
142 + 482 = 2500, which is not equal to 512 = 2601
Hence, (14, 48, 51) is not a Pythagorean triplet.
(iv) The two smallest numbers are 10 and 24. The sum of their squares is:
102 + 242 = 676 = 262
Hence, (10, 24, 26) is a Pythagorean triplet.
(v) The two smallest numbers are 16 and 63. The sum of their squares is:
162 + 632 = 4225 = 652
Hence, (16, 63, 65) is a Pythagorean triplet.
(vi) The two smallest numbers are 12 and 35. The sum of their squares is:
122 + 352 = 1369, which is not equal to 382 = 1444
Hence, (12, 35, 38) is not a Pythagorean triplet.
Q.8. Observe the following pattern
(1 × 2) + (2 × 3) =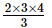
(1 × 2) + (2 × 3) + (3 × 4) =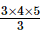
(1 × 2) + (2 × 3) + (3 × 4) + (4 × 5) =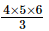
and find the value of
(1 × 2) + (2 × 3) + (3 × 4) + (4 × 5) + (5 × 6)
Ans: The RHS of the three equalities is a fraction whose numerator is the multiplication of three consecutive numbers and whose denominator is 3.
If the biggest number (factor) on the LHS is 3, the multiplication of the three numbers on the RHS begins with 2.
If the biggest number (factor) on the LHS is 4, the multiplication of the three numbers on the RHS begins with 3.
If the biggest number (factor) on the LHS is 5, the multiplication of the three numbers on the RHS begins with 4.
Using this pattern, (1 x 2) + (2 x 3) + (3 x 4) + (4 x 5) + (5 x 6) has 6 as the biggest number. Hence, the multiplication of the three numbers on the RHS will begin with 5. Finally, we have:
1 × 2 + 2 × 3 + 3 × 4 + 4 × 5 + 5 × 6 =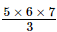 = 70
= 70
Q.9. Observe the following pattern
1 = 1/2{1 × (1 + 1)}
1 + 2 = 1/2{2 × (2 + 1)}
1 + 2 + 3 = 1/2{3 × (3 + 1)}
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 1/2{4 × (4 + 1)}
and find the values of each of the following:
(i) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + ... + 50
(ii) 31 + 32 + ... + 50
Ans: Observing the three numbers for right hand side of the equalities:
The first equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 1, has 1, 1 and 1 as the three numbers.
The second equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 2, has 2, 2 and 1 as the three numbers.
The third equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 3, has 3, 3 and 1 as the three numbers.
The fourth equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 4, has 4, 4 and 1 as the three numbers.
Hence, if the biggest number on the LHS is n, the three numbers on the RHS will be n, n and 1.
Using this property, we can calculate the sums for (i) and (ii) as follows:
(i) 1 + 2 + 3 +........ + 50 = 12 × 50 × (50 + 1) = 1275
(ii) The sum can be expressed as the difference of the two sums as follows:
31 + 32 + .....+ 50 = (1 + 2 + 3 + ......+ 50) − ( 1 + 2 + 3 + ......+30)
The result of the first bracket is exactly the same as in part (i).
1 + 2 + ....+ 50 = 1275
Then, the second bracket:
1+2+......+30 = 12(30×(30+1)) = 465
Finally, we have:
31 + 32 + .... + 50 = 1275 − 465 = 810
Q.10. Observe the following pattern
12 = 1/6[1 × (1 + 1) × (2 × 1 + 1)]
12 + 22 = 1/6[2 × (2 + 1)×(2 × 2 + 1)]
12 + 22 + 32 = 1/6[3 × (3 + 1) × (2 × 3 + 1)]
12 + 22 + 32 + 42 = 1/6[4 × (4 + 1) × (2 × 4 + 1)]
and find the values of each of the following:
(i) 12 + 22 + 32 + 42 + ... + 102
(ii) 52 + 62 + 72 + 82 + 92 + 102 + 112 + 122
Ans: Observing the six numbers on the RHS of the equalities:
The first equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 1, has 1, 1, 1, 2, 1 and 1 as the six numbers.
The second equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 2, has 2, 2, 1, 2, 2 and 1 as the six numbers.
The third equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 3, has 3, 3, 1, 2, 3 and 1 as the six numbers.
The fourth equality, whose biggest number on the LHS is 4, has numbers 4, 4, 1, 2, 4 and 1 as the six numbers.
Note that the fourth number on the RHS is always 2 and the sixth number is always 1. The remaining numbers are equal to the biggest number on the LHS.
Hence, if the biggest number on the LHS is n, the six numbers on the RHS would be n, n, 1, 2, n and 1.
Using this property, we can calculate the sums for (i) and (ii) as follows:
(i) 12 + 22 + .......+ 102 = 1/6×[10×(10+1)×(2×10+1)]
= 16 × [10 × 11 × 12]
= 385.
(ii) The sum can be expressed as the difference of the two sums as follows:
52 + 62 +.......+ 122 = ( 12 + 22 +......+122) − ( 12 + 22 +......+42)
The sum of the first bracket on the RHS:
12 + 22 +.....+122 = 1/6[12×(12+1)×(2×12+1)]
= 650
The second bracket is:
12 + 22 + ......+ 42 = 1/6 × [4 × (4 + 1) × (2 × 4 + 1)] = 16 × 4 × 5 × 9 = 30
Finally, the wanted sum is:
52 + 62 + ...... + 122 = (12 + 22 +..... + 122) − ( 12 + 22 +..... + 122)
= 650 − 30
= 620
Q.11. Which of the following numbers are squares of even numbers?
121, 225, 256, 324, 1296, 6561, 5476, 4489, 373758
Ans: The numbers whose last digit is odd can never be the square of even numbers. So, we have to leave out 121, 225, 6561 and 4489, leaving only 256, 324, 1296, 5476 and 373758.
For each number, use prime factorisation method and make pairs of equal factors.
(i) 256 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2
= (2 x 2) x (2 x 2) x (2 x 2) x (2 x 2)
There are no factors that are not paired. Hence, 256 is a perfect square. The square of an even number is always even. Hence, 256 is the square of an even number.
(ii) 324 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 x 3
= (2 x 2) x (3 x 3) x (3 x 3)
There are no factors that are not paired. Hence, 324 is a perfect square. The square of an even number is always even. Hence, 324 is the square of an even number.
(iii)1296 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 x 3
= (2 x 2) x (2 x 2) x (3 x 3) x (3 x 3)
There are no factors that are not paired. Hence, 1296 is a perfect square. The square of an even number is always even. Hence, 1296 is the square of an even number.
(iv) 5476 = 2 x 2 x 37 x 37
= (2 x 2) x (37 x 37)
There are no factors that are not paired. Hence, 5476 is a perfect square. The square of an even number is always even. Hence, 5476 is the square of an even number.
(v) 373758 = 2 x 3 x 7 x 11 x 809
Here, each factor appears only once, so grouping them into pairs of equal factors is not possible. It means that 373758 is not the square of an even number.
Hence, the numbers that are the squares of even numbers are 256, 324, 1296 and 5476.
Q.12. By just examining the units digits, can you tell which of the following cannot be whole squares?
(i) 1026
(ii) 1028
(iii) 1024
(iv) 1022
(v) 1023
(vi) 1027
Ans: If the units digit of a number is 2, 3, 7 or 8, the number cannot be a whole square.
(i) 1026 has 6 as the units digit, so it is possibly a perfect square.
(ii) 1028 has 8 as the units digit, so it cannot be a perfect square.
(iii) 1024 has 4 as the units digit, so it is possibly a perfect square.
(iv) 1022 has 2 as the units digit, so it cannot be a perfect square.
(v) 1023 has 3 as the units digit, so it cannot be a perfect square.
(vi) 1027 has 7 as the unit digit, so it cannot be a perfect square.
Hence, by examining the units digits, we can be certain that 1028, 1022, 1023 and 1027 cannot be whole squares.
Q.13. Write five numbers for which you cannot decide whether they are squares.
Ans: A number whose unit digit is 2, 3, 7 or 8 cannot be a perfect square.
On the other hand, a number whose unit digit is 1, 4, 5, 6, 9 or 0 might be a perfect square (although we will have to verify whether it is a perfect square or not).
Applying the above two conditions, we cannot quickly decide whether the following numbers are squares of any numbers:
1111, 1444, 1555, 1666, 1999
Q.14. Write five numbers which you cannot decide whether they are square just by looking at the unit's digit.
Ans: A number whose unit digit is 2, 3, 7 or 8 cannot be a perfect square.
On the other hand, a number whose unit digit is 1, 4, 5, 6, 9 or 0 might be a perfect square although we have to verify that.
Applying these two conditions, we cannot determine whether the following numbers are squares just by looking at their unit digits:
1111, 1001, 1555, 1666 and 1999
Q.15. Write true (T) or false (F) for the following statements.
(i) The number of digits in a square number is even.
(ii) The square of a prime number is prime.
(iii) The sum of two square numbers is a square number.
(iv) The difference of two square numbers is a square number.
(v) The product of two square numbers is a square number.
(vi) No square number is negative.
(vii) There is no square number between 50 and 60.
(viii) There are fourteen square number upto 200.
Ans:
(i) False
Example: 100 is the square of a number but its number of digits is three, which is not an even number.
(ii) False
If p is a prime number, its square is p2, which has at least three factors: 1, p and p2. Since it has more than two factors, it is not a prime number.
(iii) False
1 is the square of a number (1 = 12). But 1 + 1 = 2, which is not the square of any number.
(iv) False
4 and 1 are squares (4 = 22, 1 = 12). But 4 − 1 = 3, which is not the square of any number.
(v) True
If a2 and b2 are two squares, their product is a2 x b2 = (a x b)2, which is a square.
(vi) True
The square of a negative number will be positive because negative times negative is positive.
(vii) True
72 = 49 and 82 = 64. 7 and 8 are consecutive numbers and hence there are no square numbers between 50 and 60.
(viii) True
142 is equal to 196, which is below 200. There are 14 square numbers below 200.
|
79 videos|408 docs|31 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|

















