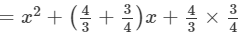RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Math Chapter 6 - Algebraic Expressions and Identities (Part-5 ) | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
Question 1:Write the following squares of binomials as trinomials:
(i) (x + 2)2
(ii) (8a + 3b)2
(iii) (2m + 1)2
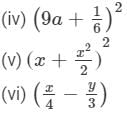
(x) (a2b − bc2)2
(xii) (x2 − ay)2
Answer 1: We will use the identities (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2 and (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2 to convert the squares of binomials as trinomials.
(i) (x+2)2=x2+2×x×2+b2=x2+4x+b2
(ii) (8a+3b)2=(8a)2+2(8a)(3b)+(6b)2=64a2+48ab+36b2(iii) (2m+1)2=(2m)2+2(2m)(1)+12=4m2+4m+1
(iv) (9a+1/6)2=(9a)2+2(9a)(1/6)+(1/6)2=81a2+3a+1/36
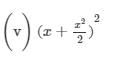
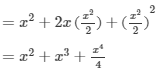
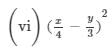
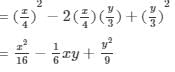
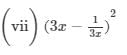
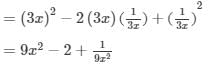
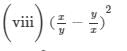
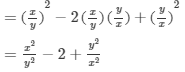
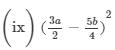
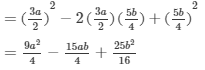
(x) (a2b−bc2)2=(a2b)2−2(a2b)(bc2)+(bc2)2=a4b2−2a2b2c2+b2c4 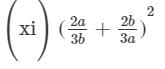
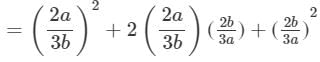
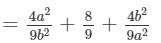
(xii) (x2−ay)2=(x2)2−2x2(ay)+(ay)2=x4−2x2ay+a2y2
Question 2: Find the product of the following binomials:
(i) (2x + y)(2x + y)
(ii) (a + 2b)(a − 2b)
(iii) (a2 + bc)(a2 − bc)
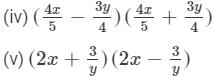
(vi) (2a3 + b3)(2a3 − b3)
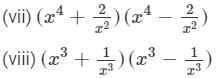
Answer 2: (i) We will use the identity (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2 in the given expression to find the product.
(2x+y)(2x+y)=(2x+y)2=(2x)2+2(2x)(y)+y2=4x2+4xy+y2(ii) We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
(a+2b)(a−2b)=a2−(2b)2=a2−4b2 (iii) We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
(a2+bc)(a2−bc)=(a2)2−(bc)2=a4−b2c2 (iv)We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
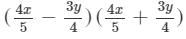
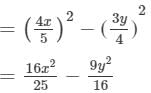
(v) We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
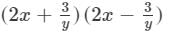
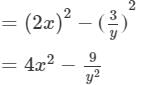
(vi) We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
(2a3+b3)(2a3−b3)=(2a3)2−(b3)2=4a6−b6 (vii) We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
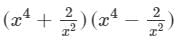
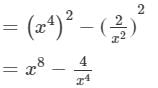
(viii) We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 in the given expression to find the product.
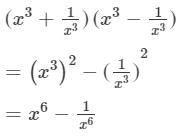
Question 3: Using the formula for squaring a binomial, evaluate the following:
(i) (102)2
(ii) (99)2
(iii) (1001)2
(iv) (999)2
(v) (703)2
Answer 3: (i) Here, we will use the identity (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2
(102)2=(100+2)2=(100)2+2×100×2+22=10000+400+4=10404 (ii) Here, we will use the identity (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2
(99)2=(100−1)2=(100)2−2×100×1+12=10000−200+1=9801 (iii) Here, we will use the identity (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2
(1001)2=(1000+1)2=(1000)2+2×1000×1+12=1000000+2000+1=1002001 (iv) Here, we will use the identity (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2
(999)2=(1000−1)2=(1000)2−2×1000×1+12=1000000−2000+1=998001 (v) Here, we will use the identity (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2
(703)2=(700+3)2=(700)2+2×700×3+32=490000+4200+9=494209
Question 4: Simplify the following using the formula: (a − b)(a + b) = a2 − b2:
(i) (82)2 − (18)2
(ii) (467)2 − (33)2
(iii) (79)2 − (69)2
(iv) 197 × 203
(v) 113 × 87
(vi) 95 × 105
(vii) 1.8 × 2.2
(viii) 9.8 × 10.2
Answer 4: Here, we will use the identity (a−b)(a+b)=a2 −b2
(i) Let us consider the following expression:
(82)2−(18)2=(82+18)(82−18)=100×64=6400(ii) Let us consider the following expression:
(467)2−(33)2=(467+33)(467−33)=500×434=217000
(iii) Let us consider the following expression:
(79)2−(69)2=(79+69)(79−69)=148×10=1480
(iv) Let us consider the following product:
197×203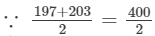 =200; therefore, we will write the above product as:
=200; therefore, we will write the above product as:
197×203=(200−3)(200+3)=(200)2−(3)2=40000−9=39991 Thus, the answer is 39991.
(v) Let us consider the following product:
113×87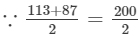 =100; therefore, we will write the above product as:
=100; therefore, we will write the above product as:
113×87=(100+13)(100−13)=(100)2−(13)2=10000−169=9831 Thus, the answer is 9831.
(vi) Let us consider the following product:
95×105
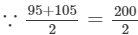 =100; therefore, we will write the above product as:
=100; therefore, we will write the above product as:
95×105=(100+5)(100−5)=(100)2−(5)2=10000−25=9975 Thus, the answer is 9975.
(vii) Let us consider the following product:
1.8×2.2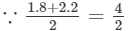 =2; therefore, we will write the above product as:
=2; therefore, we will write the above product as:
1.8×2.2=(2−0.2)(2+0.2)=(2)2−(0.2)2=4−0.04=3.96 Thus, the answer is 3.96.
(viii) Let us consider the following product:
9.8×10.2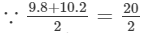 =10; therefore, we will write the above product as:
=10; therefore, we will write the above product as:
9.8×10.2=(10−0.2)(10+0.2)=(10)2−(0.2)2=100−0.04=99.96 Thus, the answer is 99.96.
Question 5: Simplify the following using the identities:
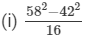
(ii) 178 × 178 − 22 × 22
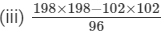
(iv) 1.73 × 1.73 − 0.27 × 0.27
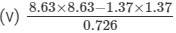
Answer 5:(i) Let us consider the following expression:
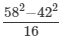
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
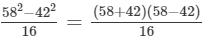
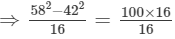
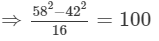
Thus, the answer is 100.
(ii) Let us consider the following expression:
178×178−22×22
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
178×178−22×22=1782−222=(178+22)(178−22)=200×156=31200
Thus, the answer is 31200.
(iii) Let us consider the following expression:
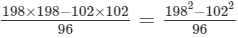
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
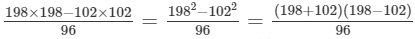
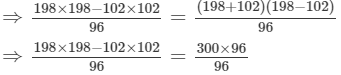
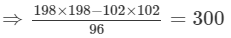
Thus, the answer is 300.
(iv) Let us consider the following expression:
1.73×1.73−0.27×0.27
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
1.73×1.73−0.27×0.27=1.732−0.272=(1.73+0.27)(1.73−0.27)=2×1.46=2.92
Thus, the answer is 2.92.
(v) Let us consider the following expression:
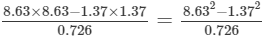
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
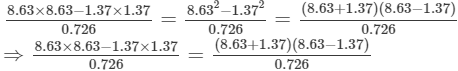
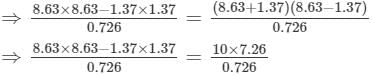
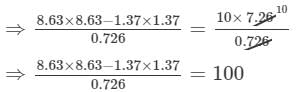
Thus, the answer is 100.
Question 6: Find the value of x, if:
(i) 4x = (52)2 − (48)2
(ii) 14x = (47)2 − (33)2
(iii) 5x = (50)2 − (40)2
Answer 6: (i) Let us consider the following equation:
4x=(52)2−(48)2
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
4x=(52)2−(48)24x=(52+48)(52−48)4x=100×4=400⇒4x=400
⇒x=100 (Dividing both sides by 4)
(ii) Let us consider the following equation:
14x=(47)2−(33)2
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
14x=(47)2−(33)214x=(47+33)(47−33)14x=80×14=1120⇒14x=1120
⇒x=80 (Dividing both sides by 14)
(iii) Let us consider the following equation:
5x=(50)2−(40)2
Using the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2, we get:
5x=(50)2−(40)25x=(50+40)(50−40)5x=90×10=900⇒5x=900
⇒x=180 (Dividing both sides by 5)
Question 7: If x+1/x =20, find the value of x2+ 1/x2 .
Answer 7: Let us consider the following equation:
x+1/x =20
Squaring both sides, we get:
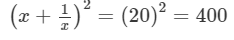
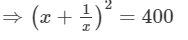
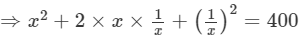
[(a+b)2=a2 +b2 +2ab]
⇒x2+2+1/x2 =400
⇒x2+1/x2 =398 (Subtracting 2 from both sides)
Thus, the answer is 398.
Question 8: If x−1/x =3, find the values of x2+1/x2 and x4+1/x4 .
Answer 8: Let us consider the following equation:
x−1/x =3
Squaring both sides, we get:
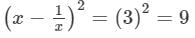
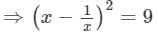
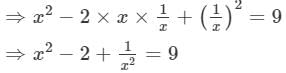
⇒x2+1/x2 =11 (Adding 2 to both sides)
Squaring both sides again, we get:
(x2+1/x2 )2=(11)2=121
⇒(x2+1/x2 )2=121
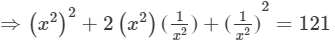
⇒x4+2+1/x4 =121
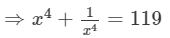
Question 9: If x2+1/x2 =18, find the values of x+1/x and x−1/x .
Answer 9: Let us consider the following expression:
x+1/x
Squaring the above expression, we get:
(x+1/x )2=x2+2×x×1/x +(1/x)2=x2−2+ 1/x2
[(a+b)2=a2+b2+2ab]
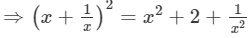
⇒(x+1/x )2=20 (∵ x2+1/x2 =18)
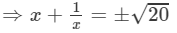 (Taking square root of both sides)
(Taking square root of both sides)
Now, let us consider the following expression:
x−1/x
Squaring the above expression, we get:
(x−1/x )2=x2−2×x×1/x +(1/x )2=x2−2+ 1/x2
⇒(x−1/x )2=x2−2+ 1/x2
⇒(x−1/x )2=16 (∵ x2+ 1/x2 =18)
⇒x−1/x =±4 (Taking square root of both sides)
Question 10: If x + y = 4 and xy = 2, find the value of x2 + y2
Answer 10: We have:
(x+y)2=x2+2xy+y2⇒x2+y2=(x+y)2−2xy ⇒x2+y2=42−2×2 (∵ x+y=4 and xy=2)
⇒x2+y2=16−4⇒x2+y2=12
Question 11: If x − y = 7 and xy = 9, find the value of x2 + y2
Answer 11: We have:
(x−y)2=x2−2xy+y2⇒x2+y2=(x−y)2+2xy ⇒x2+y2=72+2×9 (∵ x−y=7 and xy=9 )
⇒x2+y2=72+2×9⇒x2+y2=49+18⇒x2+y2=67
Question 12: If 3x + 5y = 11 and xy = 2, find the value of 9x2 + 25y2
Answer 12: We have:
(3x+5y)2=(3x)2+2(3x)(5y)+(5y)2⇒(3x+5y)2=9x2+30xy+25y2⇒9x2+25y2=(3x+5y)2−30xy ⇒9x2+25y2=112−30×2 (∵ 3x+5y=11 and xy=2)
⇒9x2+25y2=121−60⇒9x2+25y2=61
Question 13: Find the values of the following expressions:
(i) 16x2 + 24x + 9, when x=7/4
(ii) 64x2 + 81y2 + 144xy, when x = 11 and y=4/3
(iii) 81x2 + 16y2 − 72xy, when x=2/3 and y=3/4
Answer 13: (i) Let us consider the following expression:
16x2+24x+9
Now
16x2+24x+9=(4x+3)2 (Using identity (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2)
⇒16x2+24x+9=(4×7/4 +3)2 (Substituting x=7/4)⇒16x2+24x+9=(7+3)2⇒16x2+24x+9=102⇒16x2+24x+9=100
(ii) Let us consider the following expression:
64x2+81y2+144xy
Now
64x2+81y2+144xy=(8x+9y)2 (Using identity (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2)
⇒64x2+81y2+144xy=[8(11)+9(4/3)]2 (Substituting x=11 and y=4/3)⇒64x2+81y2+144xy=[88+12]2 ⇒64x2+81y2+144xy=1002 ⇒64x2+81y2+144xy=10000(iii) Let us consider the following expression: 81x2+16y2−72xy
Now
81x2+16y2−72xy=(9x−4y)2 (Using identity (a+b)2=a2−2ab+b2)
⇒81x2+16y2−72xy=[9(2/3)−4(3/4)]2 (Substituting x=2/3 and y=3/4)⇒81x2+16y2−72xy=[6−3]2 ⇒81x2+16y2−72xy=32 ⇒81x2+16y2−72xy=9
Question 14: If x+1/x =9, find the value of x4+1/x4.
Answer 14: Let us consider the following equation:
x+1/x =9
Squaring both sides, we get:
(x+1/x )2=(9)2=81
⇒(x+1/x )2=81
⇒x2+2×x×1/x +(1/x )2=81
⇒x2+2+1/x2 =81
⇒x2+1/x2 =79 (Subtracting 2 from both sides)
Now, squaring both sides again, we get:
(x2+1/x2 )2=(79)2=6241
⇒(x2+1/x2 )2=6241
⇒(x2)2+2(x2)(1/x2)+(1/x2)2=6241
⇒x4+2+1/x4=6241
⇒x4+1/x4 =6239
Question 15: If x+1/x =12, find the value of x−1/x.
Answer 15: Let us consider the following equation:
x+1/x =12
Squaring both sides, we get:
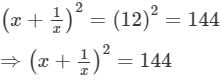
⇒x2+2×x×1/x +(1/x)2=144 [ (a+b)2=a2+b2+2ab]
⇒x2+2+1/x2 =144
⇒x2+1/x2 =142 (Subtracting 2 from both sides)
Now
(x−1/x)2=x2−2×x×1/x+(1/x)2=x2−2+1/x2 [(a−b)2=a2+b2−2ab]
⇒(x−1/x )2=x2−2+1/x2
⇒(x−1/x )2=142−2 (∵ x2+1/x2 =142)
⇒(x−1/x)2=140
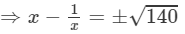 (Taking square root)
(Taking square root)
Question 16: If 2x + 3y = 14 and 2x − 3y = 2, find the value of xy.
[Hint: Use (2x + 3y)2 − (2x − 3y)2 = 24xy]
Answer 16: We will use the identity (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2 to obtain the value of xy.
Squaring (2x+3y) and (2x−3y) both and then subtracting them, we get:
(2x+3y)2−(2x−3y)2={(2x+3y)+(2x−3y)}{(2x+3y)−(2x−3y)}=4x×6y=24xy⇒(2x+3y)2−(2x−3y)2=24xy
⇒24xy=(2x+3y)2−(2x−3y)2⇒24xy=(14)2−(2)2⇒24xy=(14+2)(14−2) (∵ (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2)⇒24xy=16×12⇒xy=16× 12 /24 (Dividing both sides by 24)⇒xy=8
Question 17: If x2 + y2 = 29 and xy = 2, find the value of
(i) x + y
(ii) x − y
(iii) x4 + y4
Answer 17: (i) We have:
(x+y)2=x2+2xy+y2
⇒(x+y)=± 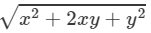
⇒(x+y)=± 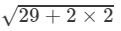 ( ∵ x2+y2=29 and xy=2)
( ∵ x2+y2=29 and xy=2)
⇒(x+y)=± 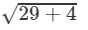
⇒(x+y)=± 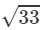
(ii) We have:
(x−y)2=x2−2xy+y2
⇒(x−y)=± 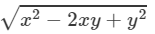
⇒(x−y)=± 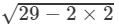 (∵ x2+y2=29 and xy=2)
(∵ x2+y2=29 and xy=2)
⇒(x−y)=± 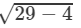
⇒(x−y)=± √25
⇒(x−y)=± 5
(iii) We have:
(x2+y2)2=x4+2x2y2+y4⇒x4+y4=(x2+y2)2−2x2y2⇒x4+y4=(x2+y2)2−2(xy)2⇒x4+y4=292−2(2)2 (∵ x2+y2=29 and xy=2)⇒x4+y4=841−8⇒x4+y4=833
Question 18: What must be added to each of the following expressions to make it a whole square?
(i) 4x2 − 12x + 7
(ii) 4x2 − 20x + 20
Answer 18: (i) Let us consider the following expression:
4x2−12x+7
The above expression can be written as:
4x2−12x+7=(2x)2−2×2x×3+7
It is evident that if 2x is considered as the first term and 3 is considered as the second term, 2 is required to be added to the above expression to make it a perfect square. Therefore, 7 must become 9.
Therefore, adding and subtracting 2 in the above expression, we get:
(4x2−12x+7)+2−2={(2x)2−2×2x×3+7}+2−2={(2x)2−2×2x×3+9}−2=(2x+3)2−2
Thus, the answer is 2.
(ii) Let's consider the following expression:
4x2−20x+20
The above expression can be written as:
4x2−20x+20=(2x)2−2×2x×5+20
It is evident that if 2x is considered as the first term and 5 is considered as the second term, 5 is required to be added to the above expression to make it a perfect square. Therefore, number 20 must become 25.
Therefore, adding and subtracting 5 in the above expression, we get:
(4x2−20x+20+5)−5={(2x)2−2×2x×5+20}+5−5={(2x)2−2×2x×5+25}−5=(2x+5)2−5
Thus, the answer is 5.
Question 19: Simplify:
(i) (x − y)(x + y) (x2 + y2)(x4 + y2)
(ii) (2x − 1)(2x + 1)(4x2 + 1)(16x4 + 1)
(iii) (4m − 8n)2 + (7m + 8n)2
(iv) (2.5p − 1.5q)2 − (1.5p − 2.5q)2
(v) (m2 − n2m)2 + 2m3n2
Answer 19: To simplify, we will proceed as follows:
(i)
(i) (x−y)(x+y)(x2+y2)(x4+y4)=(x2−y2)(x2+y2)(x4+y4) [∵ (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2]=(x4−y4)(x4+y4) [ ∵ (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2]=x8−x8 [∵ (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2(ii) (2x−1)(2x+1)(4x2+1)(16x4+1)=((2x)2−12)(4x2+1)(16x4+1) [∵(a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2] =(4x2−1)(4x2+1)(16x4+1) ={(4x2)2−(12)2}(16x4+1) [∵(a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2]=(16x4−1) (16x4+1) =(16x4)2 − 12 [∵ (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2]=256x8−1(iii) (7m−8n)2+(7m+8n)2=2(7m)2+2(8n)2 [∵ (a−b)2+(a+b)2=2a2+2b2]=98m2+128n2
(iv) (2.5p−1.5q)2−(1.5p−2.5q)2=(2.5p)2+(1.5q)2−2(2.5p)(1.5q)−[(1.5p)2+(2.5q)2−2(1.5p)(2.5q)] =(2.5p)2+(1.5q)2−2(2.5p)(1.5q)−(1.5p)2−(2.5q)2+2(1.5p)(2.5q)=(2.5p)2−(1.5p)2+(1.5q)2−(2.5q)2 =[(2.5p+1.5p)(2.5p−1.5p)]+[(1.5q+2.5)(1.5q−2.5q)] [∵(a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2] =4p×p+4q×(−q)=4p2−4q2 =4(p2−4q2 )v) (m2−n2m)2+2m3n2=(m2)2+(n2m)2 [∵ (a−b)2+2ab=a2+b2]=m4+n4m2
Question 20: Show that:
(i) (3x + 7)2 − 84x = (3x − 7)2
(ii) (9a − 5b)2 + 180ab = (9a + 5b)2
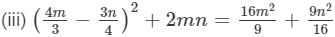
(iv) (4pq + 3q)2 − (4pq − 3q)2 = 48pq2
(v) (a − b)(a + b) + (b − c)(b + c) + (c − a)( c + a) = 0
Answer 20:
(i) LHS=(3x+7)2−84x=(3x+7)2−4×3x×7=(3x−7)2 [∵ (a+b)2−4ab=(a−b)2]=RHSBecause LHS is equal to RHS, the given equation is verified. (ii) LHS=(9a−5b)2+180ab=(9a−5b)2+4×9a×5b=(9a+5b)2 [∵ (a−b)2+4ab=(a+b)2]=RHSBecause LHS is equal to RHS, the given equation is verified. (iii) LHS=(4m/3 −3n/4)2+2mn=(4m/3 - 3n/4)2+2×4m/3 × 3n/4=(4m/3)2+(3n/4)2 [∵ (a−b)2+2ab=a2+b2]=16m2/9 +9n2/16 =RHSBecause LHS is equal to RHS, the given equation is verified.
(iv) LHS=(4pq+3q)2−(4pq−3q)2=4(4pq)(3q) [∵(a+b)2−(a+b)2=4ab]=48pq2 =RHSBecause LHS is equal to RHS, the given equation is verified.(v) LHS=(a−b)(a+b)+(b−c)(b+c)+(c+a)(c−a)=a2−b2+b2−c2+c2−a2 [∵ (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2]=a2−b2+b2−c2+c2−a2 =0=RHSBecause LHS is equal to RHS, the given equation is verified.
Question 21: Find the following products:
(i) (x + 4) (x + 7)
(ii) (x − 11) (x + 4)
(iii) (x + 7) (x − 5)
(iv) (x − 3) ( x − 2)
(v) (y2 − 4) (y2 − 3)
(vi) (x+4/3)(x+3/4)
(vii) (3x + 5) (3x + 11)
(viii) (2x2 − 3) (2x2 + 5)
(ix) (z2 + 2) (z2 − 3)
(x) (3x − 4y) (2x − 4y)
(xi) (3x2 − 4xy) (3x2 − 3xy)
(xii) (x+1/5)(x + 5)
(xiii) (z+3/4)(z+4/3)
(xiv) (x2 + 4) (x2 + 9)
(xv) (y2 + 12) (y2 + 6)
(xvi) (y2+5/7)(y2− 14/5)
(xvii) (p2 + 16) (p2− 1/4)
Answer 21: (i) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
(x+4)(x+7)
=x2+(4+7)x+4×7
=x2+11x+28
(ii) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x+b)=x2+(b−a)x−ab.
(x−11)(x+4)
=x2+(4−11)x−11×4
=x2−7x−44
(iii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x−b)=x2+(a−b)x−ab.
(x+7)(x−5)
=x2+(7−5)x−7×5
=x2+2x−35
(iv) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x−b)=x2−(a+b)x+ab.
(x−3)(x−2)
=x2−(3+2)x+3×2
=x2−5x+6
(v) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x−b)=x2−(a+b)x+ab.
(y2−4)(y2−3)
=(y2)2−(4+3)(y2)+4×3
=y4−7y2+12
(vi) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
(x+4/3)(x+3/4)
=x2+25/12 x+1
(vii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
(3x+5)(3x+11)
=(3x)2+(5+11)(3x)+5×11
=9x2+48x+55
(viii) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x+b)=x2+(b−a)x−ab.
(2x2−3)(2x2+5)
=(2x2)2+(5−3)(2x2)−3×5
=4x4+4x2−15
(ix) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x−b)=x2+(a−b)x−ab
(z2+2)(z2−3)
=(z2)2+(2−3)(z2)−2×3
=z4−z2−6
(x) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x−b)=x2−(a+b)x+ab.
(3x−4y)(2x−4y)
=(4y−3x)(4y−2x)
(Taking common −1 from both parentheses)
=(4y)2−(3x+2x)(4y)+3x×2x
=16y2−(12xy+8xy)+6x2
=16y2−20xy+6x2
(xi) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x−b)=x2−(a+b)x+ab
(3x2−4xy)(3x2−3xy)
=(3x2)2−(4xy+3xy)(3x2)+4xy×3xy
=9x4−(12x3y+9x3y)+12x2y2
=9x4−21x3y+12x2y2
(xii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
(x+1/5)(x+5)
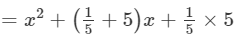
=x2+26/5 x+1
(xiii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
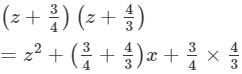
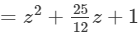
(xiv) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
(x2+4)(x2+9)
=(x2)2+(4+9)(x2)+4×9
=x4+13x2+36
(xv) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab.
(y2+12)(y2+6)
=(y2)2+(12+6)(y2)+12×6
=y4+18y2+72
(xvi) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x−b)=x2+(a−b)x−ab.
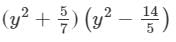
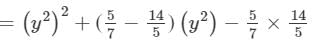
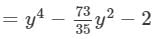
(xvii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x−b)=x2+(a−b)x−ab.
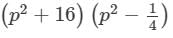
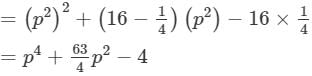
Question 22: Evaluate the following:
(i) 102 × 106
(ii) 109 × 107
(iii) 35 × 37
(iv) 53 × 55
(v) 103 × 96
(vi) 34 × 36
(vii) 994 × 1006
Answer 22: (i) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+abx+ax+b=x2+a+bx+ab
102×106
=(100+2)(100+6)
=1002+(2+6)100+2×6
=10000+800+12
=10812
(ii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab
109 × 107
=(100+9)(100+7)
=1002+(9+7)100+9×7
=10000+1600+63
=11663
(iii) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab
35 × 37
=(30+5)(30+7)
=302+(5+7)30+5×7
=900+360+35
=1295
(iv) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab
53 × 55
=(50+3)(50+5)
=502+(3+5)50+3×5
=2500+400+15
=2915
(v) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x−b)=x2+(a−b)x−ab
103 × 96
=(100+3)(100−4)
=1002+(3−4)100−3×4
=10000−100−12
=9888
(vi) Here, we will use the identity (x+a)(x+b)=x2+(a+b)x+ab
34 × 36
=(30+4)(30+6)
=302+(4+6)30+4×6
=900+300+24
=1224
(vii) Here, we will use the identity (x−a)(x+b)=x2+(b−a)x−ab
994 × 1006
=(1000−6)×(1000+6)
=10002+(6−6)×1000−6×6
=1000000−36
=999964
FAQs on RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Math Chapter 6 - Algebraic Expressions and Identities (Part-5 ) - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What are algebraic expressions? |  |
| 2. How do you simplify algebraic expressions? |  |
| 3. What are identities in algebraic expressions? |  |
| 4. How can algebraic expressions be used in real-life situations? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of studying algebraic expressions and identities? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|