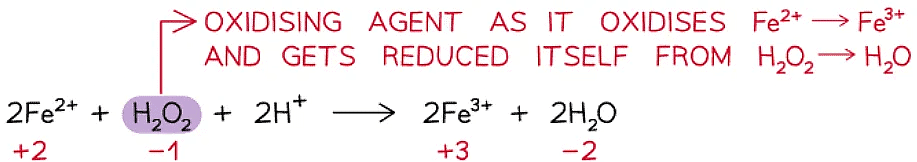Redox | Chemistry for Grade 12 PDF Download
Oxidising & Reducing Agents
Oxidising agent
- An oxidising agent is a substance that oxidises another atom or ion by causing it to lose electrons
- An oxidising agent itself gets reduced – gains electrons
- Therefore, the ox. no. of the oxidising agent decreases

Reducing agent
- A reducing agent is a substance that reduces another atom or ion by causing it to gain electrons
- A reducing agent itself gets oxidised – loses/donates electrons
- Therefore, the ox. no. of the reducing agent increases

- For a reaction to be recognised as a redox reaction, there must be both an oxidising and reducing agent
- Some substances can act both as oxidising and reducing agents
- Their nature is dependent upon what they are reacting with and the reaction conditions
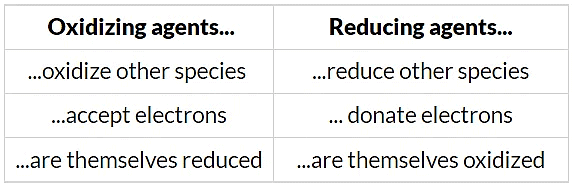
Oxidising & Reducing Agents Table
Redox Equations
- Balancing equations using redox principles is a useful skill and is best illustrated by following an example
- It is important to follow a methodical step-by-step approach so that you don't get lost:
Example: Writing overall redox reactions
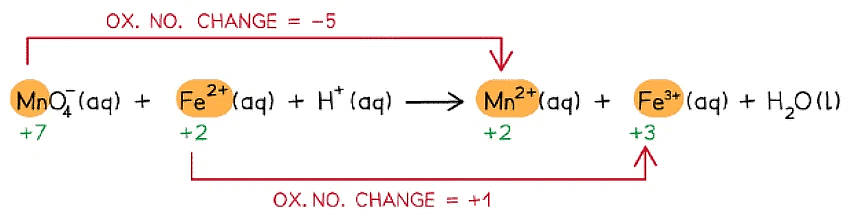
Manganate(VII) ions (MnO4- ) react with Fe2+ ions in the presence of acid (H+) to form Mn2+ ions, Fe3+ ions and water
Write the overall redox equation for this reaction
Step 1: Write the unbalanced equation and identify the atoms which change in oxidation state
Step 2: Deduce the oxidation state changes
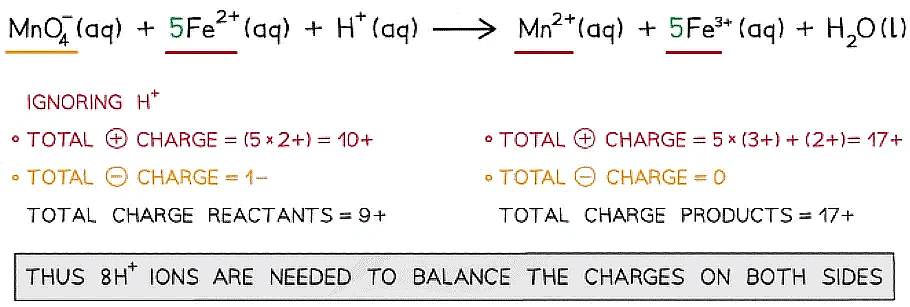
Step 3: Balance the oxidation state changes
Step 4: Balance the charges
Step 5: Finally, balance the atoms
Interpreting & Predicting Redox Reactions
- All of the species involved in a chemical reaction might not be known
- You can be asked to interpret the information given to you and predict any other chemicals involved in the reaction
- You can use the method shown in the Redox Equations section above
- The worked example below is a method that works for balancing ionic half equations but can also be used to help predict redox equations
Example: Write complete equations for the following reactions:
(i) Hydrogen iodide reacting with sulfuric acid to form hydrogen sulfide, iodine and one other product
Step 1: Start with what you know:
- HI + H2SO4 → H2S + I2
Step 2: Consider any unaccounted for elements
- The only element that is not currently considered is oxygen
Step 3: Make a common and appropriate suggestion for the missing product
- Most of these questions are in solution so there is always H2O, H+ and OH- available
Missing product suggestion = 4H2O
HI + H2SO4 → H2S + I2 + 4H2OStep 4: Balance the remaining chemicals
8HI + H2SO4 → H2S + 4I2 + 4H2O
(ii) Lead(II) chloride, chlorine and one other product being formed from the reaction of concentrated hydrochloric acid with lead(IV) oxide
Step 1: Start with what you know:
- PbO2 + HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2
Step 2: Consider any unaccounted elements
- The only element that is not currently considered is oxygen
Step 3: Make a common and appropriate suggestion for the missing product
- Missing product suggestion = 2H2O
PbO2 + HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2OStep 4: Balance the remaining chemicals
- PbO2 + 4HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
|
207 videos|373 docs|227 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Grade 12 exam
|

|