Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Entrepreneurship Class 12 > Revision Notes- Business Arithmetic
Revision Notes- Business Arithmetic | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Unit of Sale, Unit Cost and Break Even Analysis
- Unit of sale is required to understand the economies of a business in an easy and standardized manner.
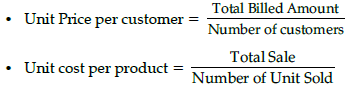
- Gross profit = Selling price per unit – Cost price per unit.
- Break-Even Point is the level of sales that equals all expenses required for generating the sales. It is neither loss nor profit.
- At Break-Even Level: Total revenue = Total expenses
- Break even analysis helps in setting profit goals and sales targets.
- Sales Mix is the proportion in which two or more products are sold.
- The calculation method for break-even point of sales mix is based on the contribution approach method.
Computation of Working Capital
- Money needed to fund the normal, day-to-day operations of a business is known as working capital.
- Operating cycle or cash conversion cycle is the length of time between a firm’s purchase of inventory and the receipt of cash from accounts receivable.
- Gross working capital is the sum total of all current assets of the business. These include cash, inventory (raw materials, work in process, finished goods, spares etc.) and accounts receivable (or trade debtors).
- Net working capital is the excess of current assets over current liabilities.
Inventory Control, Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Return on Investment (ROI) and Return on Equity (ROE)
- Inventory is required directly or indirectly to make a sale (of the end product) and for also getting the final product.
- Inventory control system is designed to bring about expected control over the inventory and its utilization.
- Economic order quantity is the order quantity of inventory that minimizes the total cost of inventory management.
- Re-order point is the level of inventory when an order should be made with suppliers to bring the inventory up by the economic order quantity.
- Carrying cost refers to the total cost of holding inventories. This includes warehousing cost such as rent, utilities and salaries, financial cost such as opportunity cost and inventory cost related to perishability, pilferage, shrinkage and insurance.
- To determine how much to order, E.O.Q. is used.
- ROI is the ratio that reflects the overall profitability of business.
- Investment means the long term funds deployed in business.
The document Revision Notes- Business Arithmetic | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Entrepreneurship Class 12.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
19 videos|62 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes- Business Arithmetic - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the unit of sale? |  |
Ans. The unit of sale refers to the specific quantity or measurement in which a product or service is sold. It could be a single item, a pack, a case, or any other defined unit that represents a saleable unit.
| 2. How is unit cost calculated? |  |
Ans. Unit cost is calculated by dividing the total cost of producing or acquiring a product by the number of units produced or acquired. The formula for unit cost is:
Unit Cost = Total Cost / Number of Units
For example, if the total cost of producing 100 units is $1,000, the unit cost would be $10 ($1,000 / 100 units).
| 3. What is break-even analysis? |  |
Ans. Break-even analysis is a financial calculation that helps determine the point at which a company's total revenue equals its total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. It allows businesses to assess the minimum sales volume or revenue needed to cover all costs. The break-even point is where the company starts making a profit.
| 4. How is working capital computed? |  |
Ans. Working capital is computed by subtracting a company's current liabilities from its current assets. The formula for working capital is:
Working Capital = Current Assets - Current Liabilities
Working capital represents the funds available to cover a company's day-to-day operational expenses and is an indicator of its short-term liquidity.
| 5. What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)? |  |
Ans. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a formula used in inventory management to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. It takes into account factors such as the cost per unit, ordering costs, and carrying or holding costs. The EOQ formula is:
EOQ = √((2 * Annual Demand * Ordering Cost) / Carrying Cost per Unit)
By calculating the EOQ, businesses can find the balance between ordering too much inventory (resulting in higher carrying costs) and ordering too little (leading to frequent orders and higher ordering costs).
Related Searches


















