Routes & Network Diagrams | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Importance of Routes and Networks Diagram |

|
| What are Routes and Network Diagrams? |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
| Previous Year Questions: Routes and Network |

|
Importance of Routes and Networks Diagram
Learning routes and network diagrams is beneficial for success in the CAT exam because it helps improve logical reasoning, analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, time management, visualization skills, and strategic thinking. These qualities are highly valued in the competitive exam setting. Consistent practice and a good grasp of these concepts can greatly boost a candidate's performance in different sections of the CAT exam.

What are Routes and Network Diagrams?
Routes refer to specific paths or ways to reach a destination or achieve a goal whereas Network diagrams are visual representations that illustrate how different elements or components are connected and interact with each other. In simpler terms, they are like maps that show the relationships and connections between various parts of a system or process.
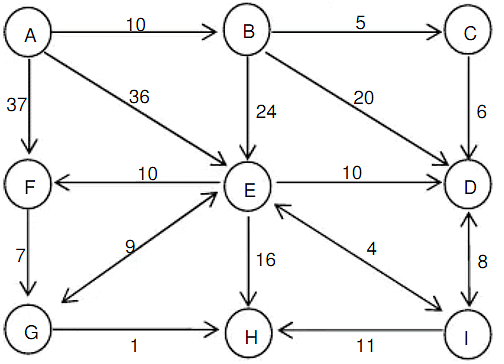
Solved Examples
Q 1: What is the total number of ways to reach A to B in the network given?

B. 16
C. 20
D. 22

A. 200
B. 800
C. 700
D. 1000
Answer: D
Solution:
Since the flow from Vaishali to Jyotishmati is 300 as demand is 400 the deficient 100 would be met by flow from Vidisha. Again the demand of 700 in Panchal is to be met by flow from Jyotishmati which can get it from Vidisha.
Thus, the quantity moved from Avanti to Vidisha is 200 + 100 + 700 = 1000
Previous Year Questions: Routes and Network
Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.
Export cargo of a trader can go through seven cities P, Q, R, S, T, U and V. The following cities have a two way connection i.e., Cargo can move in both directions between them; S and U, P and Q, Q and R, V and T, R and T, V and U. Cargo can move only in one direction from U to Q.
Q1: If the trader wants the cargo to move from City S to City T then excluding cities S and T, what is the minimum number of cities that the cargo has to cross in transit?
(a)4
(b)3
(c)2
(d)5
Ans: (c)
Sol:
From the figure, Excluding cities S and T cargo can go from city S to city T in 2 ways i.e S-U-Q-R-T and S-U-V-T.
The shortest path from S to T is S-U-V-T.
Therefore the minimum number of cities that the cargo has to cross in transit is 2.
Q2: If the trader wants the cargo to go to City U from City P through the longest route, how many cities will he be required to cross (excluding cities P and U)?
(a)2
(b)4
(c)3
(d)5
Ans: (b)
Sol:
From the figure, Cargo can go from city P to city U in only one possible way i.e. P-Q-R-T-V-U.
Going through this path, the cargo will have to pass through 4 cities.
Hence, option (b).
Q3: To move cargo from City P to City U, which of the following statements will minimise the number of cities to be crossed in transit?
(a) Connect cities U to R with a two way connection
(b) Connect cities P to S with a one way connection from cities S to P
(c) Connect cities U to Q with a two way connection
(d) Connect cities R to V with a two way connection
Ans: (c)
Sol: Consider option A. The path is P-Q-R-U. We have to cross 2 intermediate cities in it.
Consider option B. If we connect cities from P to S with a one way connection from cities S to P. The path formed will be P-Q-R-T-V-U.
It becomes a longer path than option A.
Using option C, the path formed is the shortest path. The path formed is P-Q-U. This smaller than that in option A.
Consider option D. The path formed using option D is longer compared to the path formed using option C. Hence options A, B, and D are eliminated.
Hence, option (c).
|
88 videos|119 docs|91 tests
|
FAQs on Routes & Network Diagrams - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What are routes and network diagrams? |  |
| 2. Why are routes and network diagrams important? |  |
| 3. How are routes and network diagrams created? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of using network diagrams? |  |
| 5. Can network diagrams be used in other fields apart from IT? |  |
|
88 videos|119 docs|91 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|

















